Java集合
1、集合框架的概述
- 集合、数组都是对多个数据进行存储操作的结构,简称Java容器。(说明:此时的存储,主要指的是内存层面的存储,不涉及到持久化的存储(.txt,.jpg,.avi,数据库中)
- 数组在存储多个数据方面的特点:
- 一旦初始化以后,其长度就确定了。
- 数组一旦定义好,其元素的类型也就确定了。我们也就只能操作指定类型的数据了。(比如:String[] arr;int[] arr1;Object[] arr2)
- 数组在存储多个数据方面的缺点:
- 一旦初始化以后,其长度就不可修改。
- 数组中提供的方法非常有限,对于添加、删除、插入数据等操作,非常不便,同时效率不高。
- 获取数组中实际元素的个数的需求,数组没有现成的属性或方法可用。
- 数组存储数据的特点:有序、可重复。对于无序、不可重复的需求,不能满足。
2、集合框架
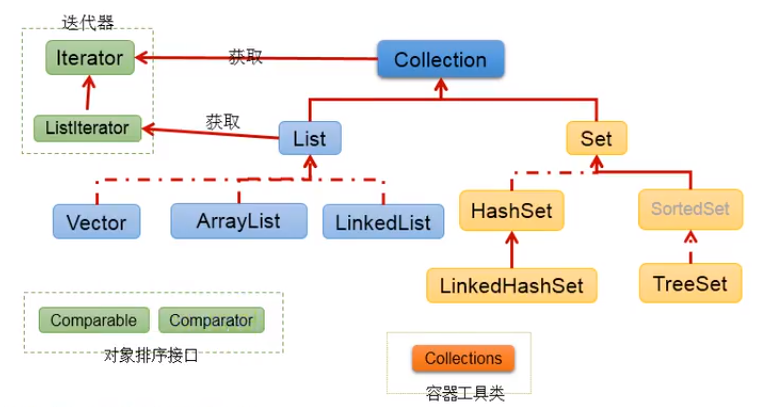
- Collection接口:单列集合,用来存储一个一个的对象。
- List接口:存储有序的、可重复的数据。 –>“动态”数组。
- ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector。
- Set接口:存储无序的、不可重复的数据 –>高中讲的“集合”。
- HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet。
- List接口:存储有序的、可重复的数据。 –>“动态”数组。
- Map接口:双列集合,用来存储一对(key - value)一对的数据 –>高中函数:y = f(x)。
- HashMap、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、Hashtable、Properties。
2.1 Collection接口
- Collection 接口是 List、Set 和 Queue 接口的父接口,该接口里定义的方法既可用于操作 Set 集合,也可用于操作 List 和 Queue 集合。
- JDK不提供此接口的任何直接实现,而是提供更具体的子接口(如:Set和List)实现。
- 在 Java5 之前,Java 集合会丢失容器中所有对象的数据类型,把所有对象都当成 Object 类型处理;从 JDK 5.0 增加了泛型以后,Java 集合可以记住容器中对象的数据类型。
1 |
|
- 向Collection接口的实现类的对象中添加数据obj时,要求obj所在类要重写equals()。
1 |
|
1 |
|
- 集合元素的遍历操作,使用迭代器Iterator接口。
- 内部的方法:hasNext() 和 next()。
- 集合对象每次调用iterator()方法都得到一个全新的迭代器对象,默认游标都在集合的第一个元素之前。
- 内部定义了remove(),可以在遍历的时候,删除集合中的元素。此方法不同于集合直接调用remove()。
1 |
|
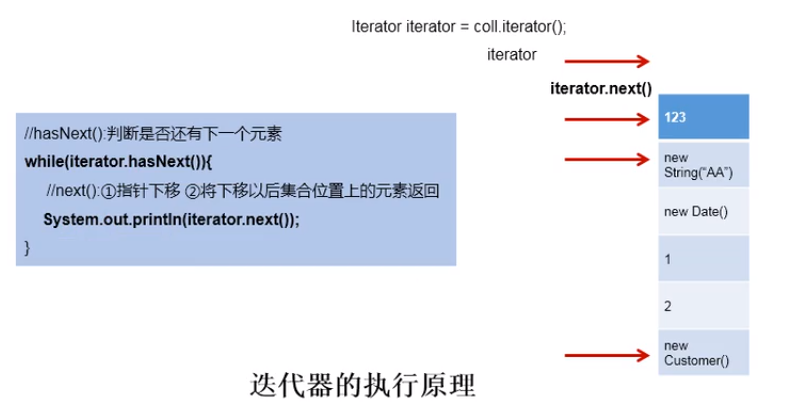
- 注意:如果还未调用next()或在上一次调用 next 方法之后已经调用了 remove 方法,再调用remove都会报IllegalStateException。
1 |
|
2.2 List接口
List接口:存储有序的、可重复的数据。
ArrayList:作为List接口的主要实现类;线程不安全的,效率高;底层使用Object[] elementData存储。
- jdk7
- ArrayList list = new ArrayList()底层创建了长度是10的Object[]数组elementData。
- list.add(123)即elementData[0] = new Integer(123),如果此次的添加导致底层elementData数组容量不够,则扩容。默认情况下,扩容为原来的容量的1.5倍,同时需要将原有数组中的数据复制到新的数组中。
- jdk8
- ArrayList list = new ArrayList()底层Object[] elementData初始化为{},并没有创建长度为10的数组。
- list.add(123)即第一次调用add()时,底层才创建了长度10的数组,并将数据123添加到elementData[0]。
- 后续的添加和扩容操作与jdk7无异。
- 即jdk7中的ArrayList的对象的创建类似于单例的饿汉式,而jdk8中的ArrayList的对象的创建类似于单例的懒汉式,延迟了数组的创建,节省内存。
- jdk7
LinkedList:对于频繁的插入、删除操作,使用此类效率比ArrayList高;底层使用双向链表存储。
- LinkedList list = new LinkedList()内部声明了Node类型的first和last属性,默认值为null。
- list.add(123)将123封装到Node中,创建了Node对象,体现了LinkedList的双向链表的说法。node的定义为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}Vector:作为List接口的古老实现类;线程安全的,效率低;底层使用Object[] elementData存储。
- jdk7和jdk8中通过Vector()构造器创建对象时,底层都创建了长度为10的数组。在扩容方面,默认扩容为原来的数组长度的2倍。
同:三个类都是实现了List接口;存储数据的特点相同:存储有序的、可重复的数据。
1 |
|
ArrayList源码解析
- 属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
//默认容量的大小
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
//空数组常量
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
//默认的空数组常量
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
//存放元素的数组,从这可以发现 ArrayList 的底层实现就是一个 Object数组
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
//数组中包含的元素个数
private int size;
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
//数组的最大上限
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;- 构造方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27//构造方法1
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
//当我们指定了初始大小的时候,elementData 的初始大小就变成了我们所指定的初始大小
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
//构造方法2
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
//默认情况下,elementData 是一个大小为 0 的空数组
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}- get 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
//先是判断一下有没有越界,之后就可以直接通过数组下标来获取元素
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* Checks if the given index is in range. If not, throws an appropriate
* runtime exception. This method does *not* check if the index is
* negative: It is always used immediately prior to an array access,
* which throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if index is negative.
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
// Positional Access Operations
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}- add 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//检查是否需要扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//添加元素
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
//如果是第一次添加元素(此时elementData为空)则设置数组的容量为10
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
//此时的DEFAULT_CAPACITY=10,minCapacity=0+1=1
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
//首次添加元素10-0=10>0
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
//扩容
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//新容量为原来的1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}LinkedList源码解析
- 属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18//链表的节点个数
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
//指向头节点的指针
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
//指向尾节点的指针
transient Node<E> last;- 结点结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12//Node 是在 LinkedList 里定义的一个静态内部类,它表示链表每个节点的结构,包括一个数据域 item,一个后置指针 next,一个前置指针 prev。
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}- add方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
//当前节点的前驱指向尾节点,后继指向 null
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
//尾指针指向新的尾节点
last = newNode;
//如果原来有尾节点,则更新原来节点的后继指针,否则更新头指针
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
2.3 Set接口
Collection接口:单列集合,用来存储一个一个的对象。
Set接口:存储无序的、不可重复的数据。(Set接口中没有额外定义新的方法,使用的都是Collection中声明过的方法;**向Set(主要指HashSet、LinkedHashSet)中添加的数据,其所在的类一定要重写hashCode()和equals()**)
HashSet:作为Set接口的主要实现类;线程不安全的;可以存储null值。
- LinkedHashSet:作为HashSet的子类;遍历其内部数据时,可以按照添加的顺序遍历,对于频繁的遍历操作,LinkedHashSet效率高于HashSet。
TreeSet:可以按照添加对象的指定属性,进行排序。
向TreeSet中添加的数据,要求是相同类的对象。
两种排序方式:自然排序(实现Comparable接口) 和 定制排序(Comparator)。
- 自然排序中,比较两个对象是否相同的标准为compareTo()返回0,不再是equals()。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89public class User implements Comparable{
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
System.out.println("User equals()....");
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
User user = (User) o;
if (age != user.age) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(user.name) : user.name == null;
}
public int hashCode() { //return name.hashCode() + age;
int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + age;
return result;
}
//按照姓名从大到小排列,年龄从小到大排列
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if(o instanceof User){
User user = (User)o;
// return -this.name.compareTo(user.name);
int compare = -this.name.compareTo(user.name);
if(compare != 0){
return compare;
}else{
return Integer.compare(this.age,user.age);
}
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("输入的类型不匹配");
}
}
}
public void test1(){
TreeSet set = new TreeSet();
set.add(new User("Tom",12));
set.add(new User("Jerry",32));
set.add(new User("Jim",2));
set.add(new User("Mike",65));
set.add(new User("Jack",33));
set.add(new User("Jack",56));
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}- 定制排序中,比较两个对象是否相同的标准为compare()返回0,不再是equals()。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
public void test(){
Comparator com = new Comparator() {
//按照年龄从小到大排列
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
if(o1 instanceof User && o2 instanceof User){
User u1 = (User)o1;
User u2 = (User)o2;
return Integer.compare(u1.getAge(),u2.getAge());
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("输入的数据类型不匹配");
}
}
};
TreeSet set = new TreeSet(com);
set.add(new User("Tom",12));
set.add(new User("Jerry",32));
set.add(new User("Jim",2));
set.add(new User("Mike",65));
set.add(new User("Mary",33));
set.add(new User("Jack",33));
set.add(new User("Jack",56));
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
Set:存储无序的、不可重复的数据。
- 无序性:不等于随机性。存储的数据在底层数组中并非按照数组索引的顺序添加,而是根据数据的哈希值决定的。
- 不可重复性:保证添加的元素按照equals()判断时,不能返回true,即:相同的元素只能添加一个。
重写hashCode()原则
- 在程序运行时,同一个对象多次调用 hashCode()方法应该返回相同的值。
- 当两个对象的 equals()方法比较返回true时,这两个对象的 hashCode()方法的返回值也应相等。
- 对象中用作 equals()方法比较的Field,都应该用来计算hashCode值。
例子:
1 |
|
执行结果:
1 | AA |
发现既没有调用equals方法,而且数据重复了。而如果User类同时重写了hashCode()方法:
1 | public int hashCode() { //return name.hashCode() + age; |
则执行结果如下:
1 | User equals().... |
发现既调用了equals方法,而且数据不会重复。
- 添加数据过程
- 哈希值不一样,对象不一样;哈希值一样而equals不一样,对象也不一样。
- 以HashSet为例:
- 向HashSet中添加元素a,首先调用元素a所在类的hashCode()方法,计算元素a的哈希值,此哈希值接着通过某种算法计算出在HashSet底层数组中的存放位置(即索引位置),判断数组此位置上是否已经有元素:
- 如果此位置上没有其他元素,则元素a添加成功。①
- 如果此位置上有其他元素b(或以链表形式存在的多个元素),则比较元素a与元素b的hash值:
- 如果hash值不相同,则元素a添加成功。②
- 如果hash值相同,进而需要调用元素a所在类的equals()方法:
- equals()返回true,元素a添加失败。
- equals()返回false,则元素a添加成功。③
- 向HashSet中添加元素a,首先调用元素a所在类的hashCode()方法,计算元素a的哈希值,此哈希值接着通过某种算法计算出在HashSet底层数组中的存放位置(即索引位置),判断数组此位置上是否已经有元素:
- 对于添加成功的②和③而言:元素a与已经存在指定索引位置上数据以链表的方式存储。
- jdk 7 :元素a放到数组中,指向原来的元素。(头插法)
- jdk 8 :原来的元素在数组中,指向元素a。(尾插法)
- HashSet底层:数组+链表的结构。
- 在list中去除重复值的方法。
1 |
|
- 典型例题
1 | public class Person { |
HashSet源码解析:
- 构造器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8/**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
//HashSet本质上是创建了一个HashMap
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}- 属性
1
2
3
4private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();- add方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16/**
* Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present.
* More formally, adds the specified element <tt>e</tt> to this set if
* this set contains no element <tt>e2</tt> such that
* <tt>(e==null ? e2==null : e.equals(e2))</tt>.
* If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set
* unchanged and returns <tt>false</tt>.
*
* @param e element to be added to this set
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set did not already contain the specified
* element
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//实际上set中添加的一个个元素是放到map中的key位置,而value是Object()
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
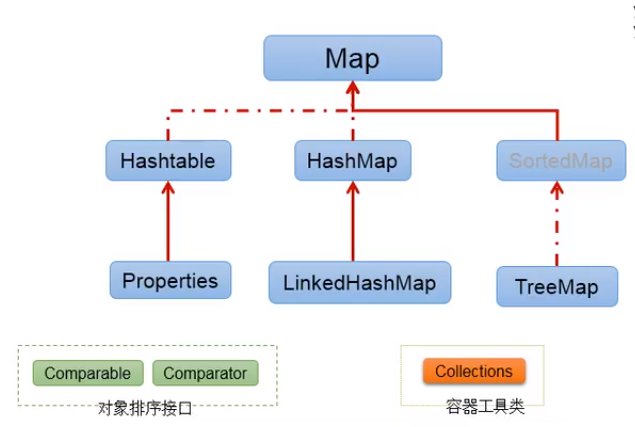
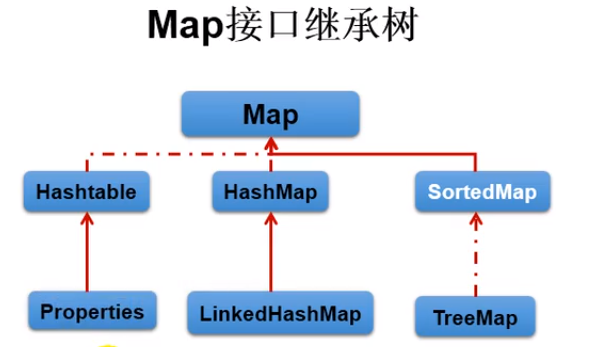
2.4 Map接口
- Map:双列数据,存储key-value对的数据。
- HashMap:作为Map的主要实现类;线程不安全的,效率高;可以存储null的key和value。
- LinkedHashMap:保证在遍历map元素时,可以按照添加的顺序实现遍历。(原因:在原有的HashMap底层结构基础上,添加了一对指针,指向前一个和后一个元素。对于频繁的遍 历操作,此类执行效率高于HashMap)
TreeMap:保证按照添加的key-value对进行排序,实现排序遍历。此时考虑key的自然排序或定制排序,底层使用红黑树。
- LinkedHashMap:保证在遍历map元素时,可以按照添加的顺序实现遍历。(原因:在原有的HashMap底层结构基础上,添加了一对指针,指向前一个和后一个元素。对于频繁的遍 历操作,此类执行效率高于HashMap)
- Hashtable:作为古老的实现类;线程安全的,效率低;不能存储null的key和value。
- Properties:常用来处理配置文件。key和value都是String类型。
- HashMap:作为Map的主要实现类;线程不安全的,效率高;可以存储null的key和value。
- HashMap的底层:数组+链表 (jdk7及之前),数组+链表+红黑树 (jdk 8)
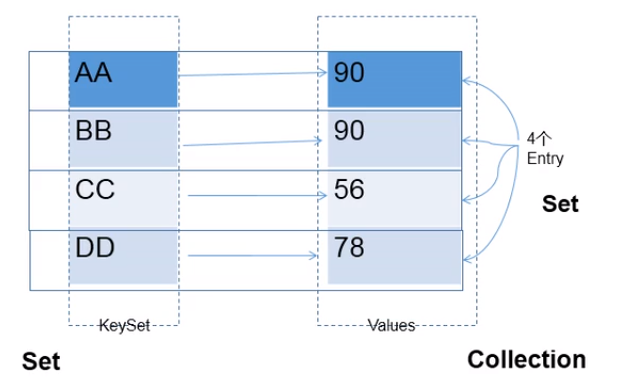
- Map中的key:无序的、不可重复的,使用Set存储所有的key(key所在的类要重写equals()和hashCode() )。
- Map中的value:无序的、可重复的,使用Collection存储所有的value(**value所在的类要重写equals()**)。
- 一个键值对:key-value构成了一个Entry对象。Map中的entry:无序的、不可重复的,使用Set存储所有的entry。
- 添加数据过程(以HashMap为例)
- jdk7
- HashMap map = new HashMap():底层创建了长度是16的一维数组Entry[] table。
- map.put(key1,value1):首先,调用key1所在类的hashCode()计算key1哈希值,此哈希值经过某种算法计算以后,得到在Entry数组中的存放位置。
- 如果此位置上的数据为空,此时的key1-value1添加成功。①
- 如果此位置上的数据不为空,(意味着此位置上存在一个或多个数据(以链表形式存在)),比较key1和已经存在的一个或多个数据的哈希值:
- 如果key1的哈希值与已经存在的数据的哈希值都不相同,此时key1-value1添加成功。②
- 如果key1的哈希值和已经存在的某一个数据(key2-value2)的哈希值相同,继续比较:调用key1所在类的equals(key2)方法比较:
- 如果equals()返回false:此时key1-value1添加成功。③
- 如果equals()返回true:使用value1替换value2。
②和③:此时key1-value1和原来的数据以链表的方式存储。在不断的添加过程中,会涉及到扩容问题,当超出临界值(且要存放的位置非空)时,扩容。默认的扩容方式: 扩容为原来容量的2倍,并将原有的数据复制过来。
- jdk8
- new HashMap():底层没有创建一个长度为16的数组。
- jdk8底层的数组是:Node[],而非Entry[]。
- 首次调用put()方法时,底层创建长度为16的数组。jdk7底层结构只有:数组+链表。jdk8中底层结构:数组+链表+红黑树。
- 形成链表时,七上八下(jdk7:新的元素指向旧的元素。jdk8:旧的元素指向新的元素)
- 当数组的某一个索引位置上的元素以链表形式存在的数据个数 > 8 且当前数组的长度 > 64时,此时此索引位置上的所有数据改为使用红黑树存储。
- jdk7
- HashMap的使用
- Object put(Object key,Object value):将指定key-value添加到(或修改)当前map对象中。
- void putAll(Map m):将m中的所有key-value对存放到当前map中。
- Object remove(Object key):移除指定key的key-value对,并返回value。
- void clear():清空当前map中的所有数据。
- Object get(Object key):获取指定key对应的value。
- boolean containsKey(Object key):是否包含指定的key。
- boolean containsValue(Object value):是否包含指定的value。
- int size():返回map中key-value对的个数。
- boolean isEmpty():判断当前map是否为空。
- boolean equals(Object obj):判断当前map和参数对象obj是否相等。
- Set keySet():返回所有key构成的Set集合。
- Collection values():返回所有value构成的Collection集合。
- Set entrySet():返回所有key-value对构成的Set集合。
1 |
|
TreeMap的使用
- 自然排序(**自然排序中,比较两个对象是否相同的标准为:compareTo()返回0.不再是equals()**)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96public class User implements Comparable{
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
System.out.println("User equals()....");
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
User user = (User) o;
if (age != user.age) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(user.name) : user.name == null;
}
public int hashCode() { //return name.hashCode() + age;
int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + age;
return result;
}
//按照姓名从大到小排列,年龄从小到大排列
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if(o instanceof User){
User user = (User)o;
// return -this.name.compareTo(user.name);
int compare = -this.name.compareTo(user.name);
if(compare != 0){
return compare;
}else{
return Integer.compare(this.age,user.age);
}
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("输入的类型不匹配");
}
}
}
//向TreeMap中添加key-value,要求key必须是由同一个类创建的对象
//自然排序
public void test1(){
TreeMap map = new TreeMap();
User u1 = new User("Tom",23);
User u2 = new User("Jerry",32);
User u3 = new User("Jack",20);
User u4 = new User("Rose",18);
map.put(u1,98);
map.put(u2,89);
map.put(u3,76);
map.put(u4,100);
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();
Iterator iterator1 = entrySet.iterator();
while (iterator1.hasNext()){
Object obj = iterator1.next();
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) obj;
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "---->" + entry.getValue());
}
}执行结果:
1
2
3
4User{name='Tom', age=23}---->98
User{name='Rose', age=18}---->100
User{name='Jerry', age=32}---->89
User{name='Jack', age=20}---->76- 定制排序(**定制排序中,比较两个对象是否相同的标准为:compare()返回0.不再是equals()**)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33//定制排序
public void test(){
TreeMap map = new TreeMap(new Comparator() {
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
if(o1 instanceof User && o2 instanceof User){
User u1 = (User)o1;
User u2 = (User)o2;
return Integer.compare(u1.getAge(),u2.getAge());
}
throw new RuntimeException("输入的类型不匹配!");
}
});
User u1 = new User("Tom",23);
User u2 = new User("Jerry",32);
User u3 = new User("Jack",20);
User u4 = new User("Rose",18);
map.put(u1,98);
map.put(u2,89);
map.put(u3,76);
map.put(u4,100);
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();
Iterator iterator1 = entrySet.iterator();
while (iterator1.hasNext()){
Object obj = iterator1.next();
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) obj;
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "---->" + entry.getValue());
}
}执行结果:
1
2
3
4User{name='Rose', age=18}---->100
User{name='Jack', age=20}---->76
User{name='Tom', age=23}---->98
User{name='Jerry', age=32}---->89HashMap源码解析
- 属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
*/
//默认的初始容量为 16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
/**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
//最大的容量上限为 2^30
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
//默认的负载因子为 0.75
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
*/
//变成树型结构的临界值为 8
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
/**
* The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a
* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at
* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.
*/
//恢复链式结构的临界值为 6
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
/**
* The table, initialized on first use, and resized as
* necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two.
* (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow
* bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.)
*/
//哈希表
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
//哈希表中键值对的个数
transient int size;
/**
* The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in
* the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g.,
* rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
* the HashMap fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*/
//哈希表被修改的次数
transient int modCount;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
*
* @serial
*/
// (The javadoc description is true upon serialization.
// Additionally, if the table array has not been allocated, this
// field holds the initial array capacity, or zero signifying
// DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY.)
//它是通过 capacity*loadfactor 计算出来的,当 size 到达这个值时,就会进行扩容操作
int threshold;
/**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* @serial
*/
//负载因子
final float loadFactor;
/**
* The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.
* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)
* Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts
* between resizing and treeification thresholds.
*/
//当哈希表的大小超过这个阈值,才会把链式结构转化成树型结构,否则仅采取扩容来尝试减少冲突
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;- 哈希表结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43/**
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}- 构造器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
//将加载因子赋值为0.75
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}- put方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods.
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//如果哈希表为空,则先创建一个哈希表
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
//resize()用于构建数组
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//如果当前桶没有碰撞冲突,则直接把键值对插入
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//如果桶上节点的 key 与当前 key 重复,那就是要找的节点
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//如果是采用红黑树的方式处理冲突,则通过红黑树的 putTreeVal 方法去插入这个键值对
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
//否则就是传统的链式结构
else {
//采用循环遍历的方式,判断链中是否有重复的 key
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
//到了链尾还没找到重复的 key,则说明 HashMap 没有包含该键
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
//创建一个新节点插入到尾部
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//如果链的长度大于 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD 这个临界值,则把链变为红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
//找到了重复的 key
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
//这里表示在上面的操作中找到了重复的键,所以这里把该键的值替换为新值
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}- get 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
/**
* Implements Map.get and related methods.
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
//如果哈希表不为空而且key 对应的桶上不为空
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
//是否直接命中
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
//判断是否有后续节点
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
//如果当前的桶是采用红黑树处理冲突,则调用红黑树的 get 方法去获取节点
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
//不是红黑树的话,那就是传统的链式结构了,通过循环的方法判断链中是否存在该 key
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}- remove方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72/**
* Removes the mapping for the specified key from this map if present.
*
* @param key key whose mapping is to be removed from the map
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
/**
* Implements Map.remove and related methods.
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to match if matchValue, else ignored
* @param matchValue if true only remove if value is equal
* @param movable if false do not move other nodes while removing
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
//如果当前 key 映射到的桶不为空
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
//如果桶上的节点就是要找的 key,则直接命中
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
//如果是以红黑树处理冲突,则构建一个树节点
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
//如果是以链式的方式处理冲突,则通过遍历链表来寻找节点
else {
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
//比对找到的 key 的 value 跟要删除的是否匹配
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
//通过调用红黑树的方法来删除节点
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
//使用链表的操作来删除节点
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}LinkedHashMap源码解析
- 属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18/**
* The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
//头指针
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
/**
* The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
//尾指针
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
/**
* The iteration ordering method for this linked hash map: <tt>true</tt>
* for access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order.
*
* @serial
*/
//false: 基于插入顺序 true: 基于访问顺序
final boolean accessOrder;- 结点结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53/**
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* HashMap.Node subclass for normal LinkedHashMap entries.
*/
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}- put方法是HashMap里的,实际上调用时,会调用LinkHashMap重写的newNode方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
3、Collections工具类
- Collections 是一个操作 Set、List 和 Map 等集合的工具类。
- Collections 中提供了一系列静态的方法对集合元素进行排序、查询和修改等操作,还提供了对集合对象设置不可变、对集合对象实现同步控制等方法。
- 常用方法
- reverse(List):反转 List 中元素的顺序。
- shuffle(List):对 List 集合元素进行随机排序。
- sort(List):根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序。
- sort(List,Comparator):根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序。
- swap(List,int, int):将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换。
- Object max(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素。
- Object max(Collection,Comparator):根据 Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素。
- int frequency(Collection,Object):返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数。
- void copy(List dest,List src):将src中的内容复制到dest中。
- boolean replaceAll(List list,Object oldVal,Object newVal):使用新值替换 List 对象的所有旧值。