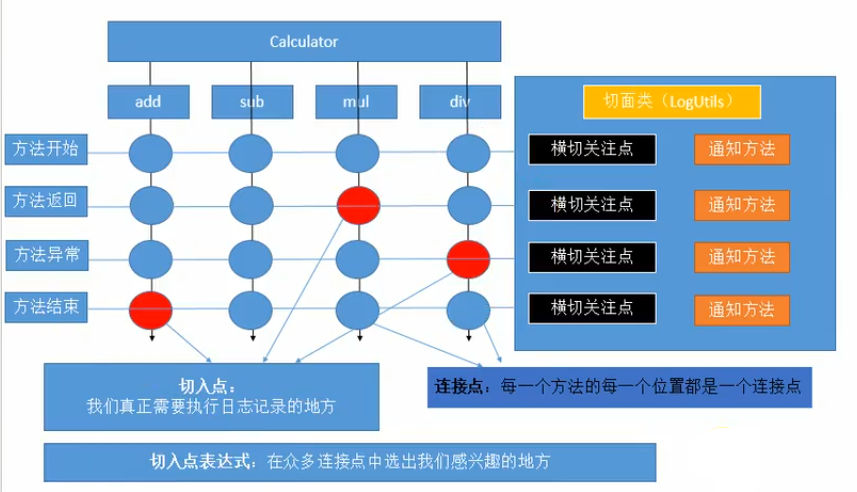
1、AOP概述
- AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming,面向切面编程):是一种新的方法论,是对传统 OOP(Object-Oriented Programming,面向对象编程)的补充。
- AOP编程操作的主要对象是切面(aspect),而切面模块化横切关注点。
- 在应用AOP编程时,仍然需要定义公共功能,但可以明确的定义这个功能应用在哪里,以什么方式应用,并且不必修改受影响的类。这样一来横切关注点就被模块化到特殊的类里——这样的类我们通常称之为“切面”。
- AOP术语:
- 横切关注点:从每个方法中抽取出来的同一类非核心业务。
- 切面(Aspect):封装横切关注点信息的类,每个关注点体现为一个通知方法。
- 通知(Advice):切面必须要完成的各个具体工作。
- 目标(Target):被通知的对象。
- 代理(Proxy):向目标对象应用通知之后创建的代理对象。
- 连接点(Joinpoint):横切关注点在程序代码中的具体体现,对应程序执行的某个特定位置。例如:类某个方法调用前、调用后、方法捕获到异常后等。
- 切入点(pointcut):定位连接点的方式。每个类的方法中都包含多个连接点,所以连接点是类中客观存在的事物。如果把连接点看作数据库中的记录,那么切入点就是查询条件——AOP可以通过切入点定位到特定的连接点。切点通过org.springframework.aop.Pointcut 接口进行描述,它使用类和方法作为连接点的查询条件。
![]()
2、实现AOP
- ①新建maven工程,导入aop模块Spring AOP(spring-aspects):
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
|
- ②定义一个业务逻辑类(MathCalculator)并加入到容器中,在业务逻辑运行的时候将日志进行打印(方法之前、方法运行结束、方法出现异常,xxx)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
public interface Calculator {
int add(int i,int j);
int sub(int i,int j);
int mul(int i,int j);
int div(int i,int j);
}
@Service
public class MathCalculator implements Calculator{
public int add(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("add目标方法执行");
return i + j;
}
public int sub(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("sub目标方法执行");
return i - j;
}
public int mul(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("mul目标方法执行");
return i*j;
}
public int div(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("div目标方法执行");
return i/j;
}
}
|
- ③定义一个日志切面类(logUtil)并加入到容器中,同时标注@Aspect注解(告知spring这是一个切面类),里面包含多个通知方法:
- 前置通知(@Before):logStart(在目标方法运行之前运行)
- 后置通知(@After):logEnd(在目标方法运行结束之后运行(无论方法正常结束还是异常结束))
- 返回通知(@AfterReturning):logReturn(在目标方法(div)正常返回之后运行)
- 异常通知(@AfterThrowing):logException(在目标方法(div)出现异常以后运行)
- spring对通知方法的要求不严格,即是private也行,但是参数列表一定要准确。
- AspectJ中的exection表达式:
- execution(访问权限符 返回值类型 方法签名(参数表))
- 通配符“*”的使用:
- 匹配一个字符或多个字符:(“execution(public int com.example.aop.MathCal*or.*(int,int))”)
- 匹配任意一个参数:(“execution(public int com.example.aop.MathCal*or.*(int,*))”)
- 只能匹配一层路径:(“execution(public int com.example.*.MathCal*or.*(int,*))”)
- 权限位置不能用*。
- 通配符“..”的使用:
- 匹配任意多个参数,任意类型参数:(“execution(public int com.example.aop.MathCal*or.*(..))”)
- 匹配任意多层路径:(“execution(public int com.aop..MathCal*or.*(int,*))”)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| @Component
@Aspect
public class logUtil {
@Before("execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println(name +"方法开始执行,参数列表为:" + Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))",returning = "result")
public static void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println(name +"方法执行完成,执行结果为:" + result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception exception){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println(name + "方法出现异常,异常信息为:" + exception);
}
@After("execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println(name + "方法执行结束");
}
}
|
还可以使用抽取可重用的切入点表达式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| @Component
@Aspect
public class logUtil2 {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public void myPoint(){
}
@Before("myPoint()")
public static void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("logUtil前置:" + name +"方法开始执行,参数列表为:" + Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "myPoint()",returning = "result")
public static void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("logUtil返回:" + name +"方法执行完成,执行结果为:" + result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPoint()",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception exception){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("logUtil异常:" + name + "方法出现异常,异常信息为:" + exception);
}
@After("myPoint()")
public static void logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("logUtil后置:" + name + "方法执行结束");
}
}
|
- ④给配置类中加 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy,并用@ComponentScan注解扫描aop包下的组件,即开启基于注解的aop模式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan("com.example.aop")
public class MainConfig {
}
|
- ⑤测试aop,如果业务逻辑类有实现接口,则默认使用的是jdk代理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
Calculator calculator = applicationContext.getBean(Calculator.class);
System.out.println(calculator);
System.out.println(calculator.getClass());
Calculator calculator2 = (Calculator) applicationContext.getBean("mathCalculator");
System.out.println(calculator2);
System.out.println(calculator2.getClass());
}
}
|
- 如果业务逻辑类没有实现接口,则是使用cglib代理,测试如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
MathCalculator calculator = applicationContext.getBean(MathCalculator.class);
System.out.println(calculator);
System.out.println(calculator.getClass());
MathCalculator calculator1 = (MathCalculator) applicationContext.getBean("mathCalculator");
System.out.println(calculator1);
System.out.println(calculator1.getClass());
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
MathCalculator bean = applicationContext.getBean(MathCalculator.class);
bean.add(1,1);
System.out.println("****************");
bean.div(1,0);
}
}
|
执行结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| add方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 1]
add目标方法执行
add方法执行结束
add方法执行完成,执行结果为:2
****************
div方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 0]
div目标方法执行
div方法执行结束
div方法出现异常,异常信息为:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
|
- 如果使用环绕通知,可以获取目标方法的完全控制权(方法是否执行、控制参数、控制返回值),目标方法的一切信息,都可以通过invocation(invoke方法传进去的参数名称)参数获取到。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| @Component
@Aspect
public class logUtil {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public void myPoint(){
}
@Around("myPoint()")
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
String name = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object proceed = null;
try {
System.out.println("【环绕前置通知】:" + name +"方法开始执行,参数列表为:" + Arrays.asList(args));
proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(args);
System.out.println("【环绕返回通知】:" + name +"方法执行完成,执行结果为:" + proceed);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("【环绕异常通知】:" + name + "方法出现异常,异常信息为:" + throwable);
throw new RuntimeException(throwable);
} finally {
System.out.println("【环绕后置通知】:" + name + "方法执行结束");
}
return proceed;
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
MathCalculator bean = applicationContext.getBean(MathCalculator.class);
bean.add(1,1);
System.out.println("****************");
bean.div(1,0);
}
}
|
测试结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| 【环绕前置通知】:add方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 1]
add目标方法执行
【环绕返回通知】:add方法执行完成,执行结果为:2
【环绕后置通知】:add方法执行结束
****************
【环绕前置通知】:div方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 0]
div目标方法执行
【环绕异常通知】:div方法出现异常,异常信息为:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
【环绕后置通知】:div方法执行结束
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
| @Component
@Aspect
public class logUtil {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public void myPoint(){
}
@Before("execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println(name +"方法开始执行,参数列表为:" + Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))",returning = "result")
public static void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println(name +"方法执行完成,执行结果为:" + result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception exception){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println(name + "方法出现异常,异常信息为:" + exception);
}
@After("execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println(name + "方法执行结束");
}
@Around("myPoint()")
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
String name = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object proceed = null;
try {
System.out.println("【环绕前置通知】:" + name +"方法开始执行,参数列表为:" + Arrays.asList(args));
proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(args);
System.out.println("【环绕返回通知】:" + name +"方法执行完成,执行结果为:" + proceed);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("【环绕异常通知】:" + name + "方法出现异常,异常信息为:" + throwable);
throw new RuntimeException(throwable);
} finally {
System.out.println("【环绕后置通知】:" + name + "方法执行结束");
}
return proceed;
}
}
|
执行结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| 【环绕前置通知】:add方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 1]
add方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 1]
add目标方法执行
【环绕返回通知】:add方法执行完成,执行结果为:2
【环绕后置通知】:add方法执行结束
add方法执行结束
add方法执行完成,执行结果为:2
****************
【环绕前置通知】:div方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 0]
div方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 0]
div目标方法执行
【环绕异常通知】:div方法出现异常,异常信息为:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
【环绕后置通知】:div方法执行结束
div方法执行结束
div方法出现异常,异常信息为:java.lang.RuntimeException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
|
总结执行顺序为:环绕前置–>普通前置–>目标方法执行–>环绕返回/异常–>环绕后置–>普通后置–>普通返回/异常。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
| @Component
@Aspect
public class LogUtil {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public void myPoint(){
}
@Before("myPoint()")
public static void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("LogUtil前置:" + name +"方法开始执行,参数列表为:" + Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "myPoint()",returning = "result")
public static void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("LogUtil返回:" + name +"方法执行完成,执行结果为:" + result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPoint()",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception exception){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("LogUtil异常:" + name + "方法出现异常,异常信息为:" + exception);
}
@After("myPoint()")
public static void logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("LogUtil后置:" + name + "方法执行结束");
}
}
@Component
@Aspect
public class AnotherLogUtil {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.MathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public void myPoint(){
}
@Before("myPoint()")
public static void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("AnotherLogUtil前置:" + name +"方法开始执行,参数列表为:" + Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "myPoint()",returning = "result")
public static void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("AnotherLogUtil返回:" + name +"方法执行完成,执行结果为:" + result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPoint()",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception exception){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("AnotherLogUtil异常:" + name + "方法出现异常,异常信息为:" + exception);
}
@After("myPoint()")
public static void logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String name = signature.getName();
System.out.println("AnotherLogUtil后置:" + name + "方法执行结束");
}
}
|
执行结果(由于这两个切面类没有用@Order注解设置优先级,所以默认先后顺序由两个类的字母排序先后决定):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| AnotherLogUtil前置:add方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 1]
LogUtil前置:add方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 1]
add目标方法执行
LogUtil后置:add方法执行结束
LogUtil返回:add方法执行完成,执行结果为:2
AnotherLogUtil后置:add方法执行结束
AnotherLogUtil返回:add方法执行完成,执行结果为:2
****************
AnotherLogUtil前置:div方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 0]
LogUtil前置:div方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 0]
div目标方法执行
LogUtil后置:div方法执行结束
LogUtil异常:div方法出现异常,异常信息为:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
AnotherLogUtil后置:div方法执行结束
AnotherLogUtil异常:div方法出现异常,异常信息为:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
|
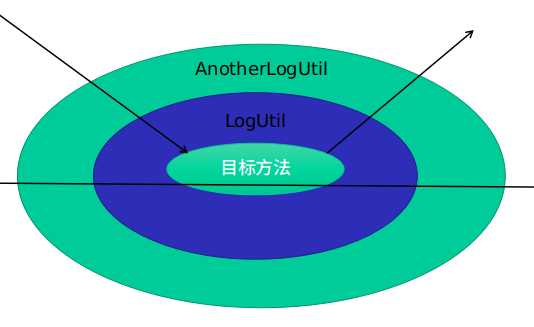
图解:
![]()
如果在上面AnotherLogUtil类里加个环绕通知,则执行结果如下,证明环绕通知只影响当前所在切面:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| 【环绕前置通知】:add方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 1]
AnotherLogUtil前置:add方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 1]
LogUtil前置:add方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 1]
add目标方法执行
LogUtil后置:add方法执行结束
LogUtil返回:add方法执行完成,执行结果为:2
【环绕返回通知】:add方法执行完成,执行结果为:2
【环绕后置通知】:add方法执行结束
AnotherLogUtil返回:add方法执行完成,执行结果为:2
****************
【环绕前置通知】:div方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 0]
AnotherLogUtil前置:div方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 0]
LogUtil前置:div方法开始执行,参数列表为:[1, 0]
div目标方法执行
LogUtil后置:div方法执行结束
LogUtil异常:div方法出现异常,异常信息为:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
【环绕异常通知】:div方法出现异常,异常信息为:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
【环绕后置通知】:div方法执行结束
AnotherLogUtil异常:div方法出现异常,异常信息为:java.lang.RuntimeException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
|