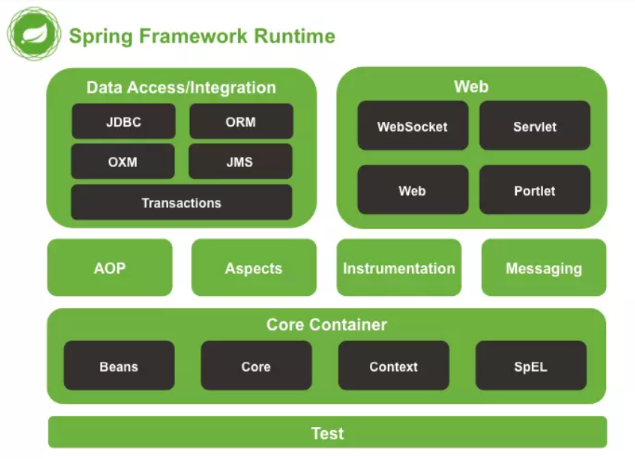
1、Spring概述
- Spring是一个IOC(DI)和AOP容器框架。
- Spring的优良特性:
- 非侵入式:基于Spring开发的应用中的对象可以不依赖于Spring的API。
- 依赖注入:DI——Dependency Injection,反转控制(IOC)最经典的实现。
- 面向切面编程:Aspect Oriented Programming——AOP。
- 容器:Spring是一个容器,因为它包含并且管理应用对象的生命周期。
- 组件化:Spring实现了使用简单的组件配置组合成一个复杂的应用。在 Spring 中可以使用XML和Java注解组合这些对象。
- 一站式:在IOC和AOP的基础上可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架和优秀的第三方类库(实际上Spring 自身也提供了表述层的SpringMVC和持久层的Spring JDBC)。
![]()
创建maven项目测试基本spring功能需要导入以下依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
|
2、@Configuration和@Bean注解
- @Configuration:从Spring3.0,@Configuration用于定义配置类,可替换xml配置文件,被注解的类内部包含有一个或多个被@Bean注解的方法,这些方法将会被AnnotationConfigApplicationContext或AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext类进行扫描,并用于构建bean定义,初始化Spring容器。
- @Bean:产生一个Bean对象,然后这个Bean对象交给Spring管理。产生这个Bean对象的方法Spring只会调用一次,随后这个Spring将会将这个Bean对象放在自己的IOC容器中。
例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
@Bean("person")
public Person person(){
return new Person("李四", 20);
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
Person person = applicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
String[] namesForType = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Person.class);
for (String name : namesForType) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
|
- 也可通过工厂bean注册组件:
- FactoryBean是一个工厂Bean,可以生成某一个类型Bean实例,它最大的一个作用是:可以让我们自定义Bean的创建过程。BeanFactory是Spring容器中的一个基本类也是很重要的一个类,在BeanFactory中可以创建和管理Spring容器中的Bean,它对于Bean的创建有一个统一的流程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| public class Color {
}
public class ColorFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<Color> {
public Color getObject() throws Exception {
System.out.println("ColorFactoryBean...getObject...");
return new Color();
}
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Color.class;
}
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
@Bean
public ColorFactoryBean colorFactoryBean(){
return new ColorFactoryBean();
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : definitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println("****************");
Object bean = applicationContext.getBean( "colorFactoryBean");
System.out.println(bean.getClass());
Object bean2 = applicationContext.getBean("&colorFactoryBean");
System.out.println(bean2.getClass());
}
}
|
- 特别地,如果用@Bean注解创建对象时,方法参数的值默认从ioc容器中获取。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| @Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Repository
public class UserDao {
private String name = "小红";
}
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
private void print() {
System.out.println(userDao);
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.example.service","com.example.dao",
"com.example.controller","com.example.bean"})
public class MainConfig {
@Bean
public UserService userService(UserDao userDao){
UserService userService = new UserService();
userService.setUserDao(userDao);
return userService;
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
UserService bean = applicationContext.getBean(UserService.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
}
|
3、@ComponentScan注解
- ComponentScan注解:根据指定的配置自动扫描package,将符合条件的组件加入到IOC容器中,该注解默认会扫描该类所在的包下所有的配置类。
- Filter[] includeFilters():指定扫描的时候只需要包含哪些组件。
- Filter[] excludeFilters():指定扫描的时候按照什么规则排除那些组件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.example")
public class MainConfig {
@Bean("person")
public Person person(){
return new Person("李四", 20);
}
}
@Controller
public class UserController {
}
@Service
public class UserService {
}
@Repository
public class UserDao {
}
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Component
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : definitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
|
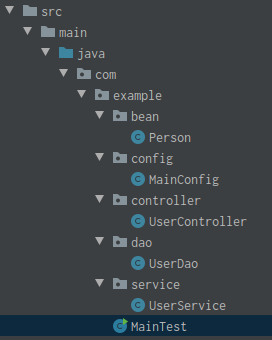
类及其所在包的目录如下:
![]()
打印如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
mainConfig
person
userController
userDao
userService
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| @Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.example",excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
})
public class MainConfig {
@Bean("person")
public Person person(){
return new Person("李四", 20);
}
}
|
则打印如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
mainConfig
person
userDao
userService
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.example",includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = Controller.class)
},useDefaultFilters = false)
public class MainConfig {
@Bean("person")
public Person person(){
return new Person("李四", 20);
}
}
|
则打印如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
mainConfig
userController
person
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| @Configuration
@ComponentScans(value = {
@ComponentScan(value = "com.example",includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type=FilterType.CUSTOM,classes={MyTypeFilter.class})
},useDefaultFilters = false)
})
public class MainConfig {
@Bean("person")
public Person person(){
return new Person("李四", 20);
}
}
public class MyTypeFilter implements TypeFilter {
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
ClassMetadata classMetadata = metadataReader.getClassMetadata();
Resource resource = metadataReader.getResource();
String className = classMetadata.getClassName();
System.out.println("--->"+className);
if(className.contains("ter")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
|
则打印如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| --->com.example.MainTest
--->com.example.bean.Person
--->com.example.config.MyTypeFilter
--->com.example.controller.UserController
--->com.example.dao.UserDao
--->com.example.service.UserService
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
mainConfig
myTypeFilter
person
|
4、@Scope注解
- @Scope注解是springIoc容器中的一个作用域,在 Spring IoC 容器中具有以下几种作用域:基本作用域singleton(单例)、**prototype(多例)**,Web 作用域(reqeust、session、globalsession),自定义作用域。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
@Scope("singleton")
@Bean("person")
public Person person(){
System.out.println("给容器中添加person组件");
return new Person("李四", 20);
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
Object person1 = applicationContext.getBean("person");
Object person2 = applicationContext.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person1 == person2);
}
}
|
5、@Lazy注解
- Spring IoC (ApplicationContext) 容器一般都会在启动的时候实例化所有单实例 bean 。如果我们想要 Spring 在启动的时候延迟加载 bean,即在调用某个 bean 的时候再去初始化,那么就可以使用 @Lazy 注解。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
@Bean("person")
@Lazy
public Person person(){
System.out.println("给容器中添加person组件");
return new Person("李四", 20);
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
Object person = applicationContext.getBean("person");
}
}
|
6、@Conditional注解
- @Conditional是Spring4新提供的注解,它的作用是按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件给容器注册bean。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
|
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
@Bean("bill")
@Conditional(WindowsCondition.class)
public Person person01(){
return new Person("Bill Gates",62);
}
@Bean("linus")
@Conditional(LinuxCondition.class)
public Person person02(){
return new Person("linus", 48);
}
}
public class LinuxCondition implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader();
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = context.getRegistry();
boolean definition = registry.containsBeanDefinition("person");
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if(property.contains("Linux")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
public class WindowsCondition implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if(property.contains("Windows")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
String[] namesForType = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Person.class);
for (String name : namesForType){
System.out.println(name);
}
Map<String, Person> beansOfType = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(Person.class);
System.out.println(beansOfType);
}
}
|
7、@Import注解
- @Import只能用在类上 ,@Import通过快速导入的方式实现把实例加入spring的IOC容器中。
- 第一种方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public class Blue {
}
public class Red {
}
@Configuration
@Import({Blue.class, Red.class})
public class MainConfig {
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : definitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| public class Blue {
}
public class Red {
}
@Configuration
@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
public class MainConfig {
}
public class MyImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
return new String[]{"com.example.bean.Blue","com.example.bean.Red"};
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : definitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| public class Blue {
}
public class Red {
}
public class RainBow {
}
@Configuration
@Import({MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class, Red.class, Blue.class})
public class MainConfig {
}
public class MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
boolean definition = registry.containsBeanDefinition("com.example.bean.Red");
boolean definition2 = registry.containsBeanDefinition("com.example.bean.Blue");
if(definition && definition2){
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(RainBow.class);
registry.registerBeanDefinition("rainBow", beanDefinition);
}
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : definitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
|
8、@Value和@PropertySource注解
- 使用@Value注解可以给bean的属性赋值。使用@PropertySource读取外部配置文件中的k/v保存到运行的环境变量中;加载完外部的配置文件以后使用${}取出配置文件的值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| @Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Person {
@Value("张三")
private String name;
@Value("#{20-2}")
private Integer age;
@Value("${person.nickName}")
private String nickName;
}
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value={"classpath:/person.properties"})
public class MainConfig {
@Bean
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
Person bean = applicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(bean);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
String property = environment.getProperty("person.nickName");
System.out.println(property);
}
}
|
person.properties文件:
9、@Autowired、@Qualifier、@Primary、@Resource和@Inject注解
- @Autowired:自动注入。默认一定要将属性赋值,否则会报错,但可以使用@Autowired(required=false)。
- 默认优先按照类型去容器中找对应的组件:applicationContext.getBean(UserDao.class);找到就赋值。
- 如果找到多个相同类型的组件,再将属性的名称作为组件的id去容器中查找:applicationContext.getBean(“userDao”)。
- @Qualifier:使用@Qualifier指定需要装配的组件的id,而不是使用属性名。
- @Primary:让Spring进行自动装配的时候,默认使用首选的bean。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| @Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Repository
public class UserDao {
private String name = "小红";
}
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao2;
private void print(){
System.out.println(userDao2);
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.example.service","com.example.dao",
"com.example.controller","com.example.bean"})
public class MainConfig {
@Bean("userDao2")
public UserDao userDao(){
return new UserDao("小明");
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
UserService bean = applicationContext.getBean(UserService.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
}
|
- 如果UserService类使用@Qualifier,则打印UserService(userDao2=UserDao(name=小红)):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("userDao")
private UserDao userDao2;
private void print(){
System.out.println(userDao2);
}
}
|
- 如果配置类使用@Primary(要发挥效果得不使用@Qualifier),则打印UserService(userDao2=UserDao(name=小明)):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| @Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.example.service","com.example.dao",
"com.example.controller","com.example.bean"})
public class MainConfig {
@Primary
@Bean("userDao2")
public UserDao userDao(){
return new UserDao("小明");
}
}
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao2;
private void print(){
System.out.println(userDao2);
}
}
|
10、@Profile注解
- @Profile:指定组件在哪个环境的情况下才能被注册到容器中,不指定则任何环境下都能注册这个组件。此注解可以标注在类和方法上。
- 加了环境标识的bean,只有这个环境被激活的时候才能注册到容器中。默认是default环境。
- 写在配置类上时,只有是指定的环境的时候,整个配置类里面的所有配置才能开始生效。
- 没有标注环境标识的bean在,任何环境下都是加载的。
- 测试根据不同环境设置切换数据源,需要导入以下依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.21</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>
|
配置文件代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
| @Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:/dbconfig.properties")
public class MainConfig implements EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
@Value("${db.user}")
private String userName;
private String driverClassName;
private StringValueResolver valueResolver;
@Profile("test")
@Bean("testDataSource")
public DataSource dataSourceTest(@Value("${db.password}")String password) throws Exception{
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test");
dataSource.setUsername(userName);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
@Profile("dev")
@Bean("devDataSource")
public DataSource dataSourceDev(@Value("${db.password}")String password) throws Exception{
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dev");
dataSource.setUsername(userName);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
@Profile("prod")
@Bean("prodDataSource")
public DataSource dataSourceProd(@Value("${db.password}")String password) throws Exception{
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/prod");
dataSource.setUsername(userName);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver stringValueResolver) {
this.valueResolver = stringValueResolver;
driverClassName = valueResolver.resolveStringValue("${db.driverClass}");
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
applicationContext.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("test","dev");
applicationContext.register(MainConfig.class);
applicationContext.refresh();
String[] namesForType = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(DataSource.class);
for (String string : namesForType) {
System.out.println(string);
}
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) applicationContext.getBean("devDataSource");
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
}
|
dbconfig.properties内容为:
1
2
3
4
| db.user=root
db.password=<你的数据库密码>
db.driverClass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
|
执行结果:
1
2
3
| testDataSource
devDataSource
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@123ef382
|