Spring监听器
1、使用ApplicationListener
Spring监听器在使用过程中可以监听到某一事件的发生,进而对事件做出相应的处理。下面先创建一个自定义监听器(实现ApplicationListener接口的bean)做测试。
- ①写一个自定义监听器(ApplicationListener实现类)来监听某个事件(ApplicationEvent及其子类)。
1
2
3
4
5
6public class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
//当容器中发布此事件以后,方法触发
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent applicationEvent) {
System.out.println("收到事件:"+applicationEvent);
}
}
- ②把监听器加入到容器。
1 |
|
- ③编写测试代码。
1 | public class MainTest { |
执行结果如下,可见在Spring容器的启动和关闭过程中曾发布过两个事件:ContextRefreshedEvent和ContextClosedEvent,同时也收到了自己发布的事件。
1 | 收到事件:org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent[source=org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@5010be6, started on Thu Dec 03 21:31:19 CST 2020] |
Spring发布事件和监听器接收事件的原理:
- ①在上方测试用例中new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class)的构造器调用的refresh()方法中调用了initApplicationEventMulticaster()方法,即初始化一个事件派发器(多播器)。
- ①获取BeanFactory。
- ②从BeanFactory中获取id=”applicationEventMulticaster”的ApplicationEventMulticaster,若没有则创建一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster。
- ③将创建的ApplicationEventMulticaster添加到BeanFactory中,以后其他组件可以直接自动注入。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29public static final String APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME = "applicationEventMulticaster";
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
this();
register(componentClasses);
refresh();
}
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
//获取BeanFactory。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
//从BeanFactory中获取applicationEventMulticaster的ApplicationEventMulticaster,若没有则创建一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster。
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
//将创建的ApplicationEventMulticaster添加到BeanFactory中。
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}- ②接着调用registerListeners()将所有项目里面的ApplicationListener注册进容器。
- ①从容器中拿到所有的ApplicationListener。
- ②将每个监听器添加到事件派发器中。
- ③派发之前步骤产生的事件(早期事件)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
//从容器中拿到所有的ApplicationListener。
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
//将每个监听器添加到事件派发器中。
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
//派发之前步骤产生的事件。
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}- ③接着调用finishRefresh()方法,现在重点分析其中publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this))方法中发布事件的流程。
- ①获取事件的多播器(派发器)即调用getApplicationEventMulticaster()。
- ②调用multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType)方法派发事件。
- ①获取到所有的ApplicationListener。
- ②如果有Executor,可以支持使用Executor进行异步派发。(可以在容器中自己继承SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,并初始化一个线程池,然后将其注册到容器中,bean的名字必须使用“applicationEventMulticaster”。)
- ③否则以同步的方式直接执行listener方法,即调用invokeListener(listener, event)方法后间接调用doInvokeListener(listener, event)方法,最后调用listener的onApplicationEvent方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
clearResourceCaches();
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
//发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件。
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
public void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
publishEvent(event, null);
}
protected void publishEvent(Object event, ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must nodoInvokeListener(listener, event)t be null");
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent<?>) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
//获取到所有的ApplicationListener遍历进行事件的派发。
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
//如果有Executor,可以支持使用Executor进行异步派发。
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
if (errorHandler != null) {
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass())) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
// -> let's suppress the exception and just log a debug message.
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}- ④用同样的方式执行测试用例中的applicationContext.publishEvent(new ApplicationEvent(“我发布的事件”) {})发布了自定义事件,并被监听器接收到。
- ⑤最后执行applicationContext.close()方法关闭容器时会执行doClose()方法进而通过调用publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this))方法发布一个事件ContextClosedEvent。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63public void close() {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
doClose();
// If we registered a JVM shutdown hook, we don't need it anymore now:
// We've already explicitly closed the context.
if (this.shutdownHook != null) {
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// ignore - VM is already shutting down
}
}
}
}
protected void doClose() {
// Check whether an actual close attempt is necessary...
if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Closing " + this);
}
LiveBeansView.unregisterApplicationContext(this);
try {
// Publish shutdown event.
//发布事件ContextClosedEvent。
publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from ApplicationListener handling ContextClosedEvent", ex);
}
// Stop all Lifecycle beans, to avoid delays during individual destruction.
if (this.lifecycleProcessor != null) {
try {
this.lifecycleProcessor.onClose();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from LifecycleProcessor on context close", ex);
}
}
// Destroy all cached singletons in the context's BeanFactory.
destroyBeans();
// Close the state of this context itself.
closeBeanFactory();
// Let subclasses do some final clean-up if they wish...
onClose();
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners != null) {
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Switch to inactive.
this.active.set(false);
}
}- ①在上方测试用例中new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class)的构造器调用的refresh()方法中调用了initApplicationEventMulticaster()方法,即初始化一个事件派发器(多播器)。
2、使用@EventListener
使用注解@EventListener可以使任何方法来监听事件。测试用例如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23public class MyEventListener {
public void listen(ApplicationEvent event) {
System.out.println("MyEventListener监听到的事件:" + event);
}
}
public class MainConfig {
public MyEventListener myEventListener(){
return new MyEventListener();
}
}
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
//自己发布一个事件
applicationContext.publishEvent(new ApplicationEvent("我发布的事件") {});
applicationContext.close();
}
}执行结果:
1
2
3MyEventListener监听到的事件:org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent[source=org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@5010be6, started on Thu Dec 03 22:38:02 CST 2020]
MyEventListener监听到的事件:com.example.MainTest$1[source=我发布的事件]
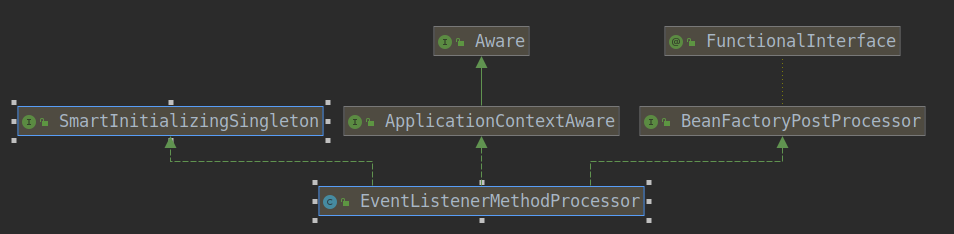
MyEventListener监听到的事件:org.springframework.context.event.ContextClosedEvent[source=org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@5010be6, started on Thu Dec 03 22:38:02 CST 2020]原理是使用EventListenerMethodProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor和SmartInitializingSingleton接口的实现类)来解析方法上的@EventListener,将其生成ApplicationListener(ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter)对象,在publishEvent时,通过getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType)函数,获取到ApplicationListener对象,通过反射调用方法。
![]()
- 重点看其实现SmartInitializingSingleton接口后重写的afterSingletonsInstantiated()方法,此方法是在容器中所有bean创建完后触发的(见finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)方法)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.beanFactory;
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "No ConfigurableListableBeanFactory set");
String[] beanNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!ScopedProxyUtils.isScopedTarget(beanName)) {
Class<?> type = null;
try {
type = AutoProxyUtils.determineTargetClass(beanFactory, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (type != null) {
if (ScopedObject.class.isAssignableFrom(type)) {
try {
Class<?> targetClass = AutoProxyUtils.determineTargetClass(
beanFactory, ScopedProxyUtils.getTargetBeanName(beanName));
if (targetClass != null) {
type = targetClass;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An invalid scoped proxy arrangement - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target bean for scoped proxy '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
try {
processBean(beanName, type);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Failed to process @EventListener " +
"annotation on bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
}
}
private void processBean(final String beanName, final Class<?> targetType) {
//查找没有注解的class
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetType) &&
AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetType, EventListener.class) &&
!isSpringContainerClass(targetType)) {
Map<Method, EventListener> annotatedMethods = null;
//查找被注解EventListener的方法。
try {
annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<EventListener>) method ->
AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable type in a method signature, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve methods for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
//添加到没有注解的集合。
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(annotatedMethods)) {
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetType);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No @EventListener annotations found on bean class: " + targetType.getName());
}
}
else {
// Non-empty set of methods
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = this.applicationContext;
Assert.state(context != null, "No ApplicationContext set");
List<EventListenerFactory> factories = this.eventListenerFactories;
Assert.state(factories != null, "EventListenerFactory List not initialized");
for (Method method : annotatedMethods.keySet()) {
for (EventListenerFactory factory : factories) {
if (factory.supportsMethod(method)) {
Method methodToUse = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, context.getType(beanName));
//创建applicationListener,通过Adapter将注解形式的listener转换为普通的listener。
ApplicationListener<?> applicationListener =
factory.createApplicationListener(beanName, targetType, methodToUse);
if (applicationListener instanceof ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) {
((ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) applicationListener).init(context, this.evaluator);
}
//添加listener到applicationContext。
context.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);
break;
}
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(annotatedMethods.size() + " @EventListener methods processed on bean '" +
beanName + "': " + annotatedMethods);
}
}
}
}