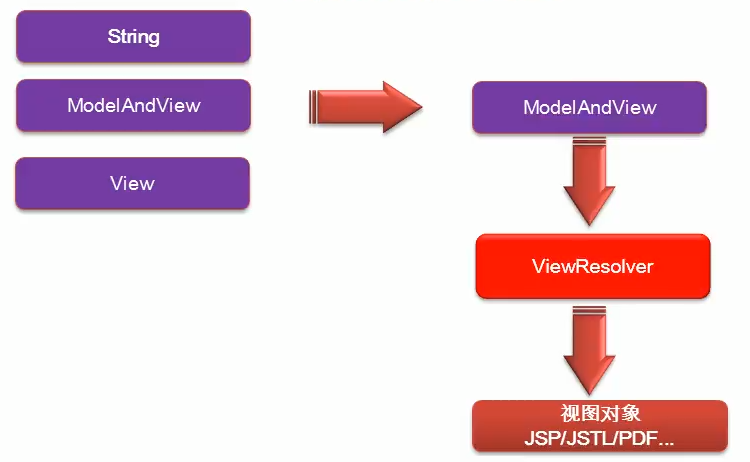
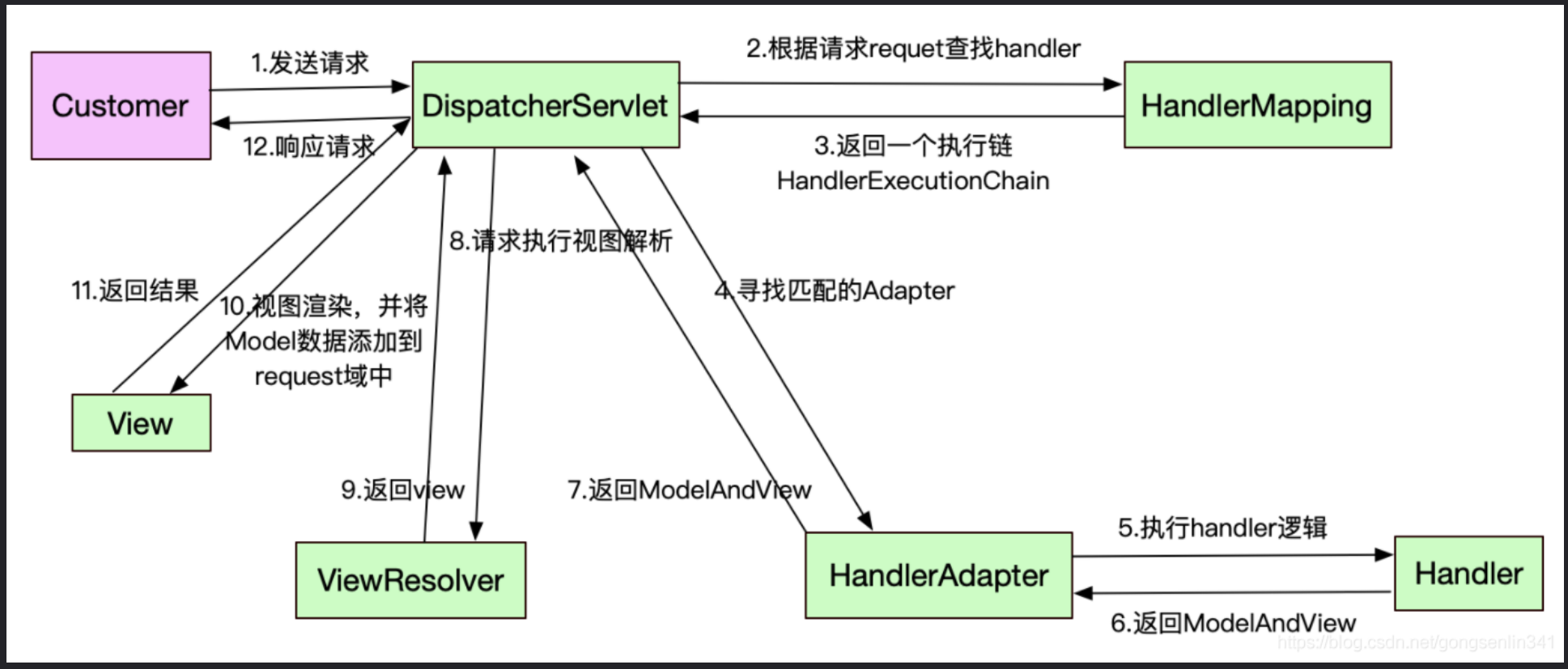
SpringMVC运行流程
Spring Web MVC是一种基于Java的实现了Web MVC设计模式的请求驱动类型的轻量级Web框架,即使用了MVC架构模式的思想,将web层进行职责解耦,基于请求驱动指的就是使用请求-响应模型,框架的目的就是帮助我们简化开发,Spring Web MVC也是要简化我们日常Web开发的。
新建一个maven项目,实现一个SpringMVC测试用例:
- ①在pom.xml中导入相关依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target>
<!--spring 版本号-->
<spring.version>5.2.11.RELEASE</spring.version>
<!--jackson 版本号-->
<jackson.version>2.11.3</jackson.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--日志-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0-alpha0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--spring 核心包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring JDBC -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring MVC -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 提供 Servlet 编译环境 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 提供 JSP 支持环境(自定义标签) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 提供 JSTL 支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--Spring MVC 对 JSON 的支持需要依赖 jackson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 启用校验支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.1.6.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.projectlombok/lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.12</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
②在resources文件夹下新建springmvc.xml文件,其内容如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
">
<!--扫描controller-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example">
</context:component-scan>
<!--配置视图解析器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
</beans>③在web.xml中配置前端控制器,并指定springmvc配置文件位置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--启动SpringMVC容器-->
<!--配置前端控制器能拦截所有请求,并智能派发-->
<!--这个前端控制器是一个servlet,应该在web.xml中配置这个servlet来拦截所有请求-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--servlet启动加载,servlet原本是第一次访问就创建对象-->
<!--load-on-startup表示服务器启动的时候创建对象,值越小优先级越高,越先创建对象-->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<!--/和/*都是拦截所有请求,但/*的范围更大,还会拦截到*.jsp这些请求,一旦拦截页面就无法显示-->
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>④web-app目录下的index.jsp文件内容如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<body>
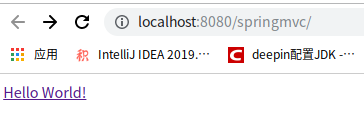
<a href="hello">Hello World!</a>
</body>
</html>⑤在WEB-INF/pages下新建success.jsp,其内容如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
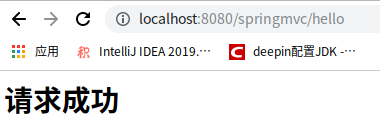
<h1>请求成功</h1>
<%System.out.println("success页面请求成功"); %>
</body>
</html>⑥编写HelloController。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class HelloController {
public String hello(){
System.out.println("请求成功");
//return "WEB-INF/pages/success.jsp";
return "success";
}
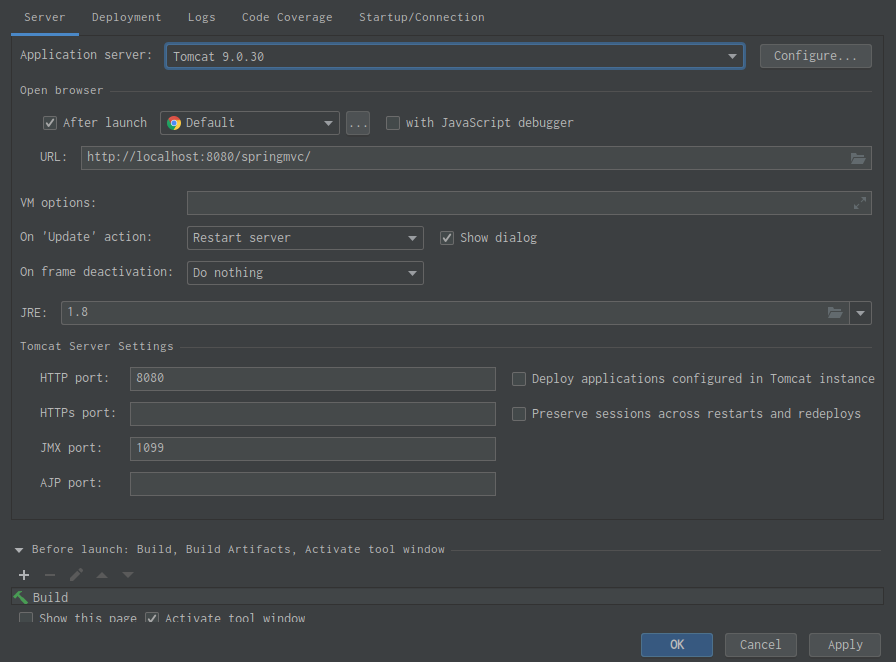
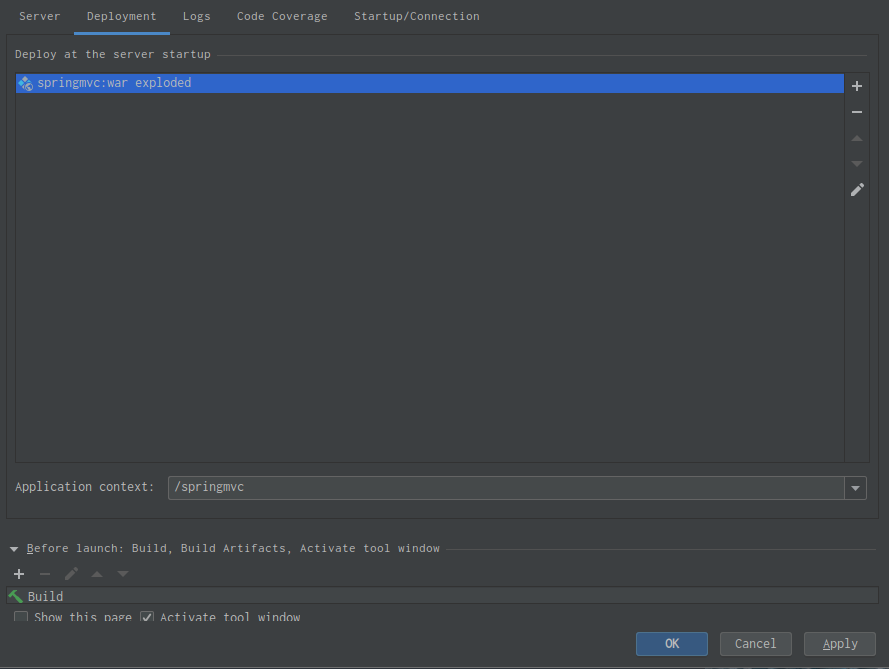
}⑦配置本地的tomcat如图:
![]()
![]()
⑧测试成功访问到页面:
![]()
![]()
分析运行过程:
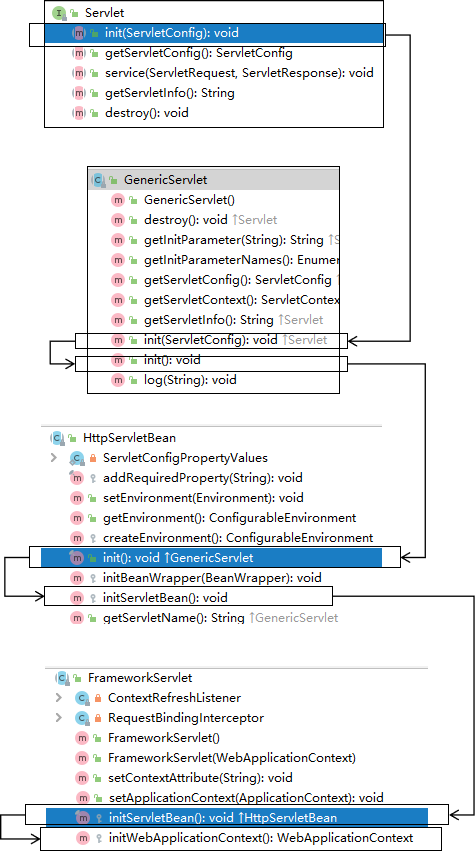
①介绍运行流程之前,先介绍SpringMVC的九大组件,也就是SpringMVC在工作时,关键是由这些组件来完成的,这些组件定义在前端控制器DispatcherServlet类中(九大组件全是接口),DispatcherServlet 本质上是一个Servlet,所以天然的遵循Servlet的生命周期。所以宏观上是Servlet生命周期来进行调度:
![]()
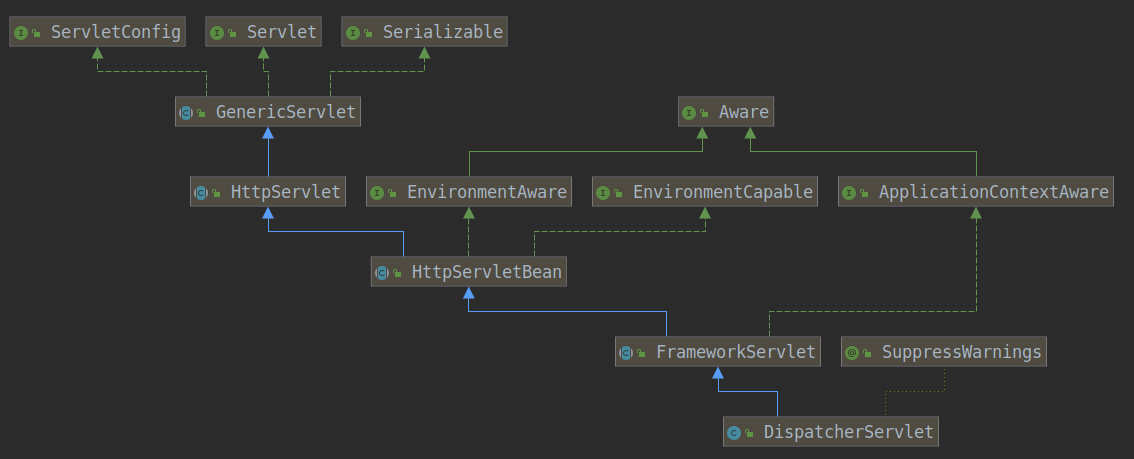
DispatcherServlet类的继承树如下图:
![]()
最终会调用到FrameworkServlet中的initServletBean()->initWebApplicationContext()->createWebApplicationContext(rootContext)创建WebApplicationContext(springMVC的IOC容器)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
// 创建WebApplicationContext
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
// 刷新WebApplicationContext
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
// 将IOC容器在应用域共享
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}1
2
3protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext( WebApplicationContext parent) {
return createWebApplicationContext((ApplicationContext) parent);
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext( ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
// 通过反射创建 IOC 容器对象
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
// 设置父容器(Spring的IOC容器)
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}接着会在initWebApplicationContext()方法中继续执行onRefresh(wac)刷新springMVC的IOC容器。FrameworkServlet中的onRefresh(wac)为空方法,交由子类DispatcherServlet实现,逻辑是调用了initStrategies(context)方法,初始化策略,即初始化DispatcherServlet的九大组件,每个初始化逻辑大致是:先去容器中找有没有这个组件(使用类型或者id找),如果没有找到就用默认配置(写在源码的配置文件中)。
1
2
3
4
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
//文件上传解析器
initMultipartResolver(context);
//区域信息解析器和国际化有关
initLocaleResolver(context);
//主题解析器:强大的主题效果更换
initThemeResolver(context);
//存放url和处理器的映射信息
initHandlerMappings(context);
//处理器的适配器
initHandlerAdapters(context);
//SpringMVC强大的异常解析功能:异常解析器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
//将请求地址转换成视图名
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
//视图解析器
initViewResolvers(context);
//SpringMVC中允许重定向携带数据的功能
initFlashMapManager(context);
}②九大组件初始化完成后,当用户发起请求来到前端控制器(DispatcherServlet)。FrameworkServlet重写了HttpServlet中的service()和doXxx(),这些方法中调用了processRequest(request, response)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14//FrameworkServlet重写HttpServlet中的service()方法
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
//调用父类HttpServlet重载的service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)方法。
super.service(request, response);
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59//HttpServlet重载的service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)方法
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}FrameworkServlet中重写HttpServlet的service方法是怎么被调用的呢?答案是HttpServlet实现了父类GenericServlet的service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)方法,其将ServletRequest与ServletResponse分别向下转型为HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse后再调用FrameworkServlet重写HttpServlet中的service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)方法。上面也已经说明了FrameworkServlet即使重写了service(request, response)方法,也会通过调用super.service(request, response)间接调用HttpServlet的service(request, response)方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18//HttpServlet实现了父类GenericServlet的service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)方法
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
HttpServletRequest request;
HttpServletResponse response;
if (!(req instanceof HttpServletRequest &&
res instanceof HttpServletResponse)) {
throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response");
}
request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
//实际上调用FrameworkServlet的service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)方法,里面间接调用HttpServlet的service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)方法
service(request, response);
}FrameworkServlet.processRequest方法(FrameworkServlet.doXxx()方法也还是会调用processRequest方法)如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
// 执行服务,doService()是一个抽象方法,在DispatcherServlet中进行了重写
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}通过查看源码,发现processRequest方法又调用了FrameworkServlet.doService(request, response)方法,此方法是FrameworkServlet类中定义的一个抽象方法,交由子类DispatcherServlet实现。
1
2
3//FrameworkServlet类
protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception;子类DispatcherServlet对其进行了实现,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
RequestPath requestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath && !ServletRequestPathUtils.hasParsedRequestPath(request)) {
requestPath = ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
// 处理请求和响应
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
if (requestPath != null) {
ServletRequestPathUtils.clearParsedRequestPath(request);
}
}
}从源码可知doService方法又调用了一个重要的方法doDispatch(request, response),此方法还是在DispatcherServlet类中,其中的代码和相关注释如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//检查是否文件上传
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
//根据当前的请求地址找到对应的类(控制器)来处理,这里/hello请求匹配到HelloController。
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
//如果没有找到对应的控制器能处理这个请求则抛错误
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
//拿到能执行这个类的所有方法的适配器(反射工具:AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter)
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
//控制器的方法被执行(通过适配器执行目标方法,将目标方法执行后的返回值作为视图名,设置保存到ModelAndView中)
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
//如果目标方法执行后没有返回值则设置一个默认的视图名(请求路径)
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//转发到目标页面
//根据方法最终执行完后封装的ModelAndView转发到对应页面,并且ModelAndView的数据可从请求域中获取。
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}大致总结此方法的运行流程:
- ①调用getHandler()方法:根据当前请求地址找到能处理这个请求的目标处理器类(处理器)。
- 根据当前请求在HandlerMapping中找到这个请求的映射信息,获取到目标处理类。
- ②调用getHandlerAdapter()方法:根据当前处理器类获取到能执行这个处理器方法的适配器。
- 根据当前处理器类,找到当前类的HandlerAdapter(适配器)。
- ③使用上面获取到的适配器执行目标方法,并且会返回一个ModelAndview对象。
- ④根据ModelAndView的信息转发到具体的页面,并可以在请求域中取出ModelAndView中的模型数据。
- ①调用getHandler()方法:根据当前请求地址找到能处理这个请求的目标处理器类(处理器)。
③给DispatcherServlet类的doDispatch方法打上断点,开启debug模式测试运行上面的用例,发送/hello请求后来到了doDispatch方法。
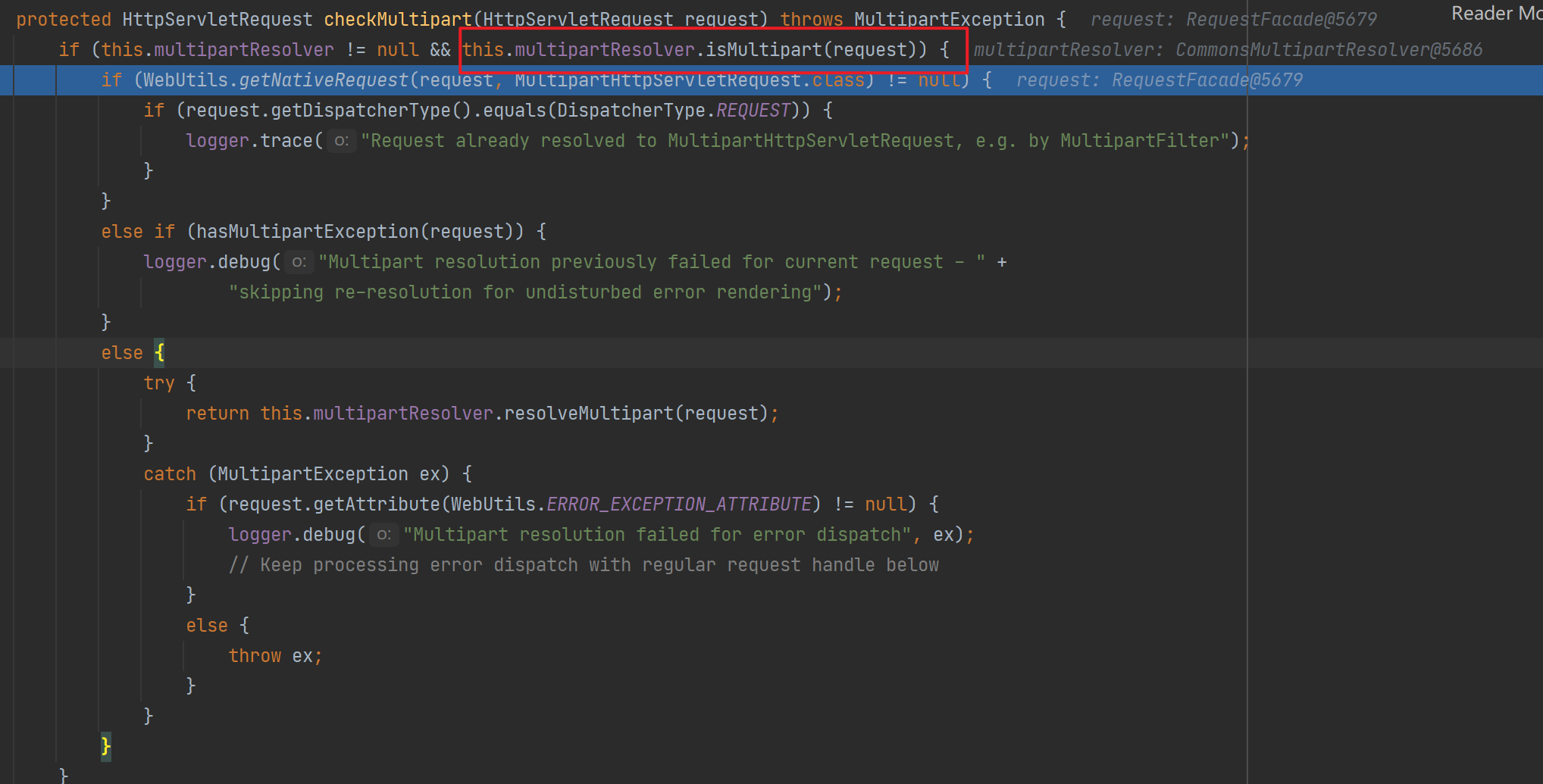
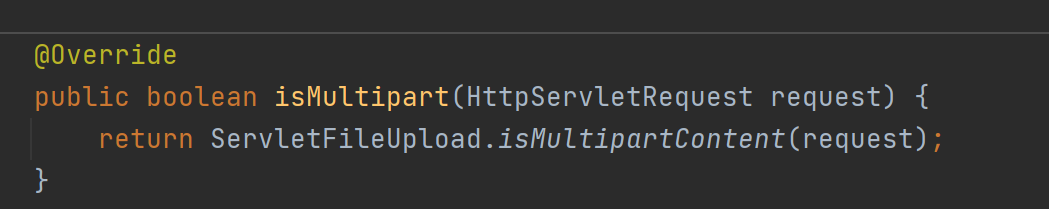
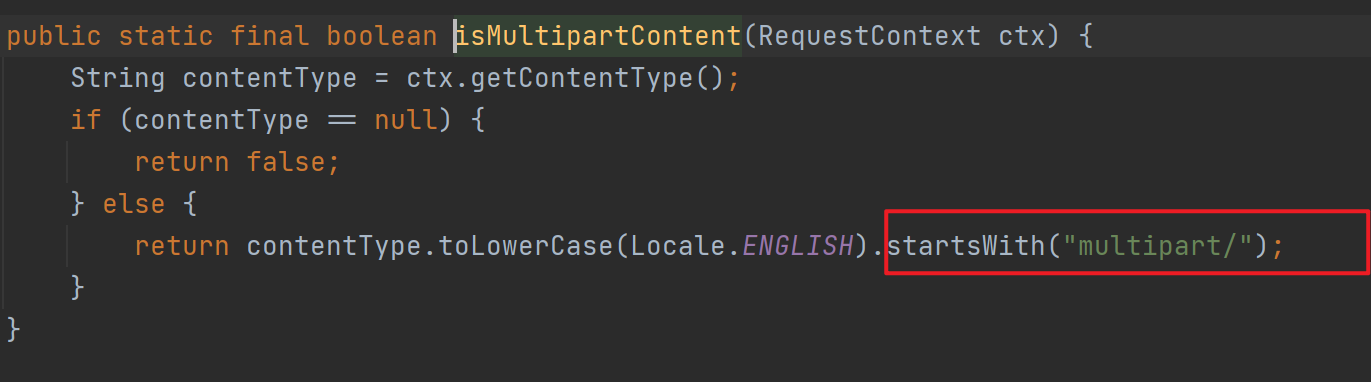
①继续执行来到checkMultipart(request)方法判断是否是文件上传请求,如果是则把request包装成processedRequest。判断的方法是请求方式为post并且请求的内容类型是multipart。
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
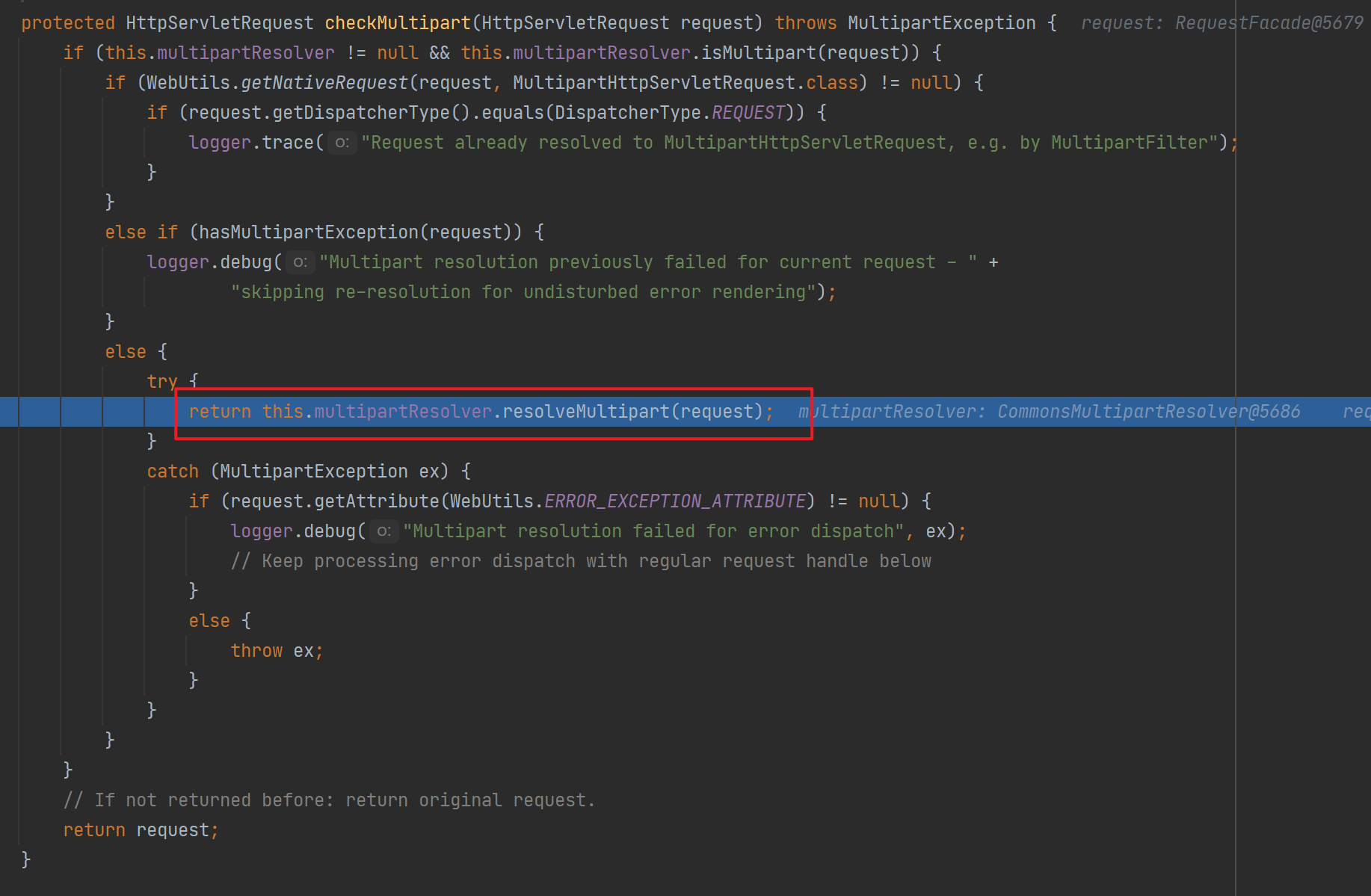
如果是文件上传请求则会调用文件处理器的resolveMultipart()方法返回一个MultipartHttpServletRequest对象。
![]()
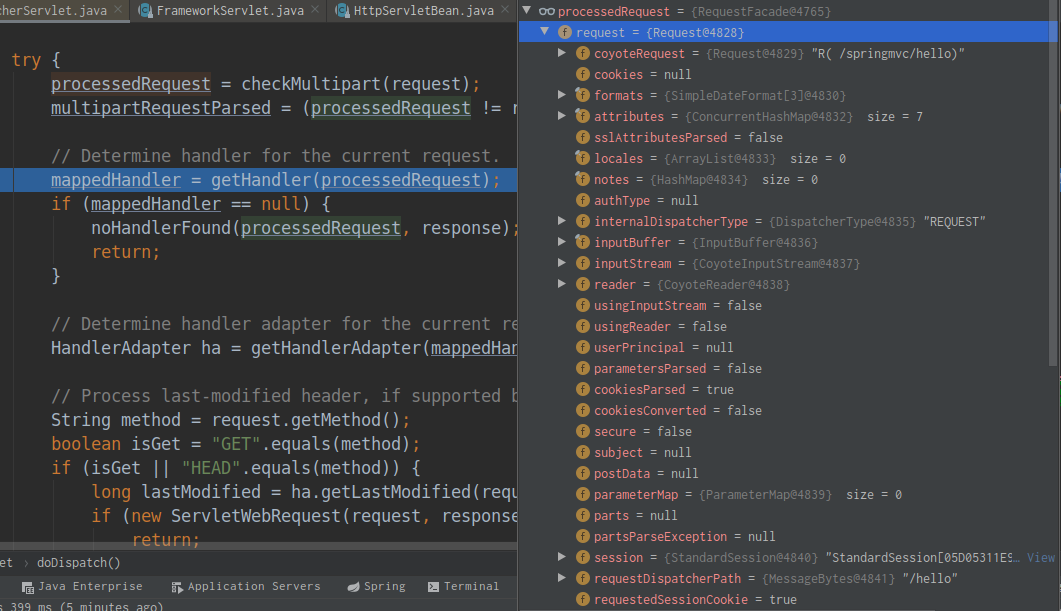
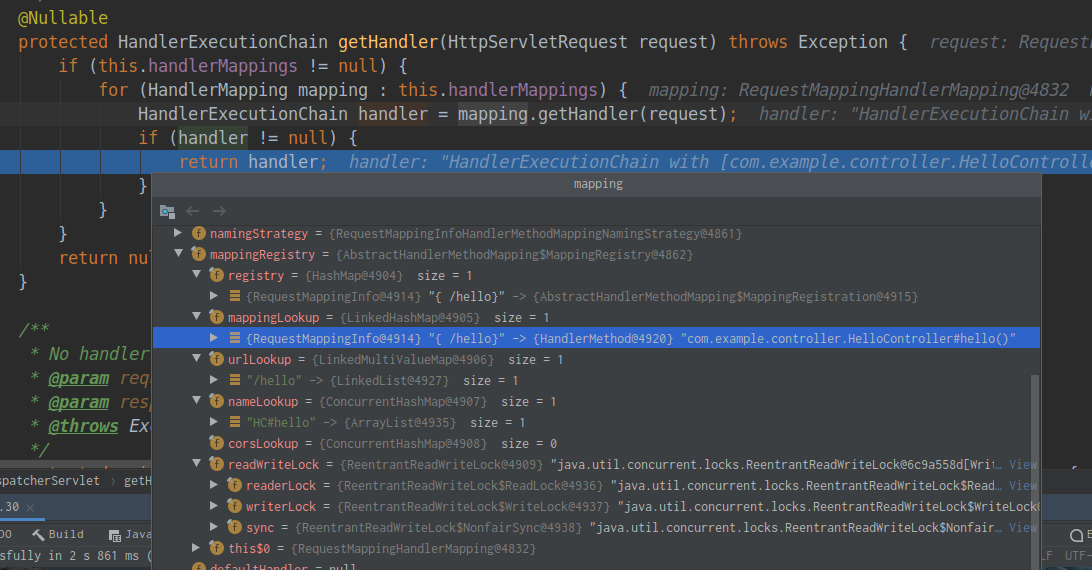
②继续执行来到getHandler(processedRequest)方法获取此请求对应的类(控制器)。此时的processedRequest包装了此请求的全部信息:
![]()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
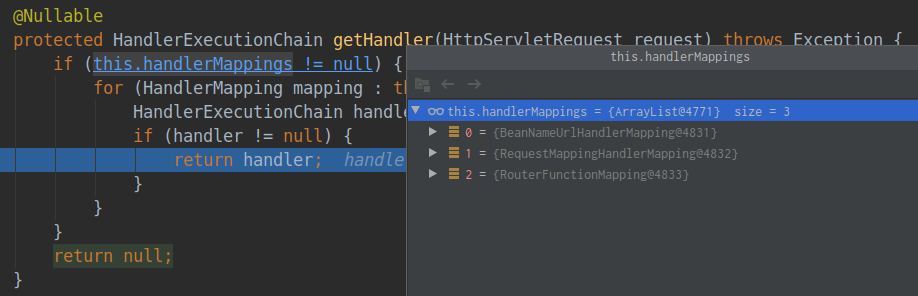
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
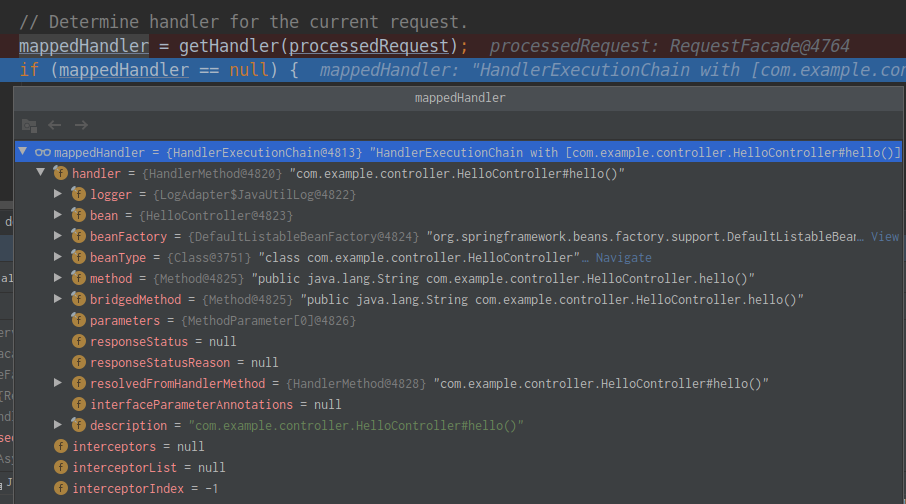
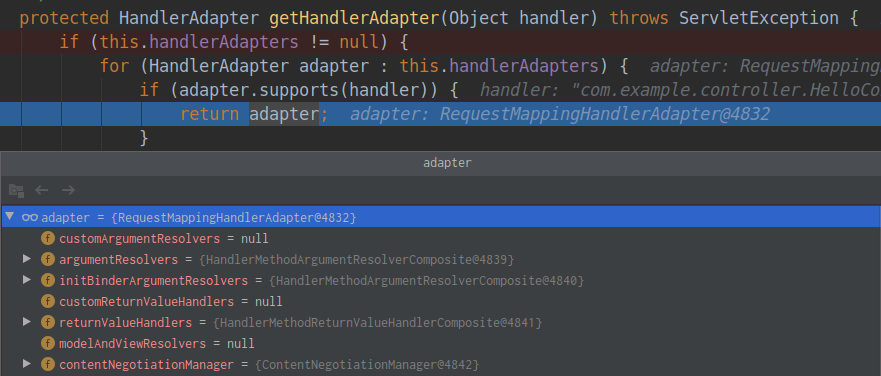
}其中的handlerMappings包含了映射信息,这些映射信息是在ioc容器启动创建controller对象时扫描每个处理器都能处理什么请求并保存在handlerMappings中的,下一次请求时就看哪个handlerMappings中有这个请求映射信息。这里一共有三个handlerMappings,并通过RequestMappingHandlerMapping找到了对应的处理器类HelloController。
![]()
![]()
![]()
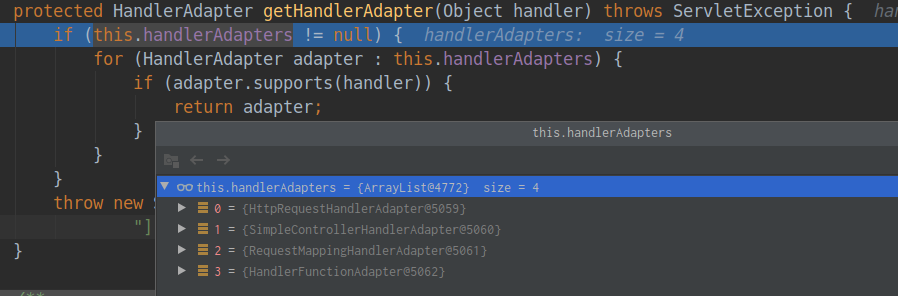
③继续执行来到了getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler())方法来获取能执行这个类的所有方法的适配器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}其中一共有四个适配器,handlerAdapters的信息如图:
![]()
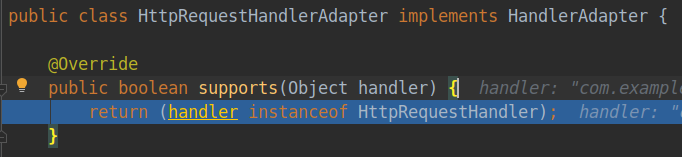
而具体如何找到对应匹配的哪个适配器,在supports方法中,不同的适配器对处理器类有不同的要求。
第一个适配器类HttpRequestHandlerAdapter要求处理器类要实现HttpRequestHandler接口。
![]()
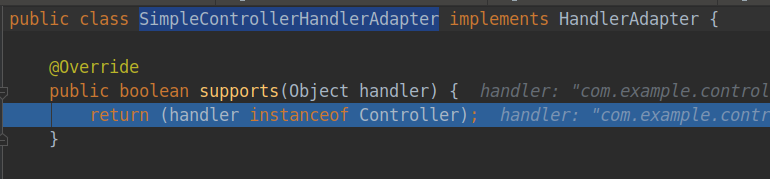
第二个适配器类SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter要求处理器要实现Controller接口。
![]()
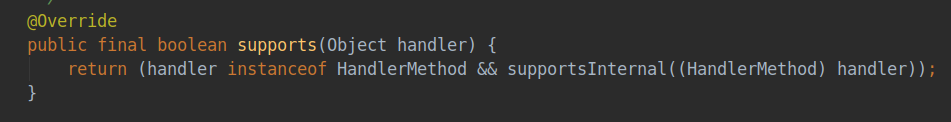
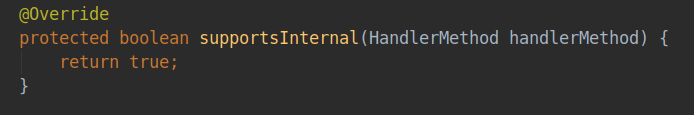
第三个适配器类RequestMappingHandlerAdapter要求处理器类是HandlerMethod类型,并且判断supportsInternal()方法返回值为true,这里supportsInternal()方法是提供给子类实现的一个方法,对于RequestMappingHandlerAdapter而言,其返回值始终是true,因为其只需要处理的handler是HandlerMethod类型的即可。其supports方法在父类AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter中定义。
![]()
![]()
可见这里是匹配到了第三个适配器RequestMappingHandlerAdapter并返回该适配器。
![]()
④继续执行来到了mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler())执行目标方法,handle方法在父类AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter类中实现,其完成的步骤如下:
- ①获取当前Spring容器中在方法上配置的标注了@ModelAttribute但是没标注@RequestMapping注解的方法,在真正调用具体的handler之前会将这些方法依次进行调用。
- ②获取当前Spring容器中标注了@InitBinder注解的方法,调用这些方法以对一些用户自定义的参数进行转换并且绑定。
- ③根据当前handler的方法参数标注的注解类型,如@RequestParam,@ModelAttribute等,获取其对应的ArgumentResolver,以将request中的参数转换为当前方法中对应注解的类型。
- ④配合转换而来的参数,通过反射调用具体的handler方法。
- ⑤通过ReturnValueHandler对返回值进行适配,比如ModelAndView类型的返回值就由ModelAndViewMethodReturnValueHandler处理,最终将所有的处理结果都统一封装为一个ModelAndView类型的返回值,这也是RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.handle()方法的返回值类型。
此方法调用了子类RequestMappingHandlerAdapter实现的handleInternal方法:
- ①判断当前是否对session进行同步处理,如果需要,则对其调用进行加锁,不需要则直接调用。
- ②判断请求头中是否包含Cache-Control请求头,如果不包含,则设置其Cache立即失效。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
checkRequest(request);
// 判断当前是否需要支持在同一个session中只能线性地处理请求
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
// 获取当前请求的session对象
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
// 为当前session生成一个唯一的可以用于锁定的key
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
// 对HandlerMethod进行参数等的适配处理,并调用目标handler
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// 如果当前不存在session,则直接对HandlerMethod进行适配
// No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// 如果当前不需要对session进行同步处理,则直接对HandlerMethod进行适配
// No synchronization on session demanded at all...
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
// 判断当前请求头中是否包含Cache-Control请求头,如果不包含,则对当前response进行处理
// 为其设置过期时间
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
// 如果当前SessionAttribute中存在配置的attributes,则为其设置过期时间。
// 这里SessionAttribute主要是通过@SessionAttribute注解生成的
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
// 如果当前不存在SessionAttributes,则判断当前是否存在Cache-Control设置
//如果存在,则按照该设置进行response处理,如果不存在,则设置response中的
// Cache的过期时间为-1,即立即失效
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}handleInternal方法又调用了invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod)完成了目标方法的执行:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
// 获取容器中全局配置的InitBinder和当前HandlerMethod所对应的Controller中配置的InitBinder,用于进行参数的绑定
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
// 获取容器中全局配置的ModelAttribute和当前当前HandlerMethod所对应的Controller中配置的ModelAttribute,这些配置的方法将会在目标方法调用之前进行调用
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
// 将handlerMethod封装为一个ServletInvocableHandlerMethod对象,该对象用于对当前request的整体调用流程进行了封装
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod =
createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
// 设置当前容器中配置的所有ArgumentResolver
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
// 设置当前容器中配置的所有ReturnValueHandler
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
// 将前面创建的WebDataBinderFactory设置到ServletInvocableHandlerMethod中
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
// 设置ParameterNameDiscoverer,该对象将按照一定的规则获取当前参数的名称
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
// 这里initModel()方法主要作用是调用前面获取到的@ModelAttribute标注的方法,从而达到@ModelAttribute标注的方法能够在目标Handler调用之前调用的目的
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
// 获取当前的AsyncWebRequest,这里AsyncWebRequest的主要作用是用于判断目标handler的返回值是否为WebAsyncTask或DefferredResult,如果是这两种中的一种,则说明当前请求的处理应该是异步的。所谓的异步,指的是当前请求会将Controller中封装的业务逻辑放到一个线程池中进行调用,待该调用有返回结果之后再返回到response中。这种处理的优点在于用于请求分发的线程能够解放出来,从而处理更多的请求,只有待目标任务完成之后才会回来将该异步任务的结果返回。
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils
.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
// 封装异步任务的线程池,request和interceptors到WebAsyncManager中
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
// 这里就是用于判断当前请求是否有异步任务结果的,如果存在,则对异步任务结果进行封装
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer)
asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found concurrent result value [" + result + "]");
}
// 封装异步任务的处理结果,虽然封装的是一个HandlerMethod,但只是Spring简单的封装的一个Callable对象,该对象中直接将调用结果返回了。这样封装的目的在于能够统一的进行右面的ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle()方法的调用
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
// 对请求参数进行处理,调用目标HandlerMethod,并且将返回值封装为一个ModelAndView对象
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
// 对封装的ModelAndView进行处理,主要是判断当前请求是否进行了重定向,如果进行了重定向,还会判断是否需要将FlashAttributes封装到新的请求中
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
} finally {
// 调用request destruction callbacks和对SessionAttributes进行处理
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}①获取当前容器中使用@InitBinder注解注册的属性转换器。这里获取InitBinder的方式主要有两种,一种是获取全局配置的InitBinder,全局类型的InitBinder需要声明的类上使用@ControllerAdvice进行标注,并且声明方法上使用@InitBinder进行标注;另一种则是获取当前handler所在类中的使用@InitBinder注解标注的方法。这两种InitBinder都会执行,只不过全局类型的InitBinder会先于局部类型的InitBinder执行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33private WebDataBinderFactory getDataBinderFactory(HandlerMethod handlerMethod)
throws Exception {
// 判断当前缓存中是否缓存了当前bean所需要装配的InitBinder方法,如果存在,则直接从缓存中取,如果不存在,则在当前bean中进行扫描获取
Class<?> handlerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
Set<Method> methods = this.initBinderCache.get(handlerType);
if (methods == null) {
// 在当前bean中查找所有标注了@InitBinder注解的方法,这里INIT_BINDER_METHODS就是一个选择器,表示只获取使用@InitBinder标注的方法
methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(handlerType, INIT_BINDER_METHODS);
this.initBinderCache.put(handlerType, methods);
}
// 这里initBinderAdviceCache是在RequestMappingHandlerAdapter初始化时同步初始化的,其内包含的方法有如下两个特点:①当前方法所在类使用@ControllerAdvice进行标注了;②当前方法使用@InitBinder进行了标注。也就是说其内保存的方法可以理解为是全局类型的参数绑定方法
List<InvocableHandlerMethod> initBinderMethods = new ArrayList<>();
this.initBinderAdviceCache.forEach((clazz, methodSet) -> {
// 这里判断的是当前配置的全局类型的InitBinder是否能够应用于当前bean,
// 判断的方式主要在@ControllerAdvice注解中进行了声明,包括通过包名,类所在的包,接口或者注解的形式限定的范围
if (clazz.isApplicableToBeanType(handlerType)) {
Object bean = clazz.resolveBean();
for (Method method : methodSet) {
initBinderMethods.add(createInitBinderMethod(bean, method));
}
}
});
// 这里是将当前HandlerMethod所在bean中的InitBinder添加到需要执行的initBinderMethods中。这里从添加的顺序可以看出,全局类型的InitBinder会在当前bean中的InitBinder之前执行
for (Method method : methods) {
Object bean = handlerMethod.getBean();
initBinderMethods.add(createInitBinderMethod(bean, method));
}
// 将需要执行的InitBinder封装到InitBinderDataBinderFactory中
return createDataBinderFactory(initBinderMethods);
}②获取当前容器中使用@ModelAttribute标注但没有使用@RequestMapping标注的方法(获取的方式与前面的InitBinder相似)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36private ModelFactory getModelFactory(HandlerMethod handlerMethod,
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) {
// 这里SessionAttributeHandler的作用是声明几个属性,使其能够在多个请求之间共享,并且其能够保证当前request返回的model中始终保有这些属性
SessionAttributesHandler sessionAttrHandler =
getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod);
// 判断缓存中是否保存有当前handler执行之前所需要执行的标注了@ModelAttribute的方法
Class<?> handlerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
Set<Method> methods = this.modelAttributeCache.get(handlerType);
if (methods == null) {
// 如果缓存中没有相关属性,那么就在当前bean中查找所有使用@ModelAttribute标注,但是没有使用@RequestMapping标注的方法,并将这些方法缓存起来
methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(handlerType, MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS);
this.modelAttributeCache.put(handlerType, methods);
}
// 获取全局的使用@ModelAttribute标注,但是没有使用@RequestMapping标注的方法,这里全局类型的方法的声明方式需要注意的是,其所在的bean必须使用@ControllerAdvice进行标注
List<InvocableHandlerMethod> attrMethods = new ArrayList<>();
this.modelAttributeAdviceCache.forEach((clazz, methodSet) -> {
// 判断@ControllerAdvice中指定的作用的bean范围与当前bean是否匹配,匹配了才会对其应用
if (clazz.isApplicableToBeanType(handlerType)) {
Object bean = clazz.resolveBean();
for (Method method : methodSet) {
attrMethods.add(createModelAttributeMethod(binderFactory, bean, method));
}
}
});
// 将当前方法中使用@ModelAttribute标注的方法添加到需要执行的attrMethods中。从这里的添加顺序可以看出,全局类型的方法将会先于局部类型的方法执行
for (Method method : methods) {
Object bean = handlerMethod.getBean();
attrMethods.add(createModelAttributeMethod(binderFactory, bean, method));
}
// 将需要执行的方法等数据封装为ModelFactory对象
return new ModelFactory(attrMethods, binderFactory, sessionAttrHandler);
}③给目标方法invocableMethod设置参数解析器,默认有26个解析器,其作用是确定将要执行的目标方法的每一个参数的值是什么,也就是说SpringMVC目标方法能写多少种参数类型取决于参数解析器。
![]()
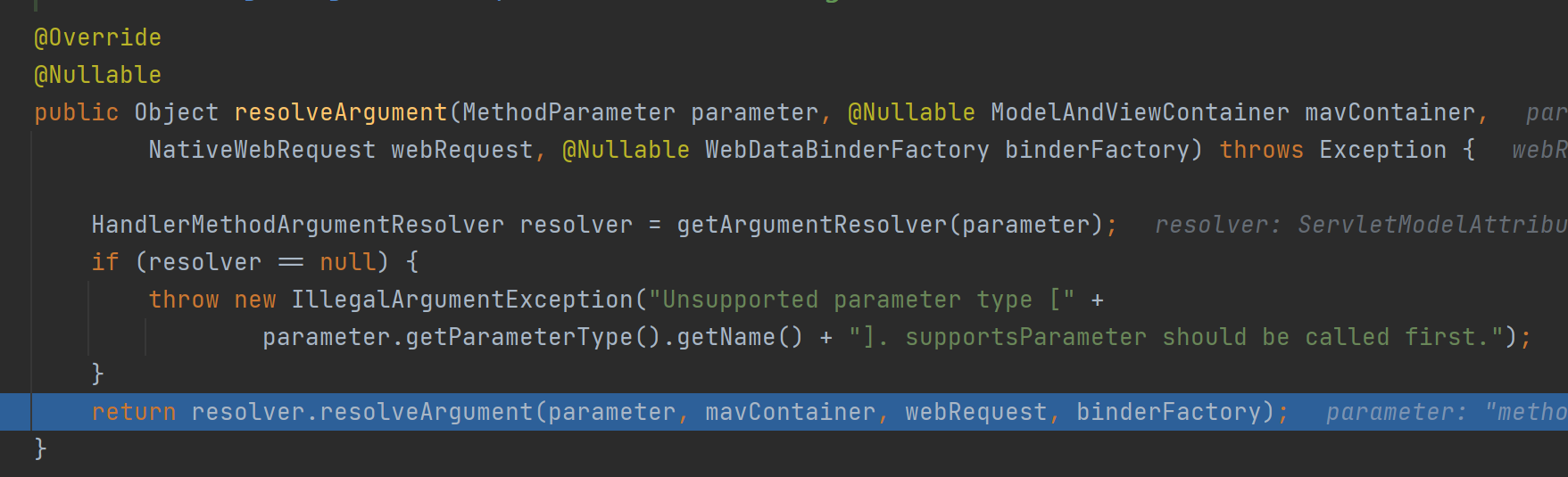
通过源码可知参数解析器实现了HandlerMethodArgumentResolver接口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public interface HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
//判断当前解析器是否支持解析此方法的参数
boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter);
//如果支持就调用解析方法
Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception;
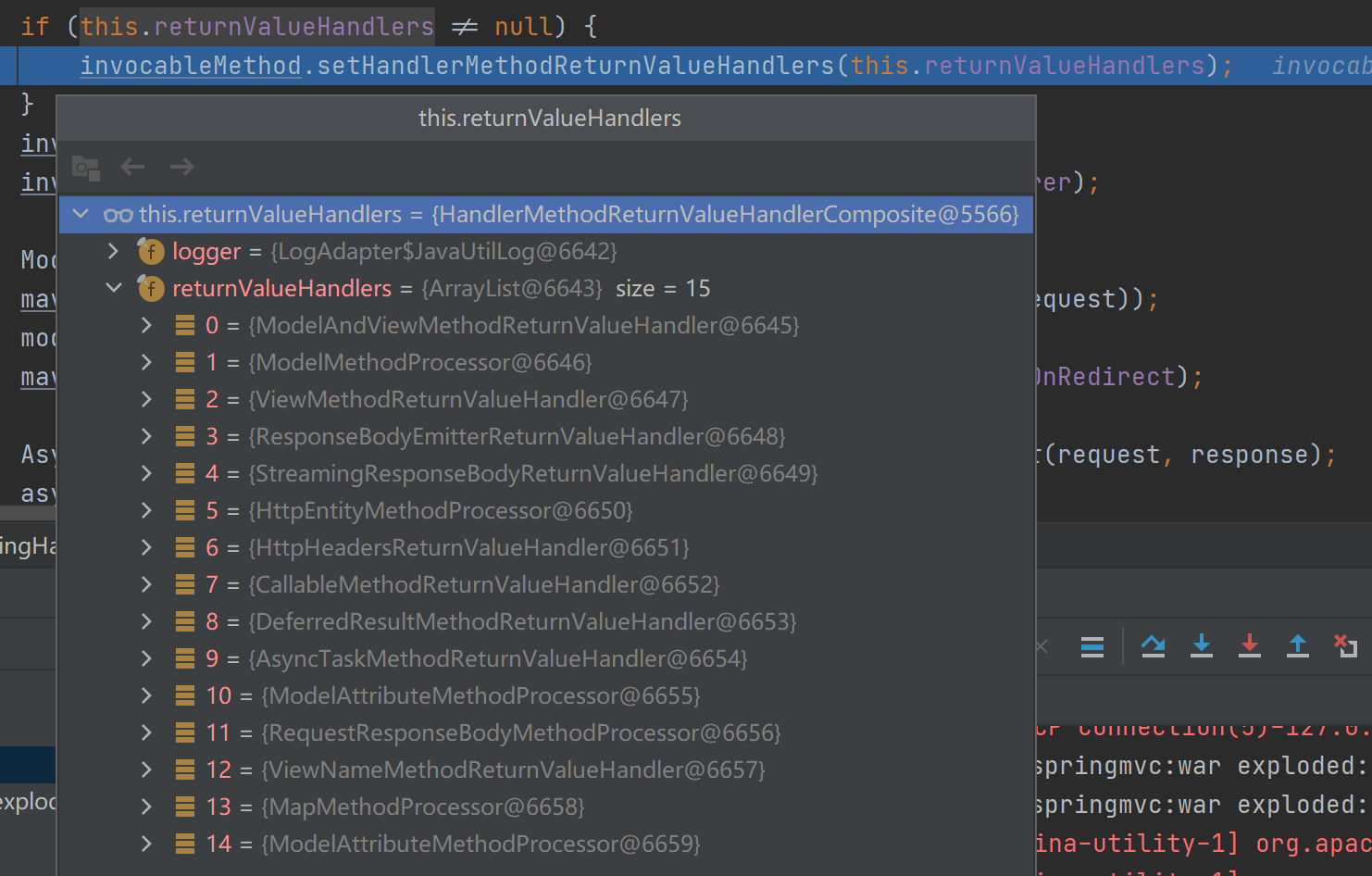
}④给目标方法invocableMethod设置返回值处理器,默认有15个。
![]()
⑤在调用目标方法之前调用@ModelAttribute标注但没有使用@RequestMapping标注的方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23public void initModel(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer container,
HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
// 在当前request中获取使用@SessionAttribute注解声明的参数
Map<String, ?> sessionAttributes =
this.sessionAttributesHandler.retrieveAttributes(request);
// 将@SessionAttribute声明的参数封装到ModelAndViewContainer中
container.mergeAttributes(sessionAttributes);
// 调用前面获取的使用@ModelAttribute标注的方法
invokeModelAttributeMethods(request, container);
// 这里首先获取目标handler执行所需的参数中与@SessionAttribute同名或同类型的参数,也就是handler想要直接从@SessionAttribute中声明的参数中获取的参数。然后对这些参数进行遍历,首先判断request中是否包含该属性,如果不包含,则从之前的SessionAttribute缓存中获取,如果两个都没有,则直接抛出异常
for (String name : findSessionAttributeArguments(handlerMethod)) {
if (!container.containsAttribute(name)) {
Object value = this.sessionAttributesHandler.retrieveAttribute(request, name);
if (value == null) {
throw new HttpSessionRequiredException("Expected session attribute '"
+ name + "'", name);
}
container.addAttribute(name, value);
}
}
}①保证@SessionAttribute声明的参数的存在。
②调用使用@ModelAttribute标注的方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35private void invokeModelAttributeMethods(NativeWebRequest request,
ModelAndViewContainer container) throws Exception {
while (!this.modelMethods.isEmpty()) {
// 这里getNextModelMethod()方法始终会获取modelMethods中的第0号为的方法,后续该方法执行完了之后则会将该方法从modelMethods移除掉,因而这里while循环只需要判断modelMethods是否为空即可
InvocableHandlerMethod modelMethod =
getNextModelMethod(container).getHandlerMethod();
// 获取当前方法中标注的ModelAttribute属性,然后判断当前request中是否有与该属性中name字段标注的值相同的属性,如果存在,并且当前ModelAttribute设置了不对该属性进行绑定,那么就直接略过当前方法的执行
ModelAttribute ann = modelMethod.getMethodAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class);
Assert.state(ann != null, "No ModelAttribute annotation");
if (container.containsAttribute(ann.name())) {
if (!ann.binding()) {
container.setBindingDisabled(ann.name());
}
continue;
}
// 通过ArgumentResolver对方法参数进行处理,并且调用目标方法
Object returnValue = modelMethod.invokeForRequest(request, container);
// 如果当前方法的返回值不为空,则判断当前@ModelAttribute是否设置了需要绑定返回值,如果设置了,则将返回值绑定到请求中,后续handler可以直接使用该参数
if (!modelMethod.isVoid()){
String returnValueName = getNameForReturnValue(returnValue,
modelMethod.getReturnType());
if (!ann.binding()) {
container.setBindingDisabled(returnValueName);
}
// 如果request中不包含该参数,则将该返回值添加到ModelAndViewContainer中,供handler使用
if (!container.containsAttribute(returnValueName)) {
container.addAttribute(returnValueName, returnValue);
}
}
}
}
⑥判断目标handler返回值是否使用了WebAsyncTask或DefferredResult封装,如果封装了,则按照异步任务的方式进行执行。
⑦处理请求参数,调用目标方法和处理返回值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 对目标handler的参数进行处理,并且调用目标handler
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
// 设置相关的返回状态
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
// 如果请求处理完成,则设置requestHandled属性
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null
|| mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
} else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
// 如果请求失败,但是有错误原因,那么也会设置requestHandled属性
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
// 遍历当前容器中所有ReturnValueHandler,判断哪种handler支持当前返回值的处理,如果支持,则使用该handler处理该返回值
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(getReturnValueHandlingErrorMessage("Error handling return value",
returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}①处理请求参数进行处理,将request中的参数封装为当前handler的参数的形式。
②通过反射调用当前handler。
先是遍历所有的参数,并且查找哪种ArgumentResolver能够处理当前参数,找到了则按照具体的Resolver定义的方式进行处理即可。在所有的参数处理完成之后,RequestMappingHandlerAdapter就会使用反射调用目标handler。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 获取目标方法的所有参数值
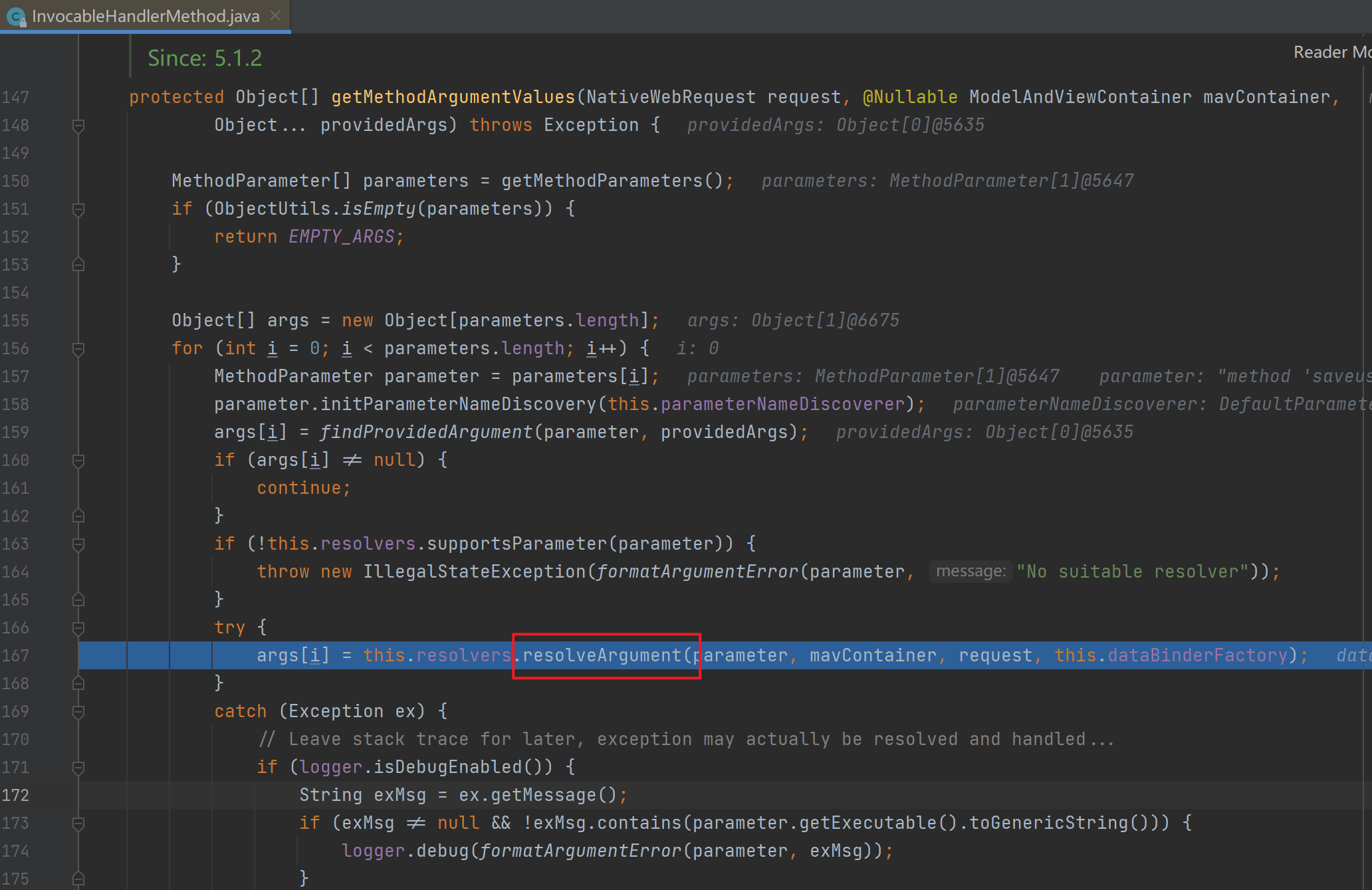
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking '" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(getMethod(),
getBeanType()) + "' with arguments " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
// 这里doInvoke()方法主要是结合处理后的参数,使用反射对目标方法进行调用
Object returnValue = doInvoke(args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method [" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(getMethod(),
getBeanType()) + "] returned [" + returnValue + "]");
}
return returnValue;
}
// 本方法主要是通过当前容器中配置的ArgumentResolver对request中的参数进行转化,将其处理为目标handler的参数的形式
private Object[] getMethodArgumentValues(NativeWebRequest request,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 获取当前handler所声明的所有参数,主要包括参数名,参数类型,参数位置,所标注的注解等等属性
MethodParameter[] parameters = getMethodParameters();
Object[] args = new Object[parameters.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
MethodParameter parameter = parameters[i];
parameter.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
// providedArgs是调用方提供的参数,这里主要是判断这些参数中是否有当前类型或其子类型的参数,如果有,则直接使用调用方提供的参数,对于请求处理而言,默认情况下,调用方提供的参数都是长度为0的数组
args[i] = resolveProvidedArgument(parameter, providedArgs);
if (args[i] != null) {
continue;
}
// 如果在调用方提供的参数中不能找到当前类型的参数值,则遍历Spring容器中所有的ArgumentResolver,判断哪种类型的Resolver支持对当前参数的解析,这里的判断方式比较简单,比如RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver就是判断当前参数是否使用@RequestParam注解进行了标注;而RequestPartMethodArgumentResolver就是用来解析文件上传请求的。
if (this.argumentResolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)) {
try {
// 如果能够找到对当前参数进行处理的ArgumentResolver,则调用其resolveArgument()方法从request中获取对应的参数值,并且进行转换
args[i] = this.argumentResolvers.resolveArgument(
parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory);
continue;
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(getArgumentResolutionErrorMessage("Failed to resolve",
i), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// 如果进行了参数处理之后当前参数还是为空,则抛出异常
if (args[i] == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not resolve method parameter at index "
+ parameter.getParameterIndex() + " in "
+ parameter.getExecutable().toGenericString()
+ ": " + getArgumentResolutionErrorMessage("No suitable resolver for",i));
}
}
return args;
}这里重点观察复杂参数Map和Model的解析流程(给这两个参数放数据实际就是往request中放数据)
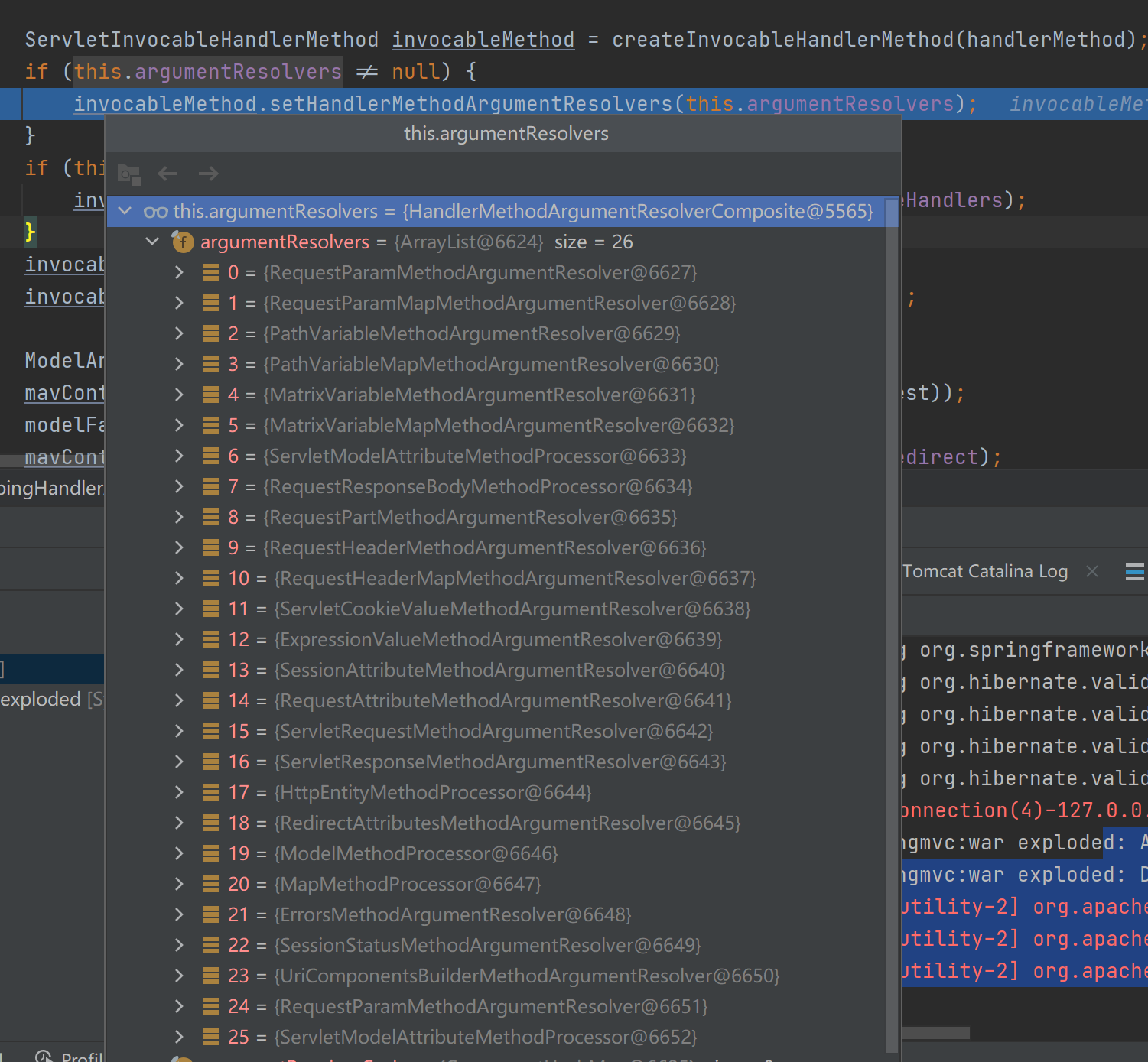
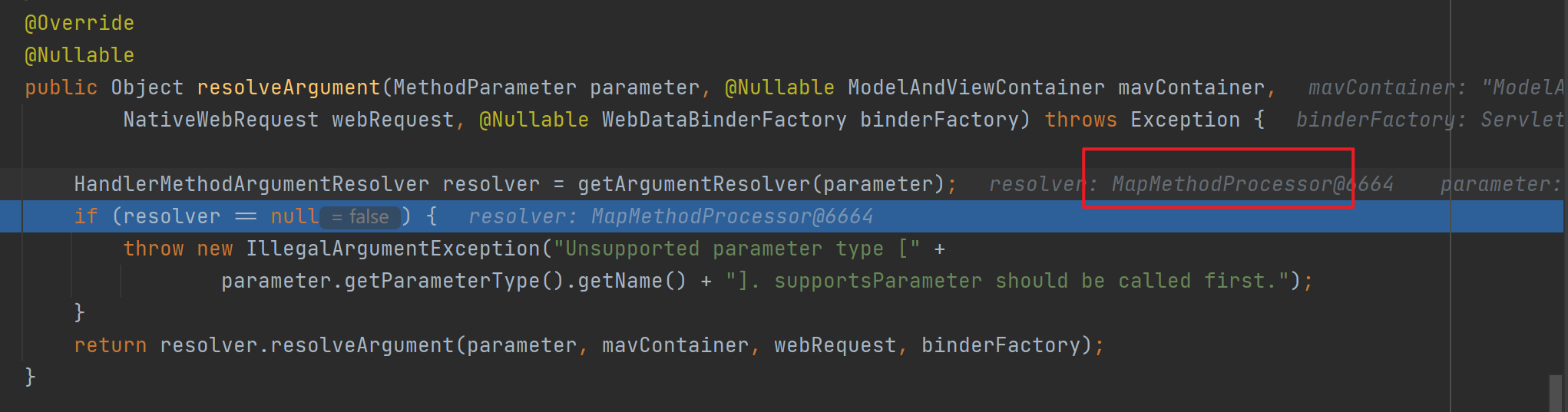
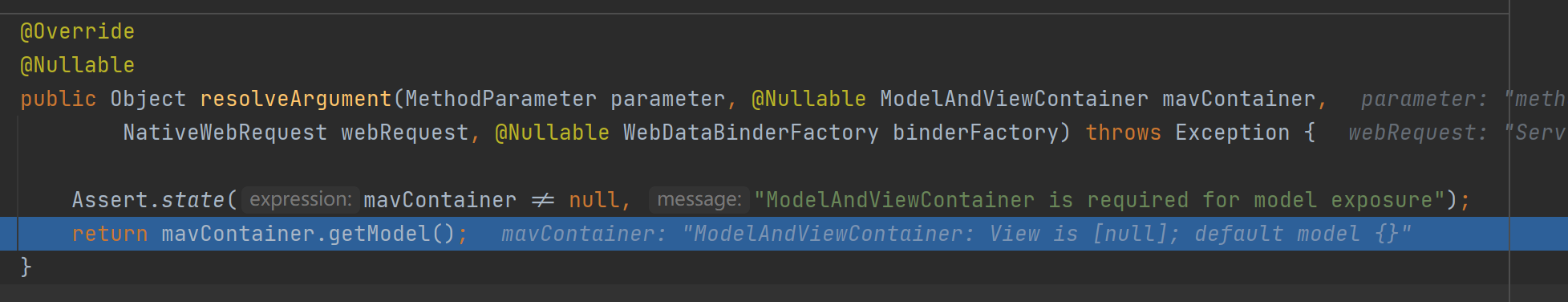
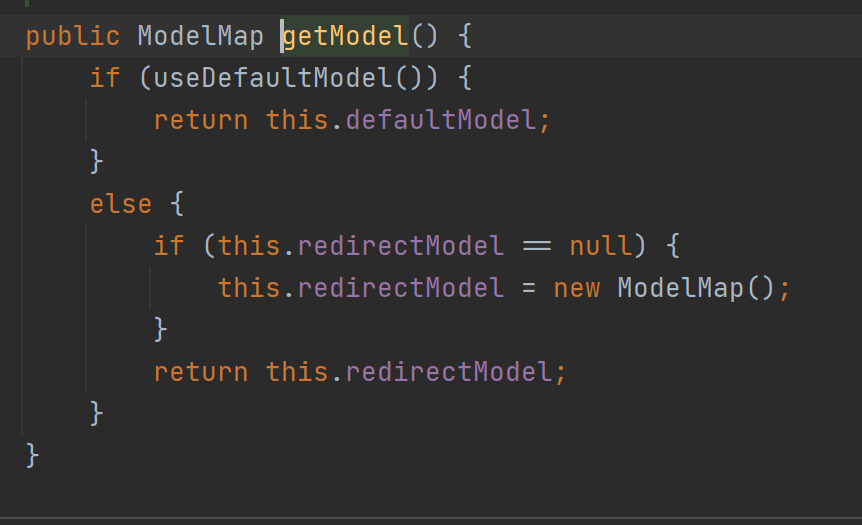
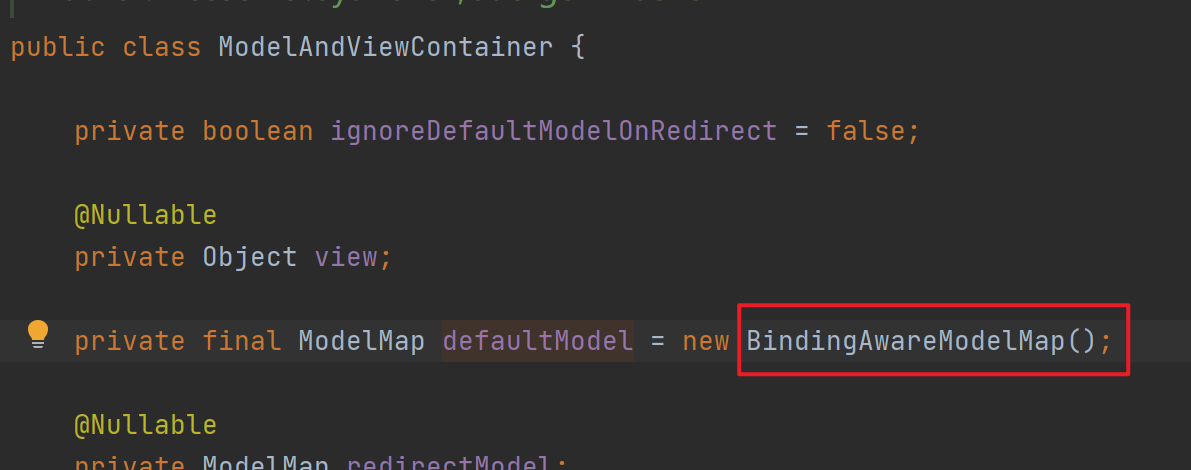
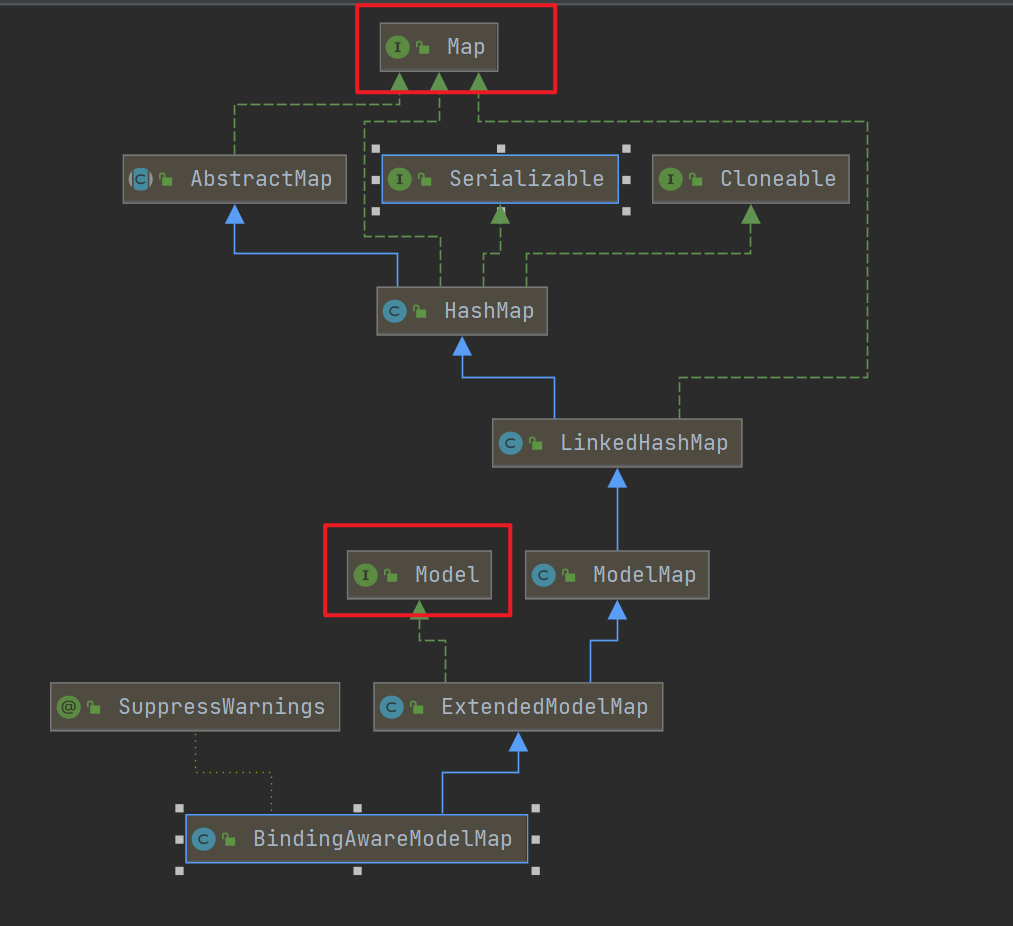
解析Map的参数解析器是MapMethodResolver,该解析器的resolveArgument方法实际上是给参数为Map通过调用mavContainer.getModel()赋值了BindingAwareModelMap(既是Model也是Map)。
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
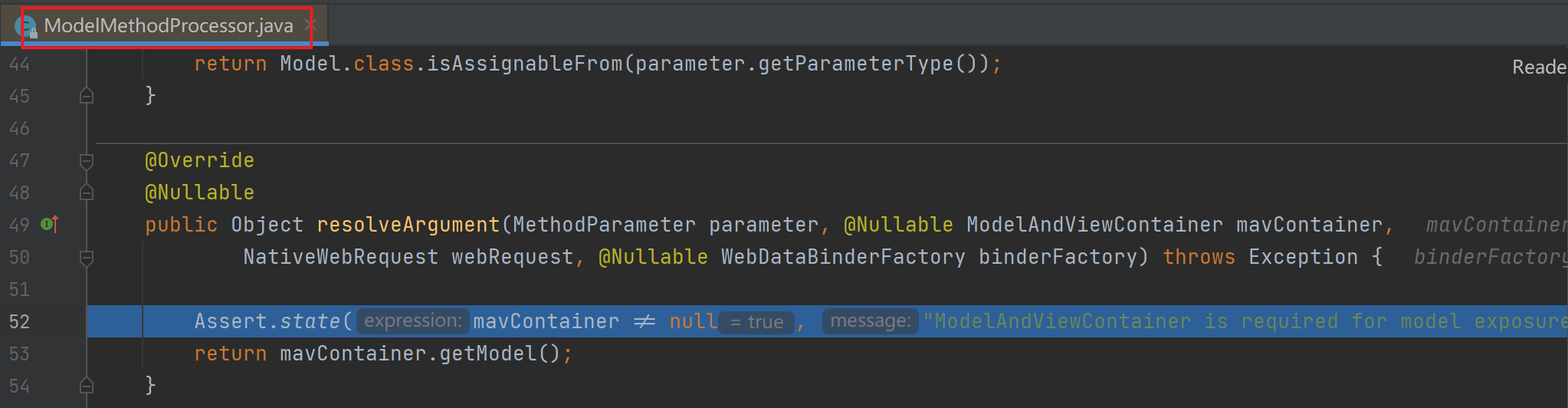
解析Model的参数解析器是ModelMethodProcessor,该解析器的resolveArgument方法实际上也是给参数为Map通过调用mavContainer.getModel()赋值了BindingAwareModelMap。从而发现无论参数是Map还是Model,最终都被赋值为相同对象的BindingAwareModelMap。
![]()
③对方法的返回值进行处理,以将其封装为一个ModelAndViewContainer对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
public void handleReturnValue( Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
// 获取能够处理当前返回值的Handler,比如如果返回值是ModelAndView类型,那么这里的handler就是ModelAndViewMethodReturnValueHandler
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler handler = selectHandler(returnValue, returnType);
if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown return value type: "
+ returnType.getParameterType().getName());
}
// 通过获取到的handler处理返回值,并将其封装到ModelAndViewContainer中
handler.handleReturnValue(returnValue, returnType, mavContainer, webRequest);
}
// 本方法的主要作用是获取能够处理当前返回值的ReturnValueHandler
private HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler selectHandler( Object value,
MethodParameter returnType) {
// 判断返回值是否为异步类型的返回值,即WebAsyncTask或DefferredResult
boolean isAsyncValue = isAsyncReturnValue(value, returnType);
// 对所有的ReturnValueHandler进行遍历,判断其是否支持当前返回值的处理。这里如果当前返回值是异步类型的返回值,还会判断当前ReturnValueHandler是否为
// AsyncHandlerMethodReturnValueHandler类型,如果不是,则会继续查找
for (HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler handler : this.returnValueHandlers) {
if (isAsyncValue && !(handler instanceof AsyncHandlerMethodReturnValueHandler)) {
continue;
}
// 判断是否支持返回值处理的主要位置,比如ModelAndViewMethodReturnValueHandler就会判断返回值是否为ModelAndView类型,如果是,则表示其是当前ReturnValuleHandler所支持的类型
if (handler.supportsReturnType(returnType)) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
public void handleReturnValue( Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
//如果返回的值是字符串类型
if (returnValue instanceof CharSequence) {
String viewName = returnValue.toString();
//给mavContainer放入返回的String值
mavContainer.setViewName(viewName);
if (isRedirectViewName(viewName)) {
mavContainer.setRedirectModelScenario(true);
}
}
else if (returnValue != null) {
// should not happen
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Unexpected return type: " +
returnType.getParameterType().getName() + " in method: " + returnType.getMethod());
}
}重点看如何处理@ResponseBody注解标注的方法的返回值。
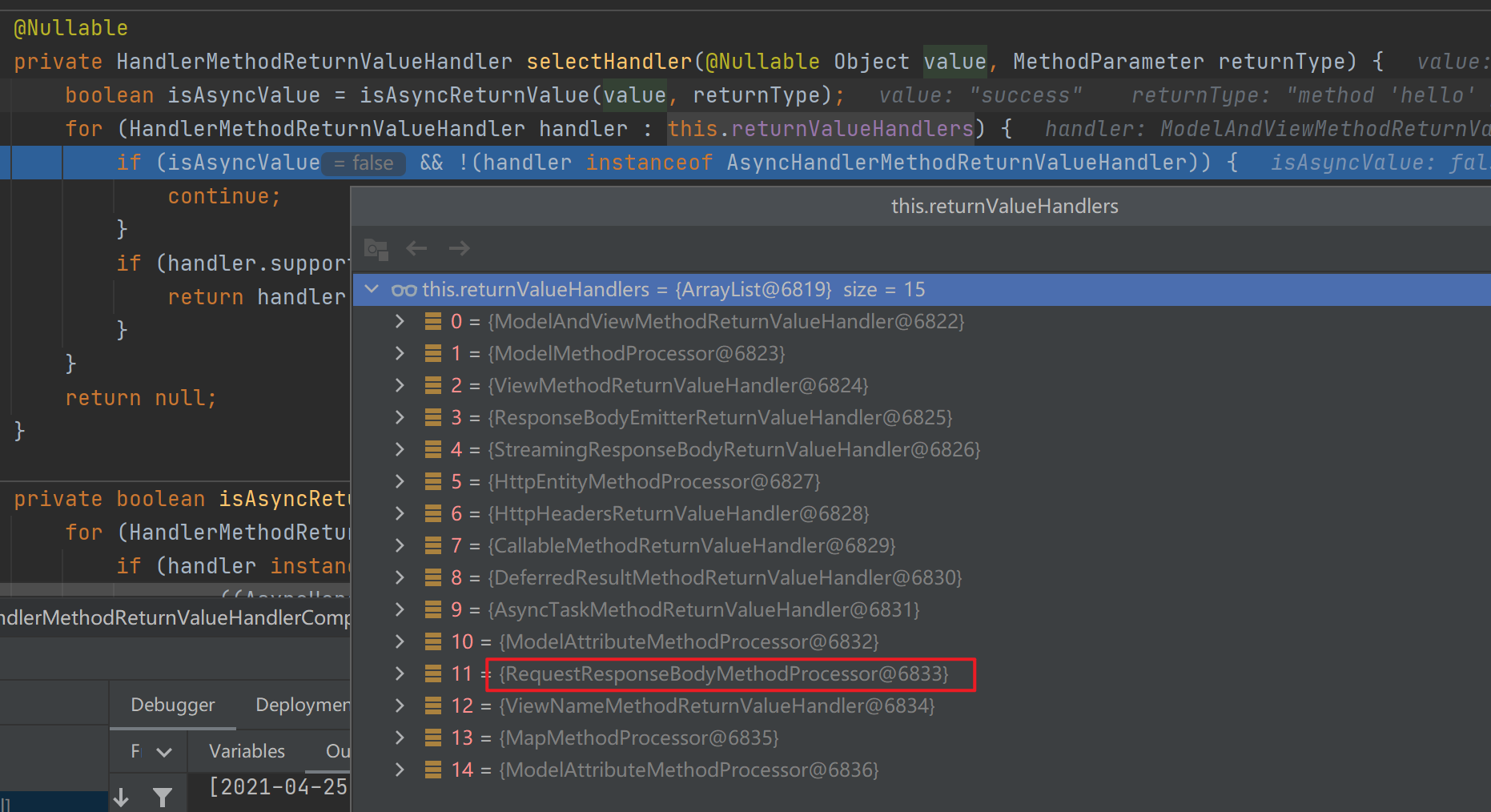
处理@ResponseBody注解标注的方法的返回值的处理器是RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor。这一步通过selectHandler()遍历所有的ReturnValueHandler并找到能处理相应的返回值类型的处理器来得到。
![]()
![]()
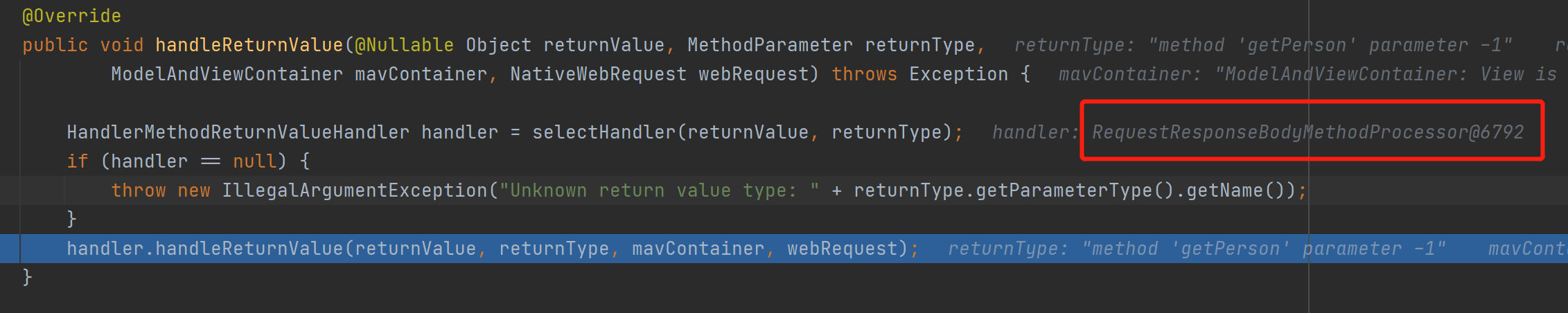
接着调用RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor.handleReturnValue()进行处理,里面调用了一个重要方法writeWithMessageConverters(),其作用是利用消息转换器进行写出操作。
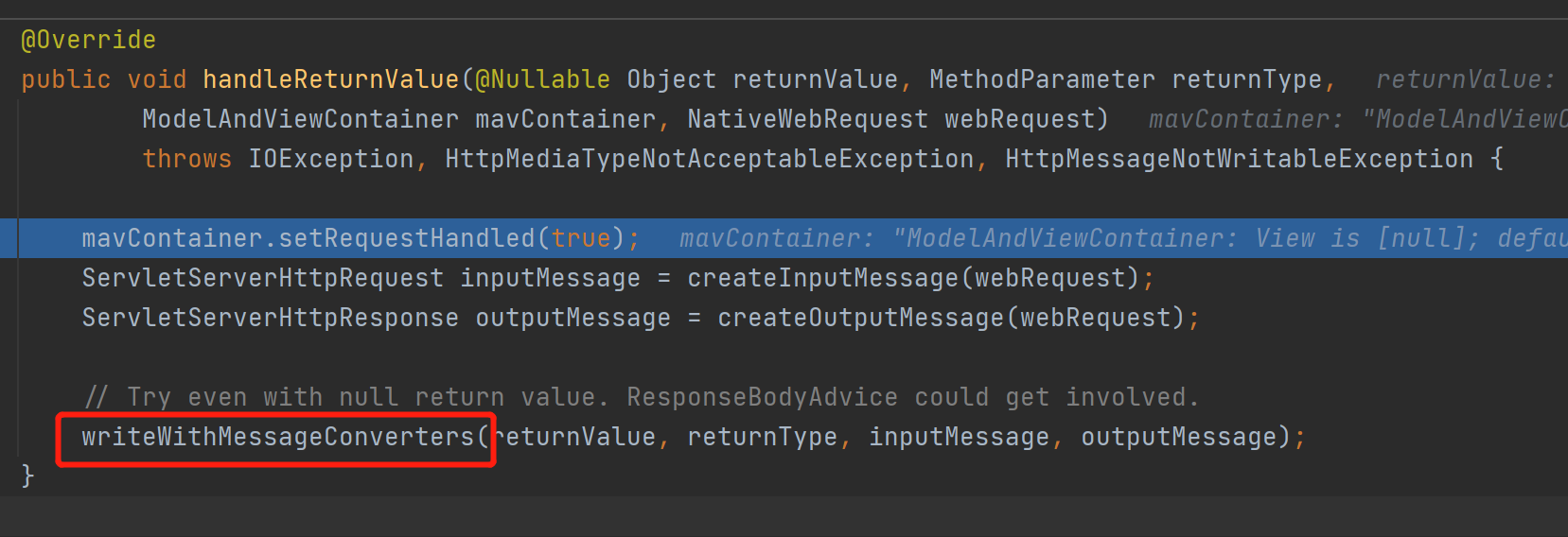
![]()
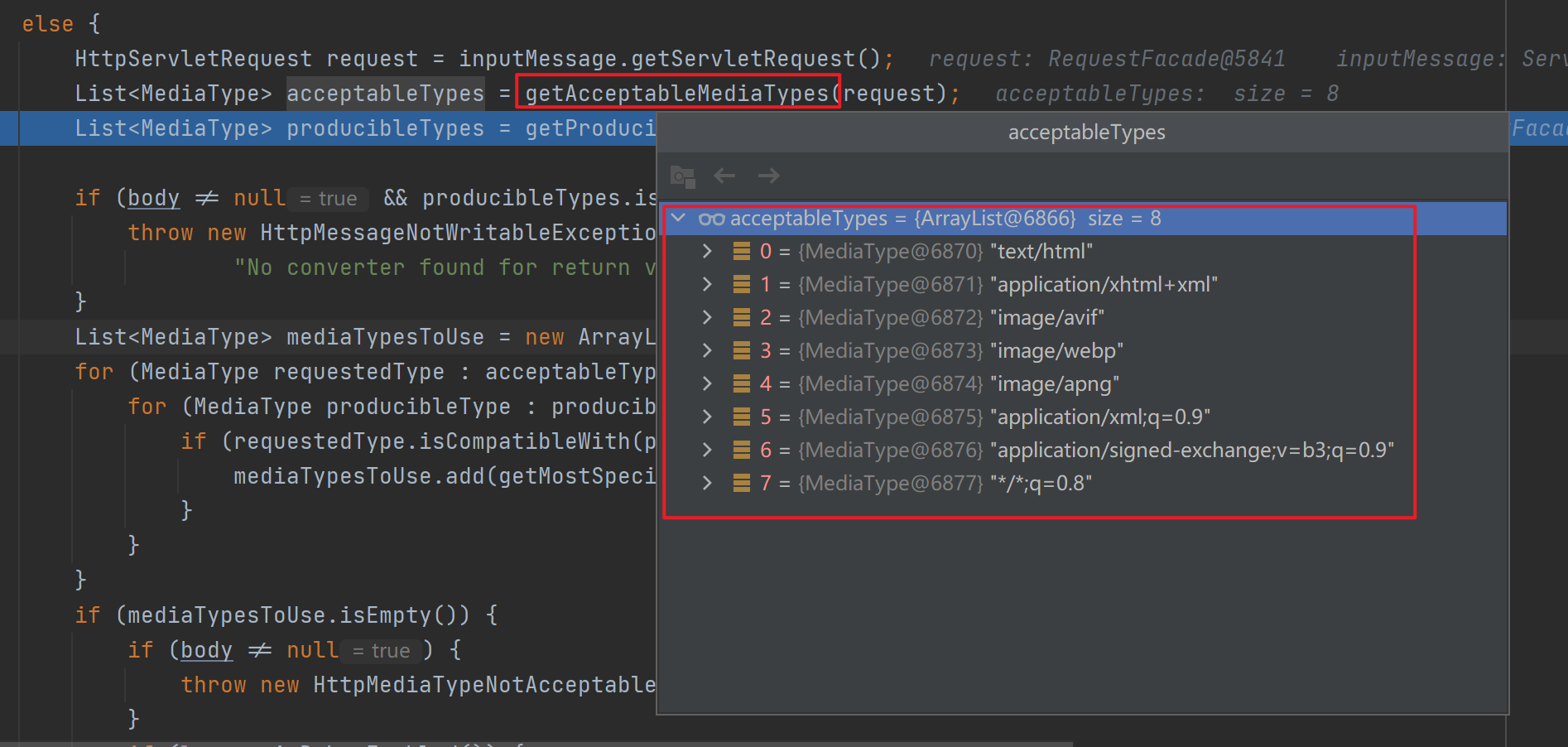
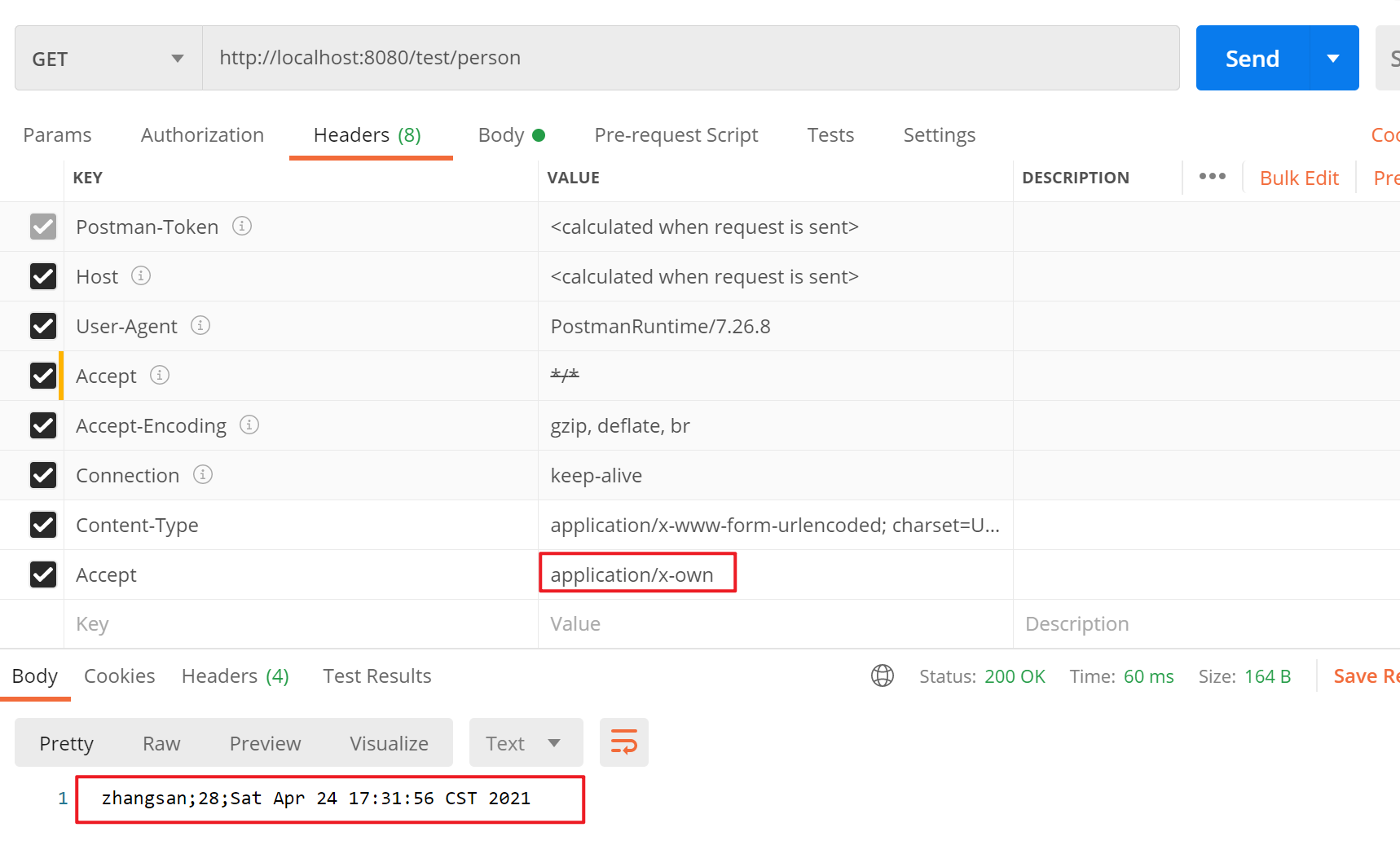
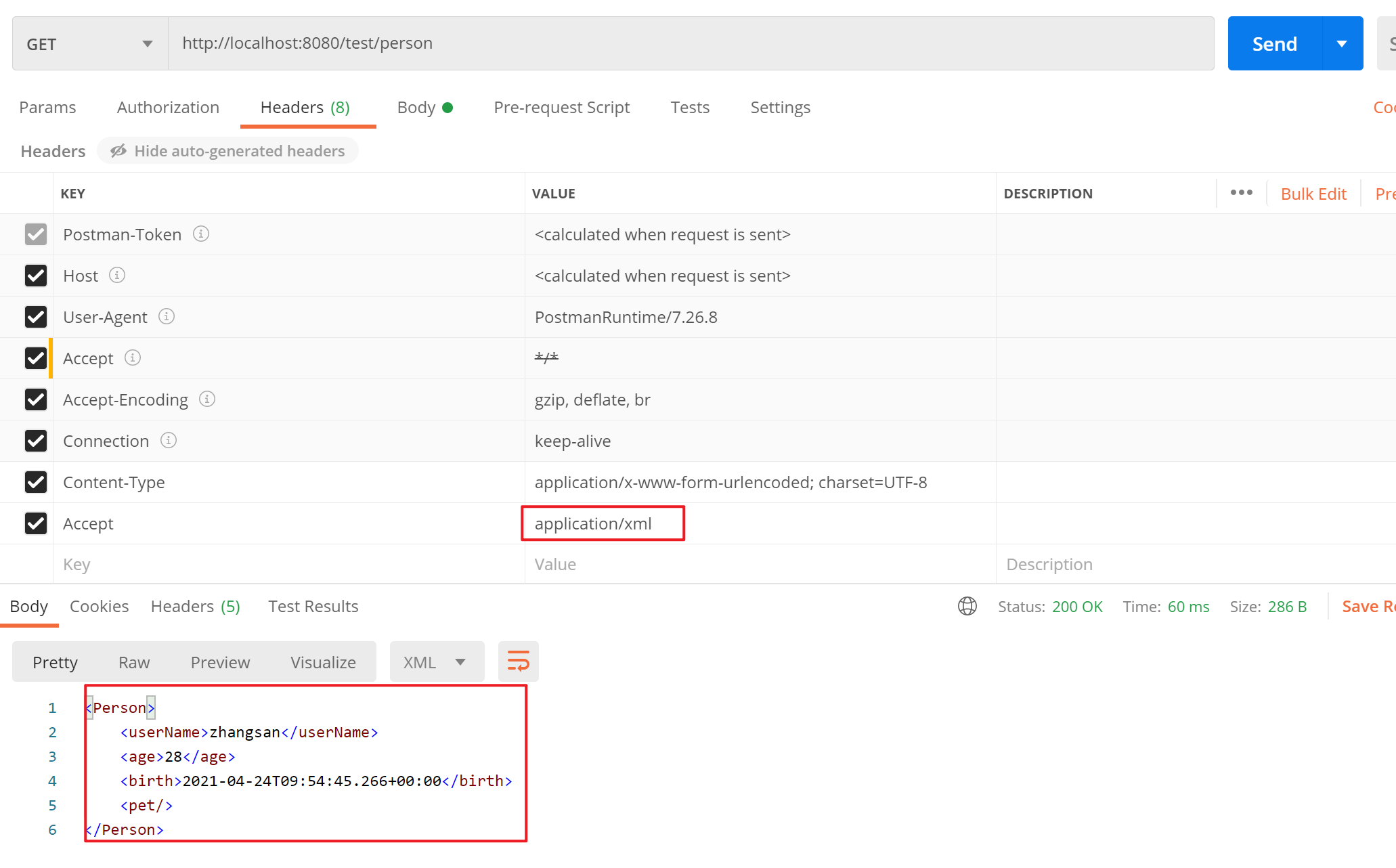
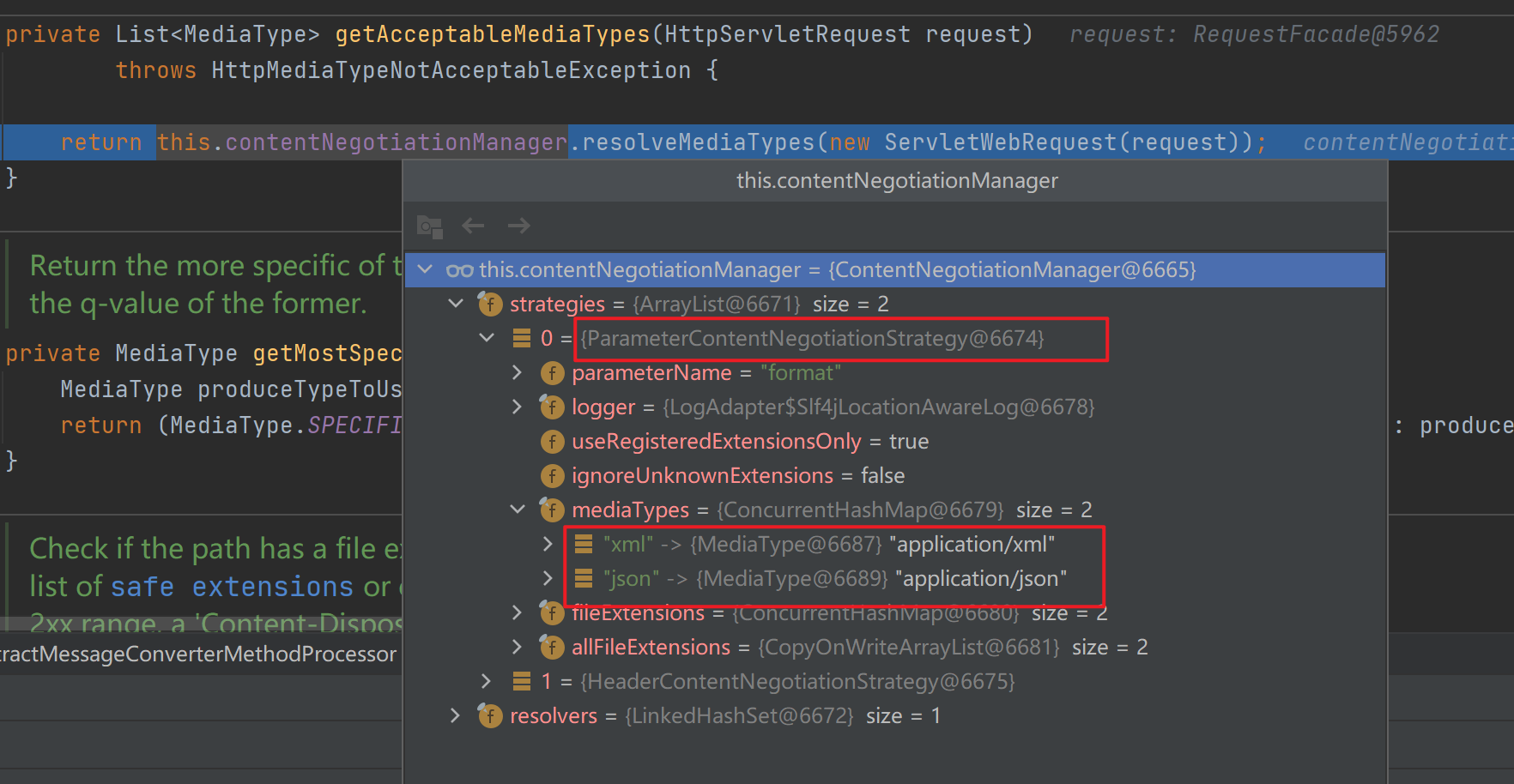
writeWithMessageConverters()方法中会先调用getAcceptableMediaTypes(),作用是根据浏览器发送过来的请求头(accept)信息获取浏览器能接收的数据类型。
![]()
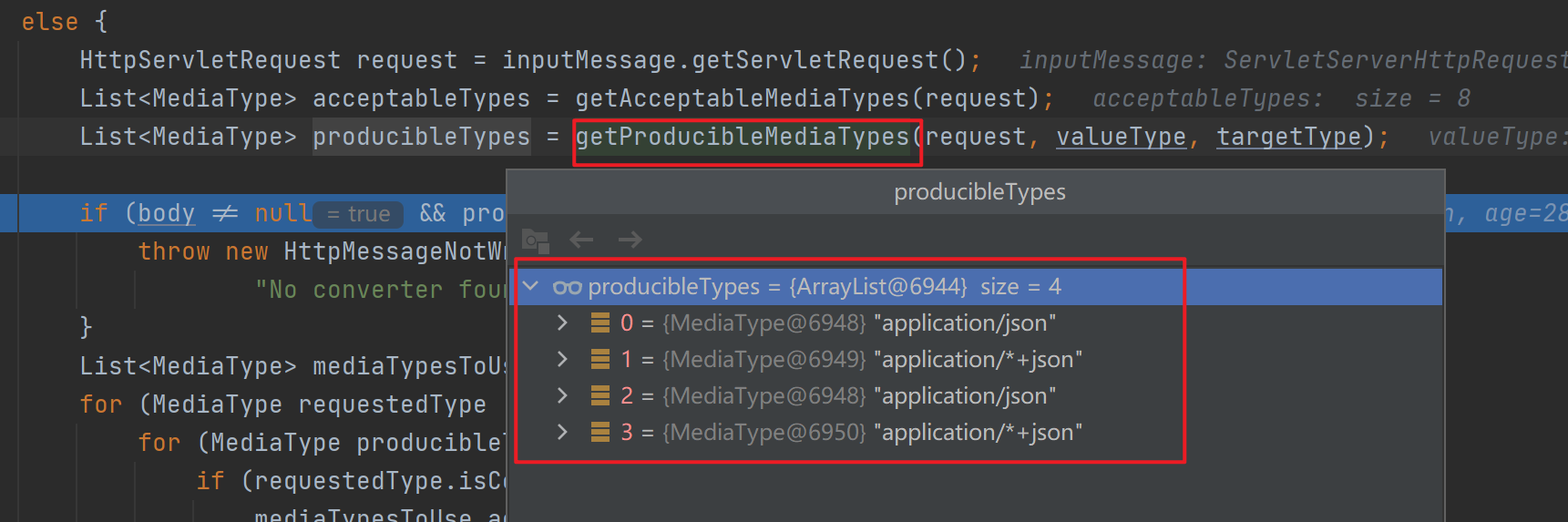
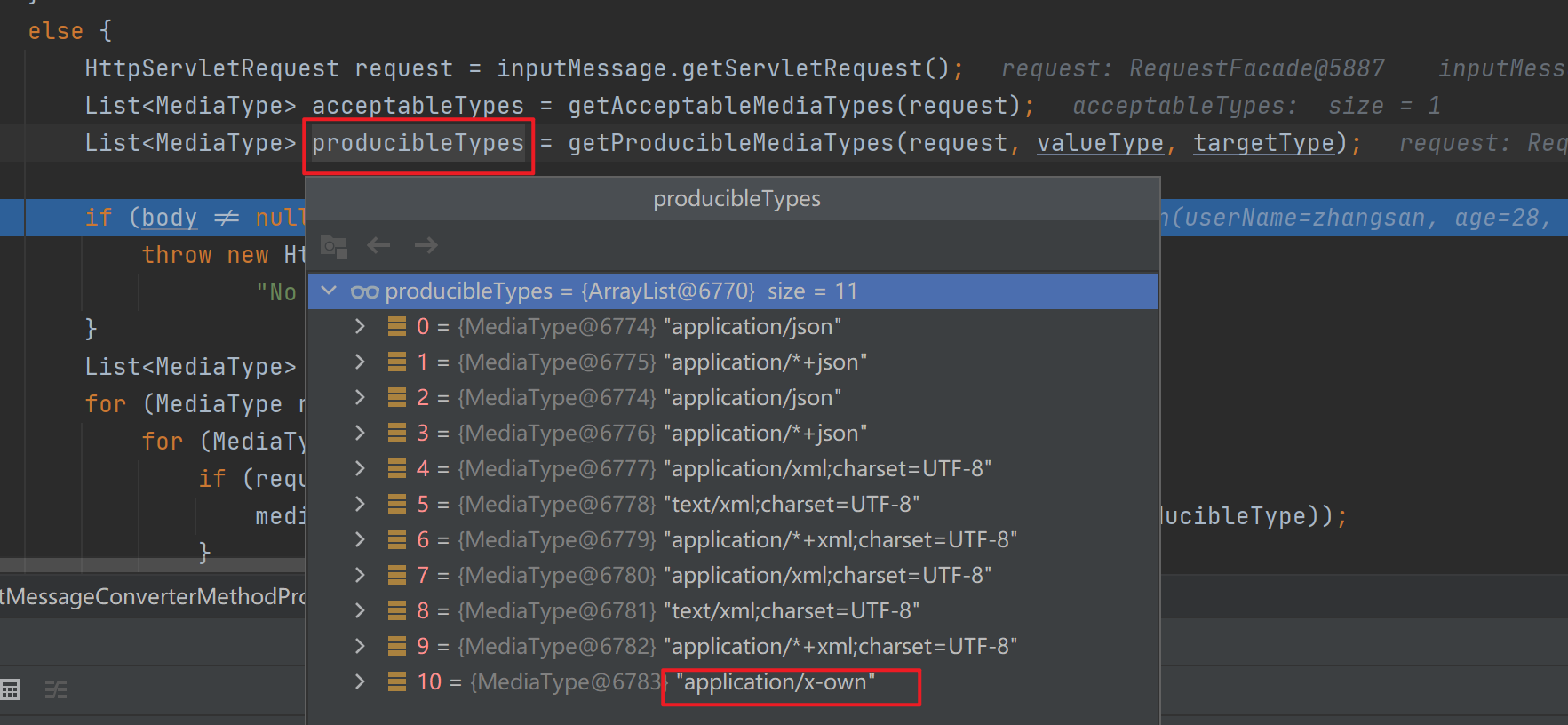
接着调用getProducibleMediaTypes()得到服务器能生产的数据类型,里面通过遍历所有的HttpMessageConverter并挨个添加能处理的返回值类型。
![]()
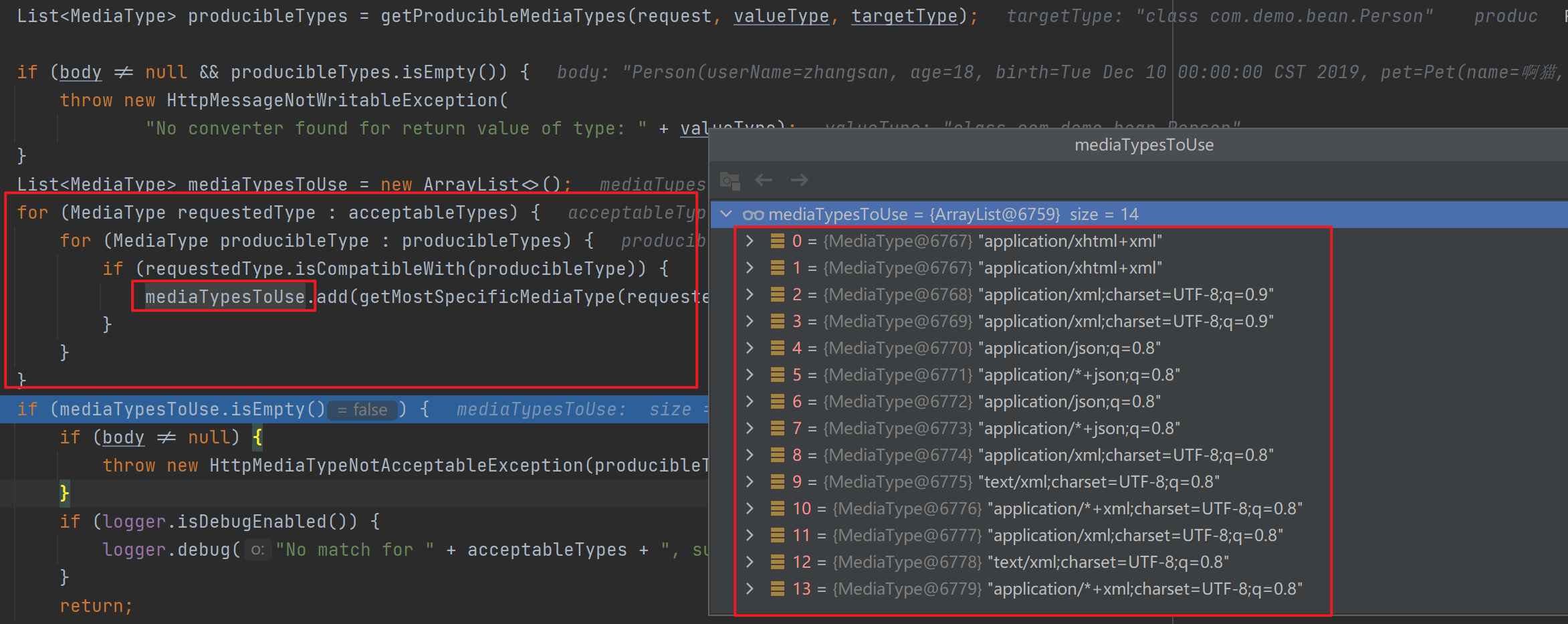
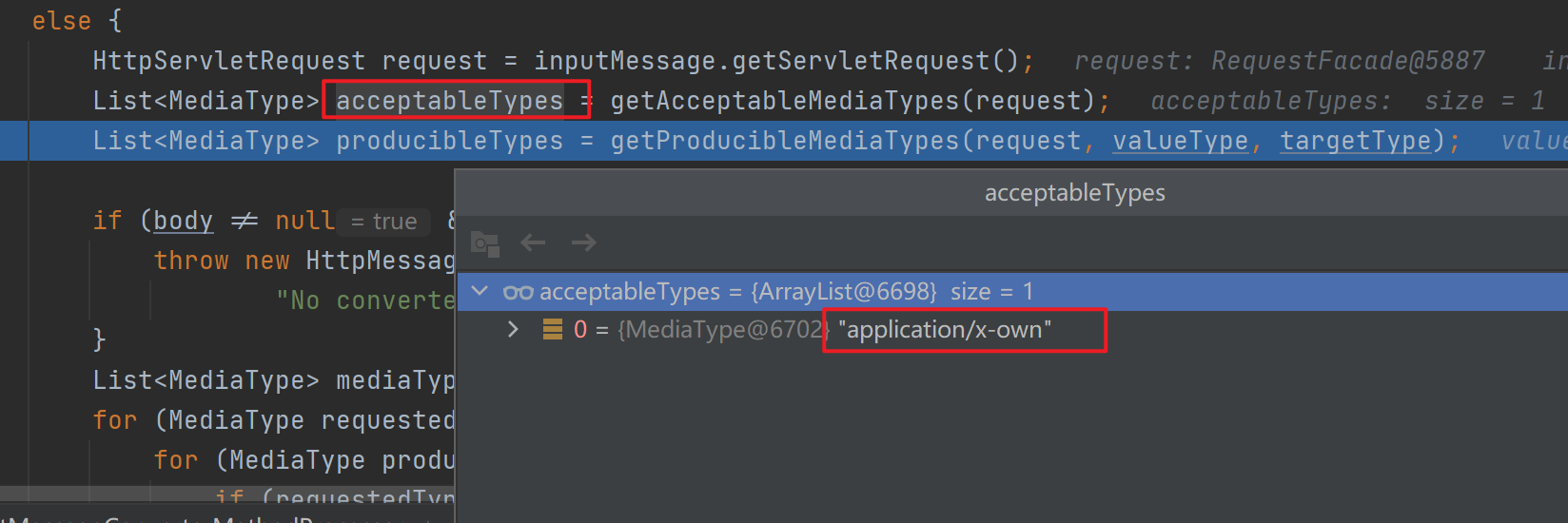
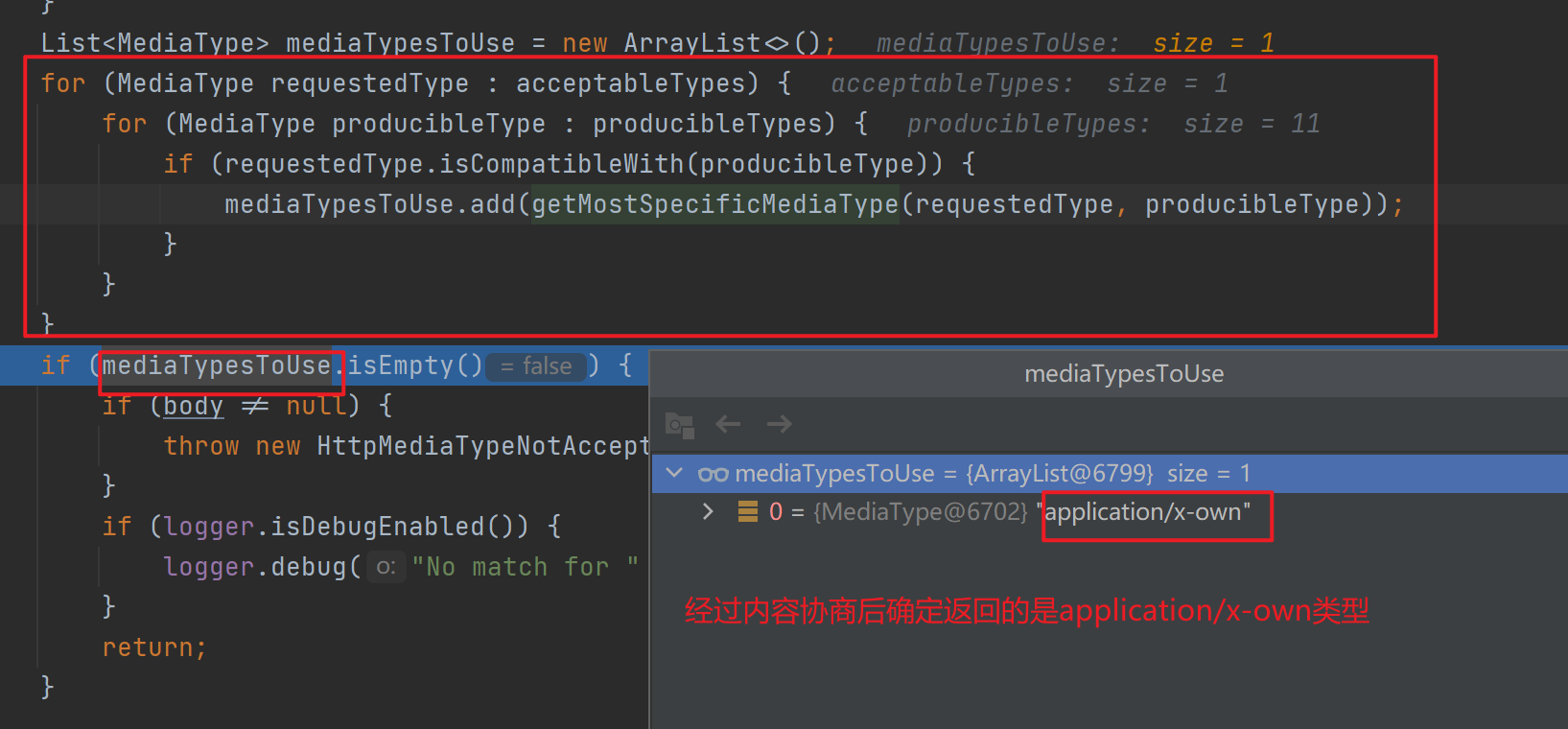
接着进行内容协商的最佳匹配,即遍历所有的acceptableTypes(浏览器能接受的),看是否能与producibleType(服务器能产生的)相匹配,有则添加,这里在遍历结束后匹配到了14个。
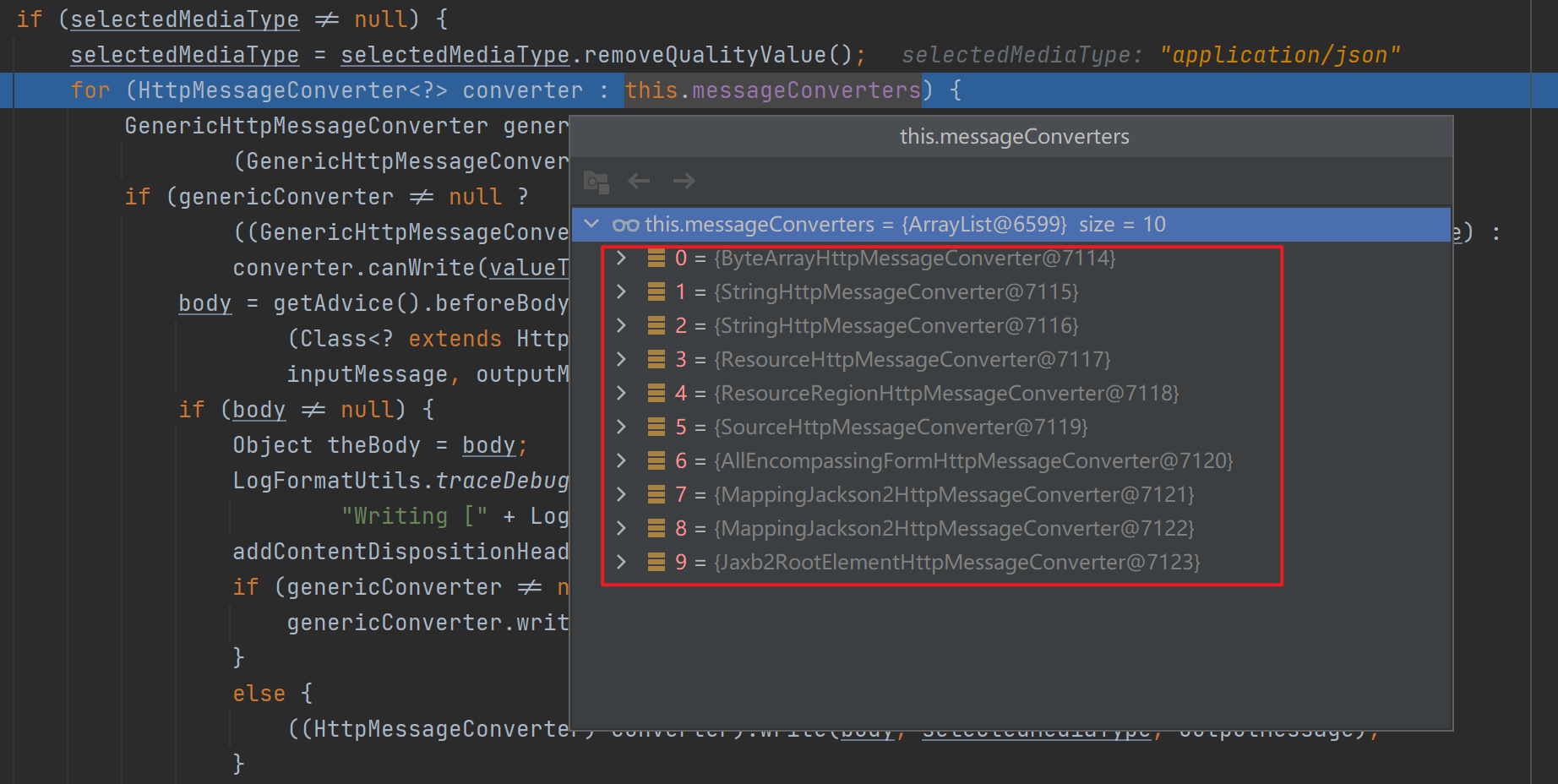
![]()
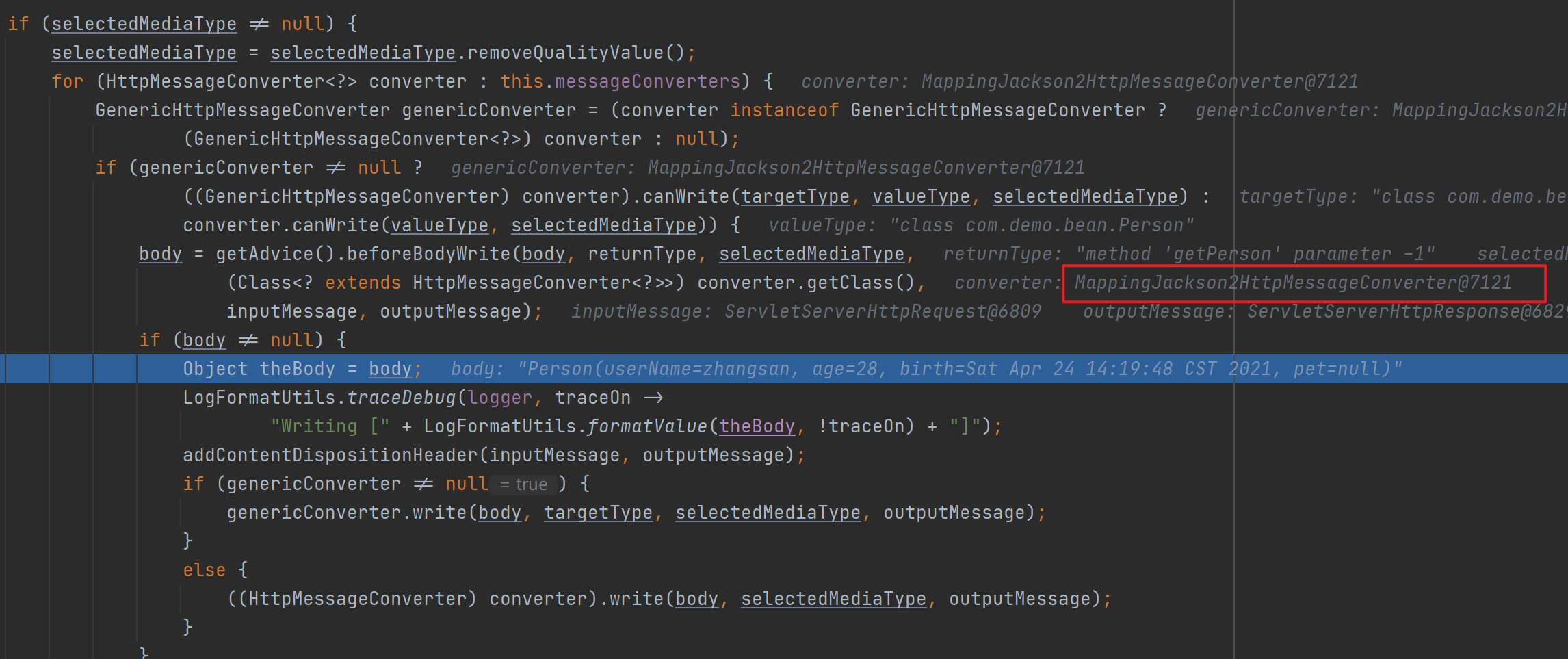
接着SpringMVC会挨个遍历所有容器底层的消息转换器HttpMessageConverter(默认有10个),看谁能将指定Class类型的对象转换为指定MediaType类型的数据(成功匹配到第一个处理器就返回)。最终找到处理器MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter。
![]()
![]()
![]()
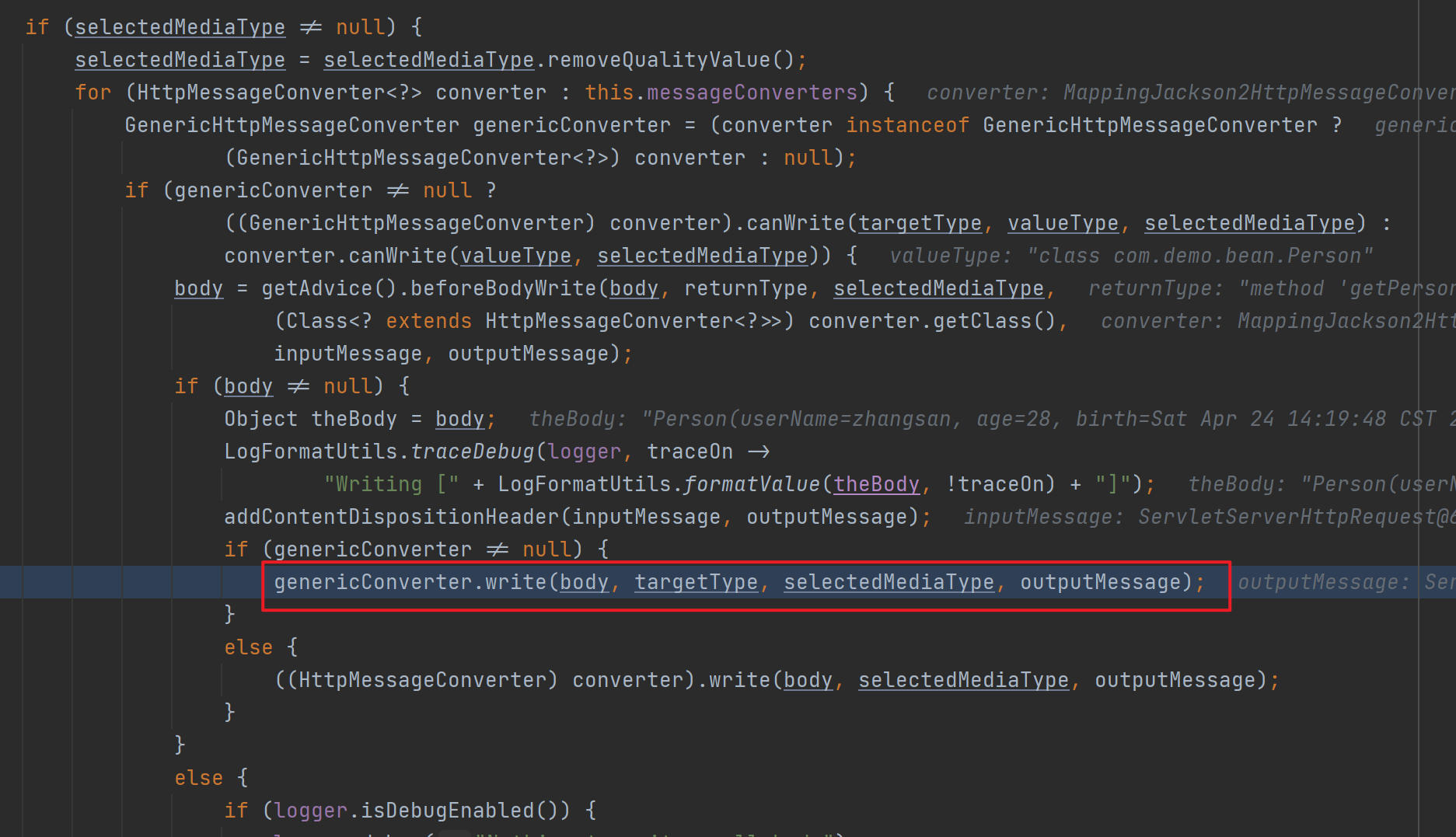
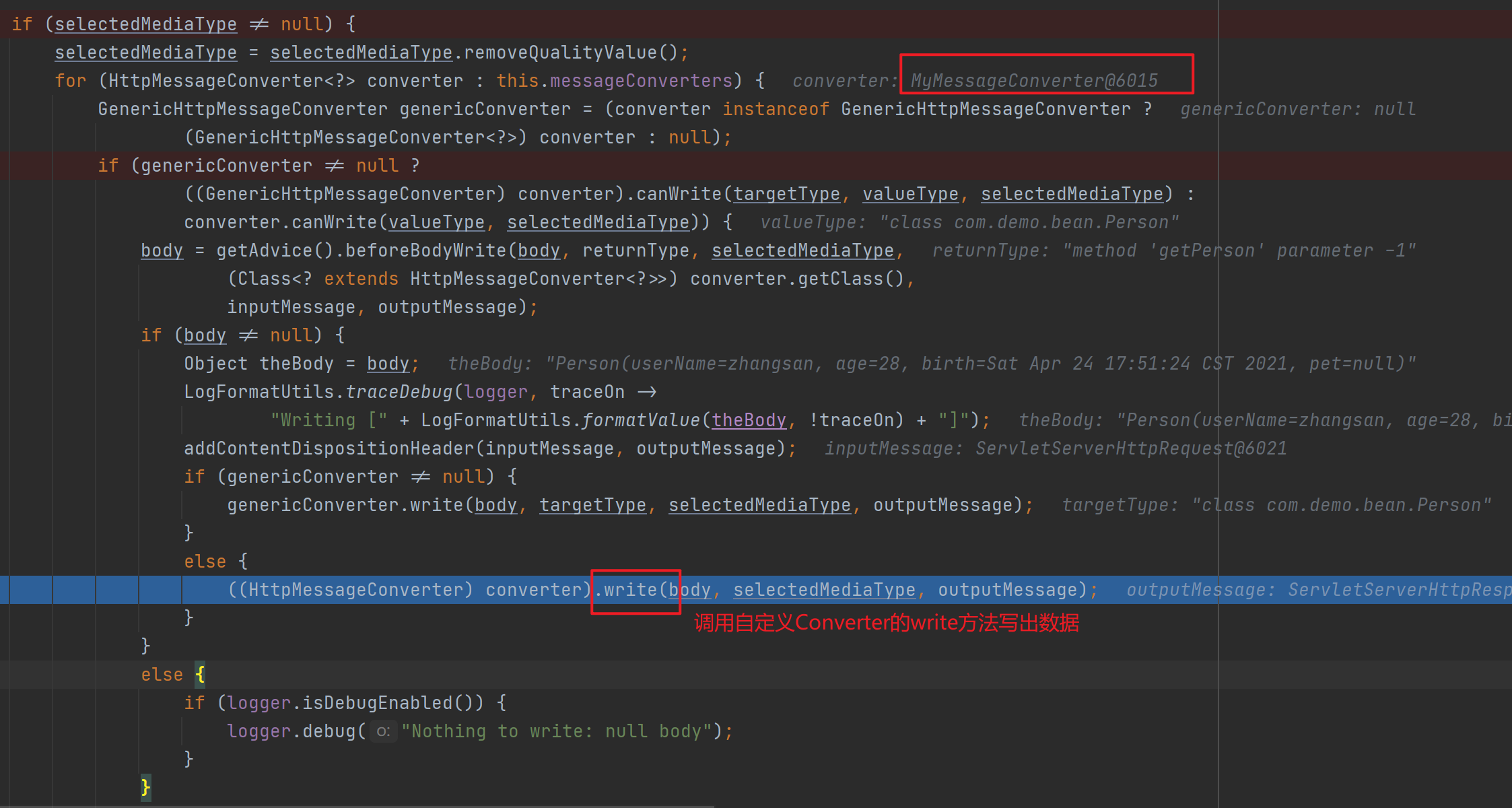
接着调用MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter.write()–>writeInternal()将返回值以json数据的形式写出去(底层利用jackson的ObjectMapper)。
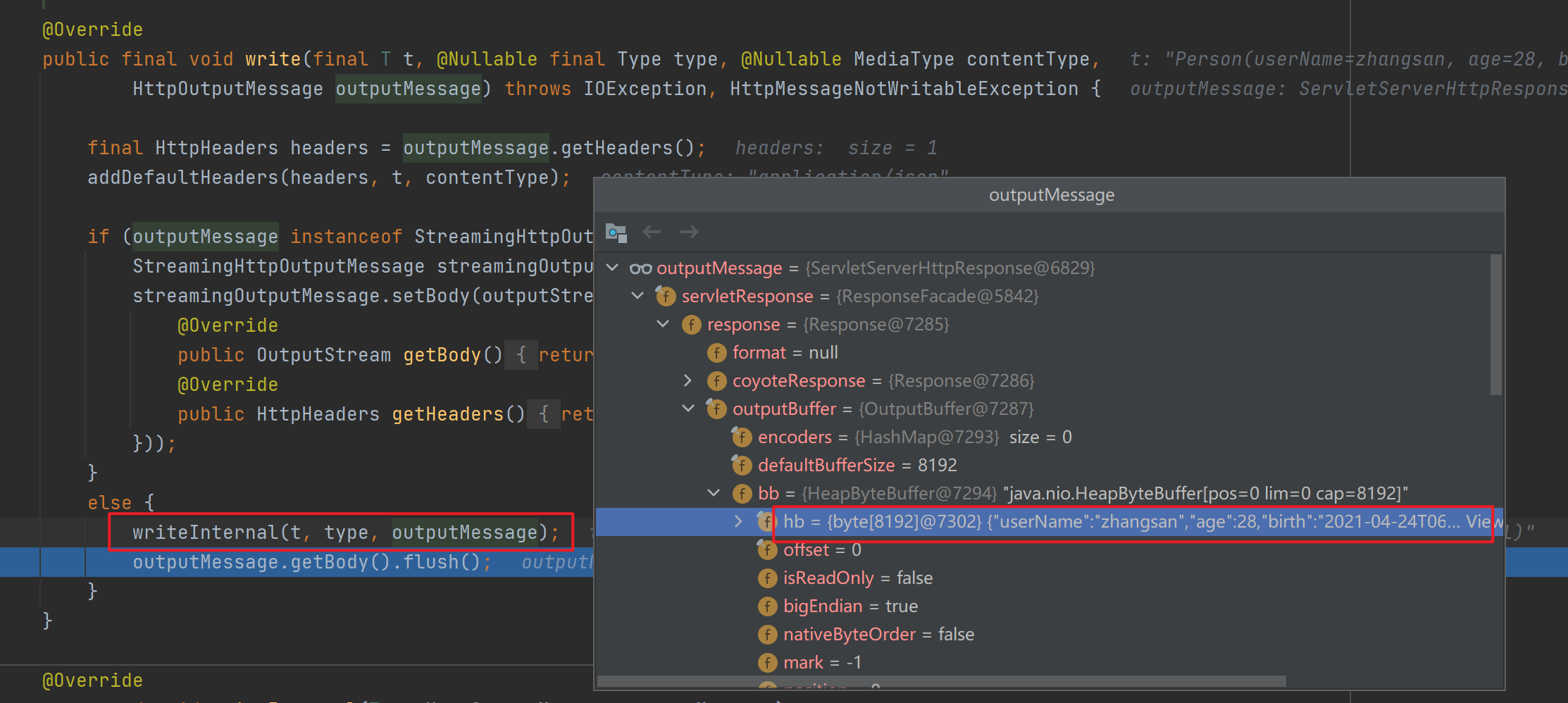
![]()
![]()
⑧执行getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest),上面步骤在方法执行的过程中将所有数据都放在ModelAndViewContainer中,包含要去的页面地址和Model数据,此方法则是将ModelAndViewContainer封装成ModelAndView对象后返回。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
private ModelAndView getModelAndView(ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
ModelFactory modelFactory, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
//将所有返回的数据都放在ModelAndViewContainer中
modelFactory.updateModel(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
return null;
}
//获取到BindingAwareModelMap
ModelMap model = mavContainer.getModel();
//将mavContainer封装成ModelAndView
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(mavContainer.getViewName(), model, mavContainer.getStatus());
if (!mavContainer.isViewReference()) {
mav.setView((View) mavContainer.getView());
}
//如果是重定向携带数据
if (model instanceof RedirectAttributes) {
Map<String, ?> flashAttributes = ((RedirectAttributes) model).getFlashAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = webRequest.getNativeRequest(HttpServletRequest.class);
if (request != null) {
RequestContextUtils.getOutputFlashMap(request).putAll(flashAttributes);
}
}
return mav;
}
public void updateModel(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer container) throws Exception {
ModelMap defaultModel = container.getDefaultModel();
if (container.getSessionStatus().isComplete()){
this.sessionAttributesHandler.cleanupAttributes(request);
}
else {
this.sessionAttributesHandler.storeAttributes(request, defaultModel);
}
if (!container.isRequestHandled() && container.getModel() == defaultModel) {
updateBindingResult(request, defaultModel);
}
}
private void updateBindingResult(NativeWebRequest request, ModelMap model) throws Exception {
//获取所有绑定在ModelAndView中的key
List<String> keyNames = new ArrayList<>(model.keySet());
for (String name : keyNames) {
Object value = model.get(name);
if (value != null && isBindingCandidate(name, value)) {
String bindingResultKey = BindingResult.MODEL_KEY_PREFIX + name;
if (!model.containsAttribute(bindingResultKey)) {
WebDataBinder dataBinder = this.dataBinderFactory.createBinder(request, value, name);
model.put(bindingResultKey, dataBinder.getBindingResult());
}
}
}
}
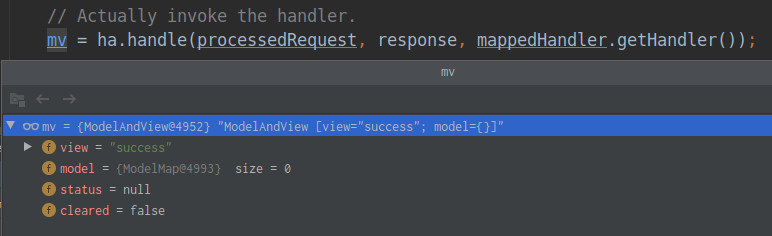
执行完毕返回了一个ModelAndView对象:
![]()
⑤继续执行来到processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException)转发到目标页面。
- 方法执行后的返回值会作为页面地址参考,转发或者重定向到页面。
- 视图解析器可能会进行页面地址的拼串。
- 任何方法的返回值最终都会包装成ModelAndView对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv,
Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
//视图渲染
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// Exception (if any) is already handled..
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}其中的render方法用于视图渲染。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale =
(this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
response.setLocale(locale);
View view;
//拿到返回的视图名
String viewName = mv.getViewName();
if (viewName != null) {
// We need to resolve the view name.
//得到视图对象,view对象定义了页面的渲染逻辑
view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
else {
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
"View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
// Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Rendering view [" + view + "] ");
}
try {
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "]", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}①里面通过ViewResolver接口(九大组件之一)来根据视图名(方法的返回值)得到view对象。具体实现在resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request)方法里。
1
2
3
4public interface ViewResolver {
View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception;
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model,
Locale locale, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//遍历所有的viewResolvers,调用它的resolveViewName方法得到view对象
if (this.viewResolvers != null) {
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
}
}
return null;
}这里发现只有一个我们之前在springmvc.xml中配置的InternalResourceViewResolver:
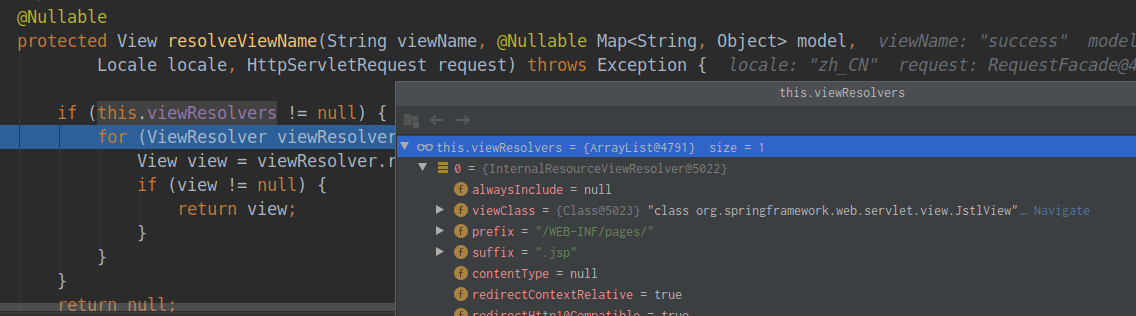
![]()
其resolveViewName方法的具体实现是(在父类AbstractCachingViewResolver类中实现,InternalResourceViewResolver类是其某一个子类),里面实际通过调用createView(viewName, locale)方法返回view对象:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
if (!isCache()) {
return createView(viewName, locale);
}
else {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(viewName, locale);
View view = this.viewAccessCache.get(cacheKey);
if (view == null) {
synchronized (this.viewCreationCache) {
view = this.viewCreationCache.get(cacheKey);
if (view == null) {
// Ask the subclass to create the View object.
view = createView(viewName, locale);
if (view == null && this.cacheUnresolved) {
view = UNRESOLVED_VIEW;
}
if (view != null && this.cacheFilter.filter(view, viewName, locale)) {
this.viewAccessCache.put(cacheKey, view);
this.viewCreationCache.put(cacheKey, view);
}
}
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatKey(cacheKey) + "served from cache");
}
}
return (view != UNRESOLVED_VIEW ? view : null);
}
}
//在UrlBasedViewResolver类中
protected View createView(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
// If this resolver is not supposed to handle the given view,
// return null to pass on to the next resolver in the chain.
if (!canHandle(viewName, locale)) {
return null;
}
// Check for special "redirect:" prefix.
//判断返回值是否以redirect:为前缀,如果是则创建了一个RedirectView对象
if (viewName.startsWith(REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX)) {
String redirectUrl = viewName.substring(REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX.length());
RedirectView view = new RedirectView(redirectUrl,
isRedirectContextRelative(), isRedirectHttp10Compatible());
String[] hosts = getRedirectHosts();
if (hosts != null) {
view.setHosts(hosts);
}
return applyLifecycleMethods(REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX, view);
}
// Check for special "forward:" prefix.
//判断返回值是否以forward:为前缀,如果是则创建了一个InternalResourceView对象
if (viewName.startsWith(FORWARD_URL_PREFIX)) {
String forwardUrl = viewName.substring(FORWARD_URL_PREFIX.length());
InternalResourceView view = new InternalResourceView(forwardUrl);
return applyLifecycleMethods(FORWARD_URL_PREFIX, view);
}
// Else fall back to superclass implementation: calling loadView.
//如果没有前缀就创建一个默认view对象
return super.createView(viewName, locale);
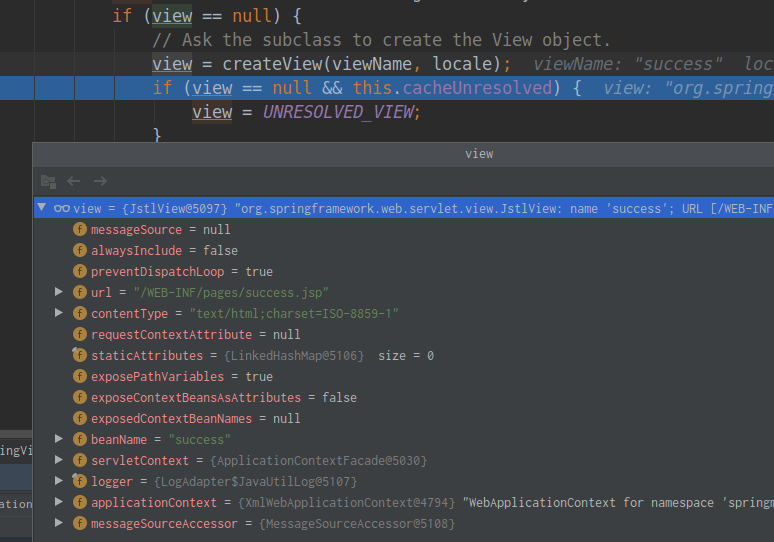
}由于我们的测试用例方法的返回值没有以redirect:或者forward:为前缀,则创建了一个默认的view对象(JstlView):
![]()
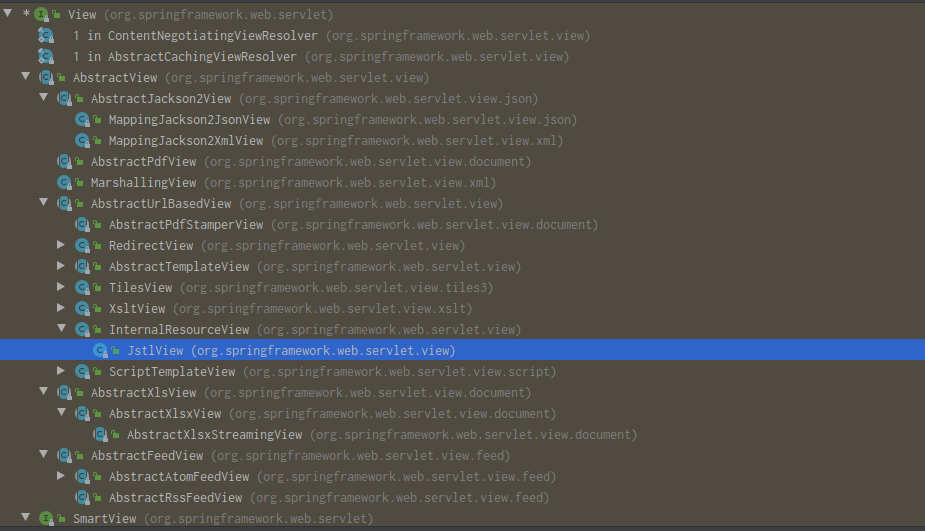
②调用view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response)方法(在AbstractView类中)进行页面渲染。View接口有很多实现类,且其中有个render方法。
![]()
![]()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public void render( Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("View " + formatViewName() +
", model " + (model != null ? model : Collections.emptyMap()) +
(this.staticAttributes.isEmpty() ? "" : ", static attributes " + this.staticAttributes));
}
Map<String, Object> mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response);
prepareResponse(request, response);
//渲染要给页面输出的数据
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response);
}其中调用了InternalResourceView类的renderMergedOutputModel方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(
Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Expose the model object as request attributes.
//将模型中数据放在请求域中
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, request);
// Expose helpers as request attributes, if any.
exposeHelpers(request);
// Determine the path for the request dispatcher.
String dispatcherPath = prepareForRendering(request, response);
// Obtain a RequestDispatcher for the target resource (typically a JSP).
//得到转发器
RequestDispatcher rd = getRequestDispatcher(request, dispatcherPath);
if (rd == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not get RequestDispatcher for [" + getUrl() +
"]: Check that the corresponding file exists within your web application archive!");
}
// If already included or response already committed, perform include, else forward.
if (useInclude(request, response)) {
response.setContentType(getContentType());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Including [" + getUrl() + "]");
}
rd.include(request, response);
}
else {
// Note: The forwarded resource is supposed to determine the content type itself.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Forwarding to [" + getUrl() + "]");
}
//通过转发器转发到页面
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
//此方法在AbstractView类中
protected void exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(Map<String, Object> model,
HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//将model中的所有数据遍历放在request中
model.forEach((name, value) -> {
if (value != null) {
request.setAttribute(name, value);
}
else {
request.removeAttribute(name);
}
});
}会发现View的作用实际上才是真正地进行转发或者重定向到页面,而视图解析器ViewResolver只是为了得到这个View视图对象。
![]()
![]()
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_34007020/article/details/92608532
补充:测试参数为pojo对象时参数解析器的解析流程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class Person {
private String userName;
private Integer age;
private Date birth;
private Pet pet;
}
public class Pet {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
public class HelloController {
public Person saveuser(Person person){
return person;
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/springmvc/saveuser" method="post">
姓名: <input name="userName" value="zhangsan"/> <br/>
年龄: <input name="age" value="18"/> <br/>
生日: <input name="birth" value="2019/12/10"/> <br/>
宠物姓名:<input name="pet.name" value="阿猫"/><br/>
宠物年龄:<input name="pet.age" value="5"/>
<input type="submit" value="保存"/>
</form>
</body>
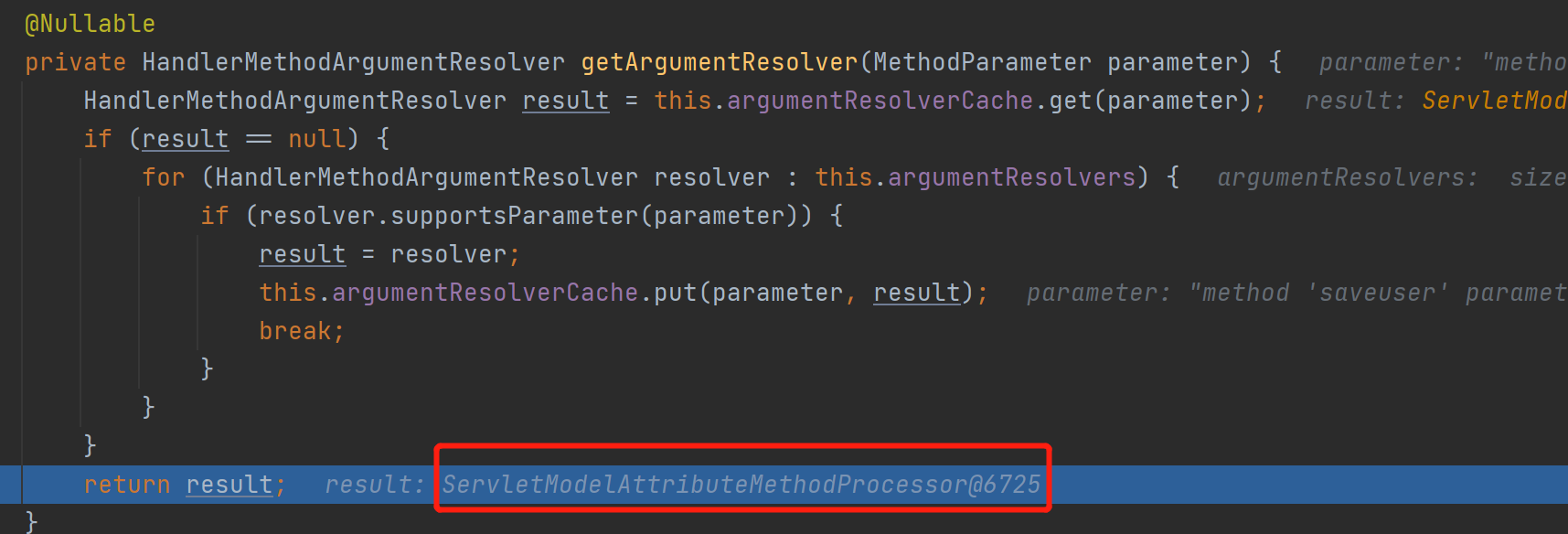
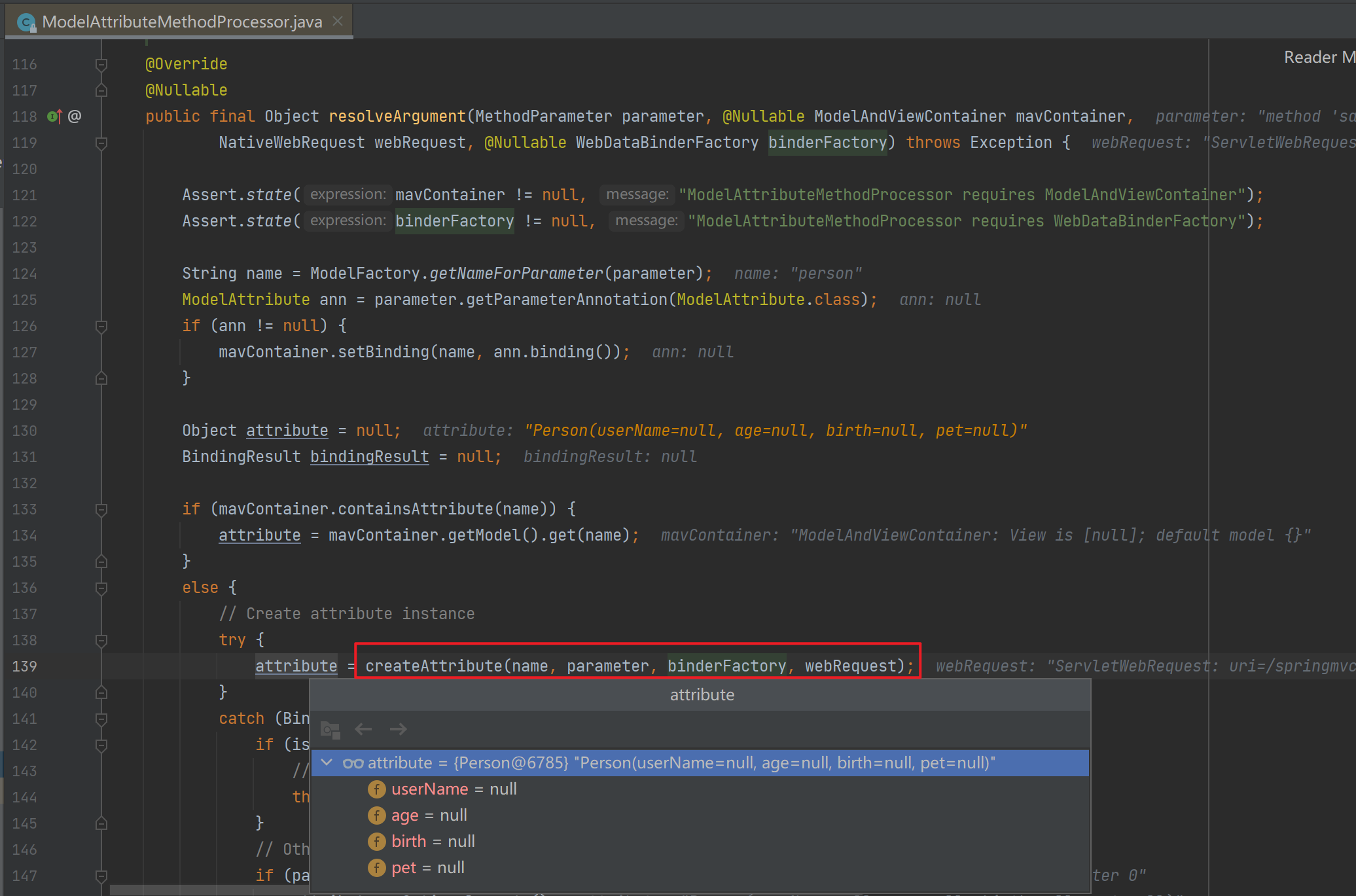
</html>打断点,运行程序后访问对应接口,来到选择合适的参数解析器的位置(HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite.getArgumentResolver()),发现解析自定义pojo的解析器是ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor。
![]()
接着进入ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor的resolveArgument逻辑。
![]()
![]()
resolveArgument()中会先调用createAttribute()创建一个空Person对象。
![]()
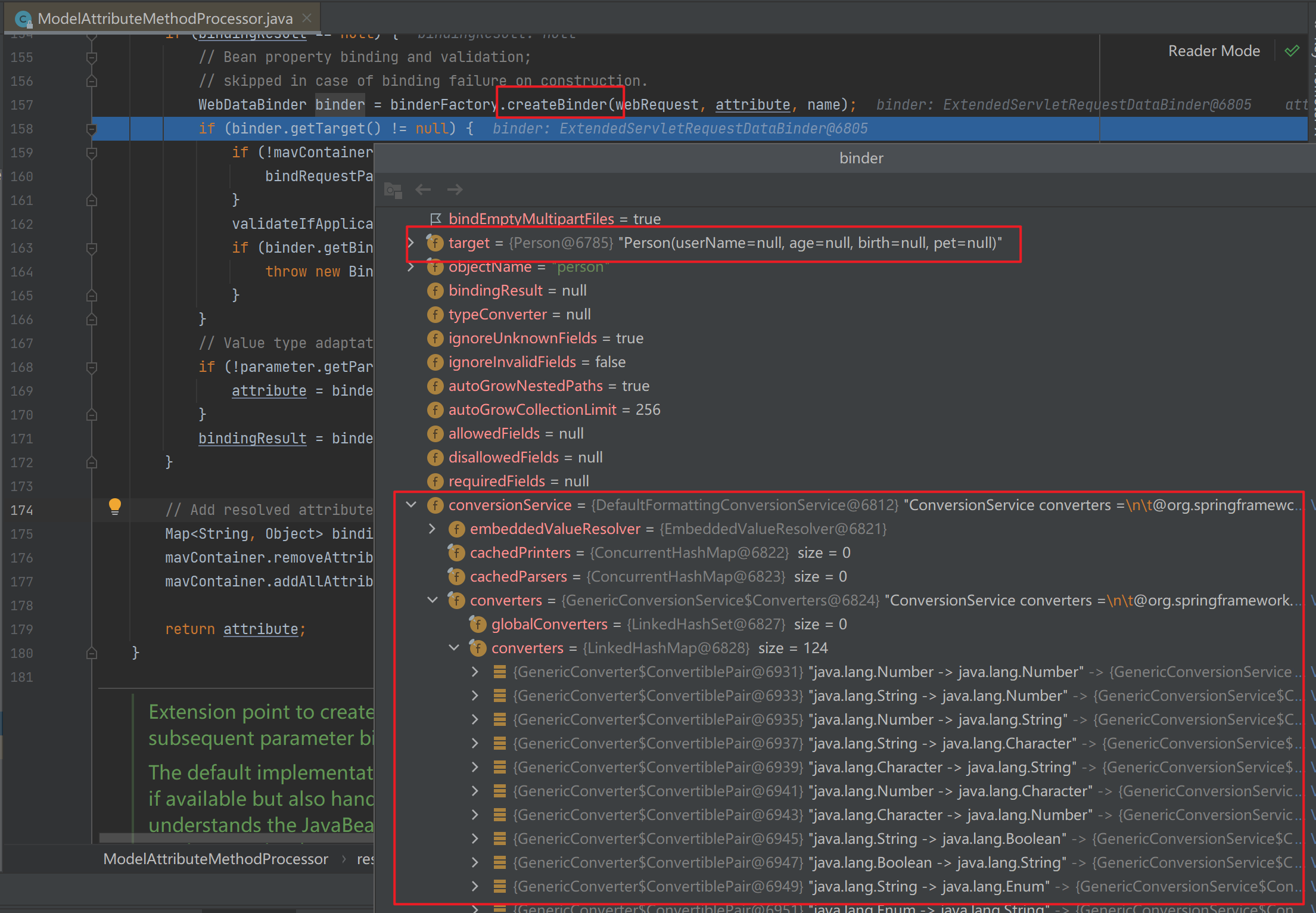
接着通过调用binderFactory.createBinder()创建一个web数据绑定器WebDataBinder,作用是利用一些Converters将请求参数的值绑定到指定的JavaBean中。其中拥有刚才创建的空Person对象,同时拥有一些数据转换器。
![]()
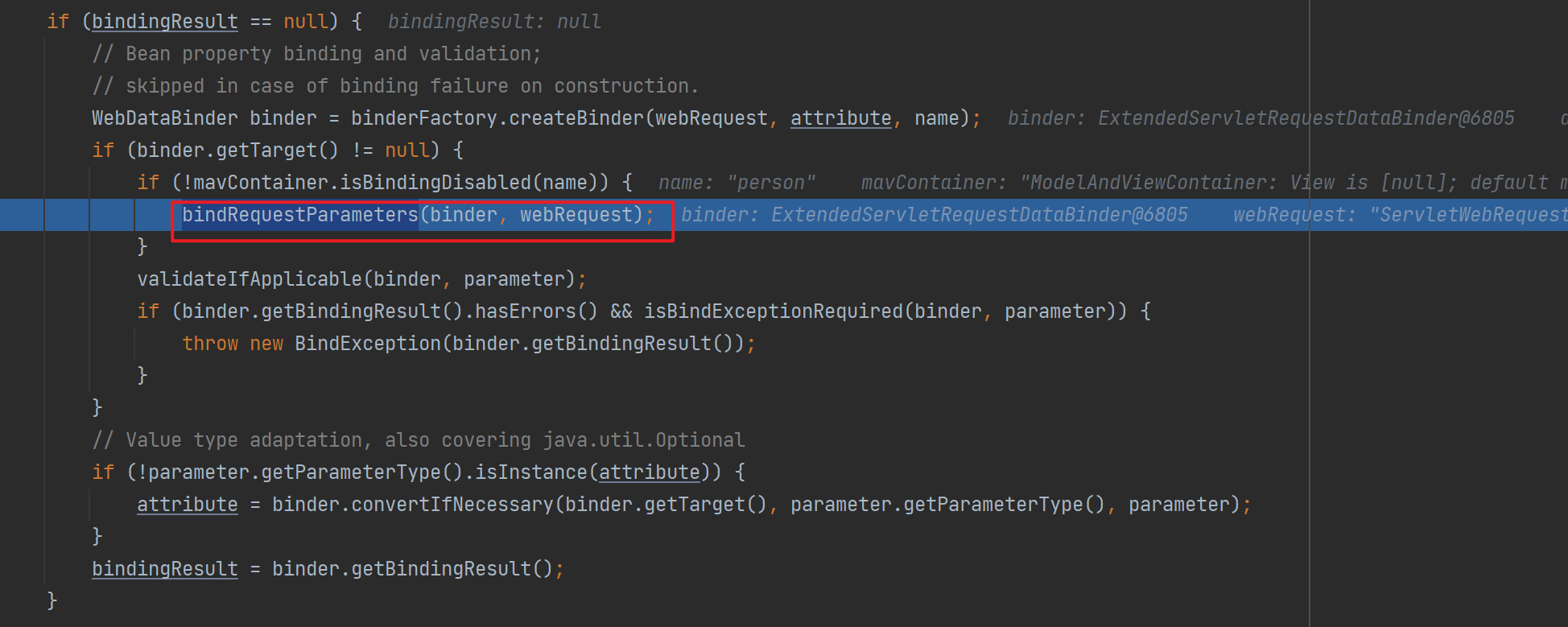
接下来通过调用bindRequestParameters()进入了绑定Person对象的流程。其中的逻辑是在设置每一个值的时候,遍历里面的所有converter并找到那个可以将这个数据类型(request带来参数的字符串)转换到指定的类型(JavaBean–Integer)的converter后进行转换并赋值工作。
![]()
如果需要自定义类型转换器,只需要向容器中注册自定义实现了Converter的Bean即可。例如下方更改pet属性的提交方式,则容器中没有可以处理此类型的转换器,此时就需要自定义转换器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/springmvc/saveuser" method="post">
姓名: <input name="userName" value="zhangsan"/> <br/>
年龄: <input name="age" value="18"/> <br/>
生日: <input name="birth" value="2019/12/10"/> <br/>
宠物: <input name="pet" value="啊猫,3"/>
<input type="submit" value="保存"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
public class WebConfig {
//WebMvcConfigurer定制化SpringMVC的功能
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
registry.addConverter(new Converter<String, Pet>() {
public Pet convert(String source) {
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(source)){
Pet pet = new Pet();
String[] split = source.split(",");
pet.setName(split[0]);
pet.setAge(Integer.parseInt(split[1]));
return pet;
}
return null;
}
});
}
};
}
}
补充:自定义MessageConverter,实现同一个请求能根据客户端需要的返回值类型动态返回。
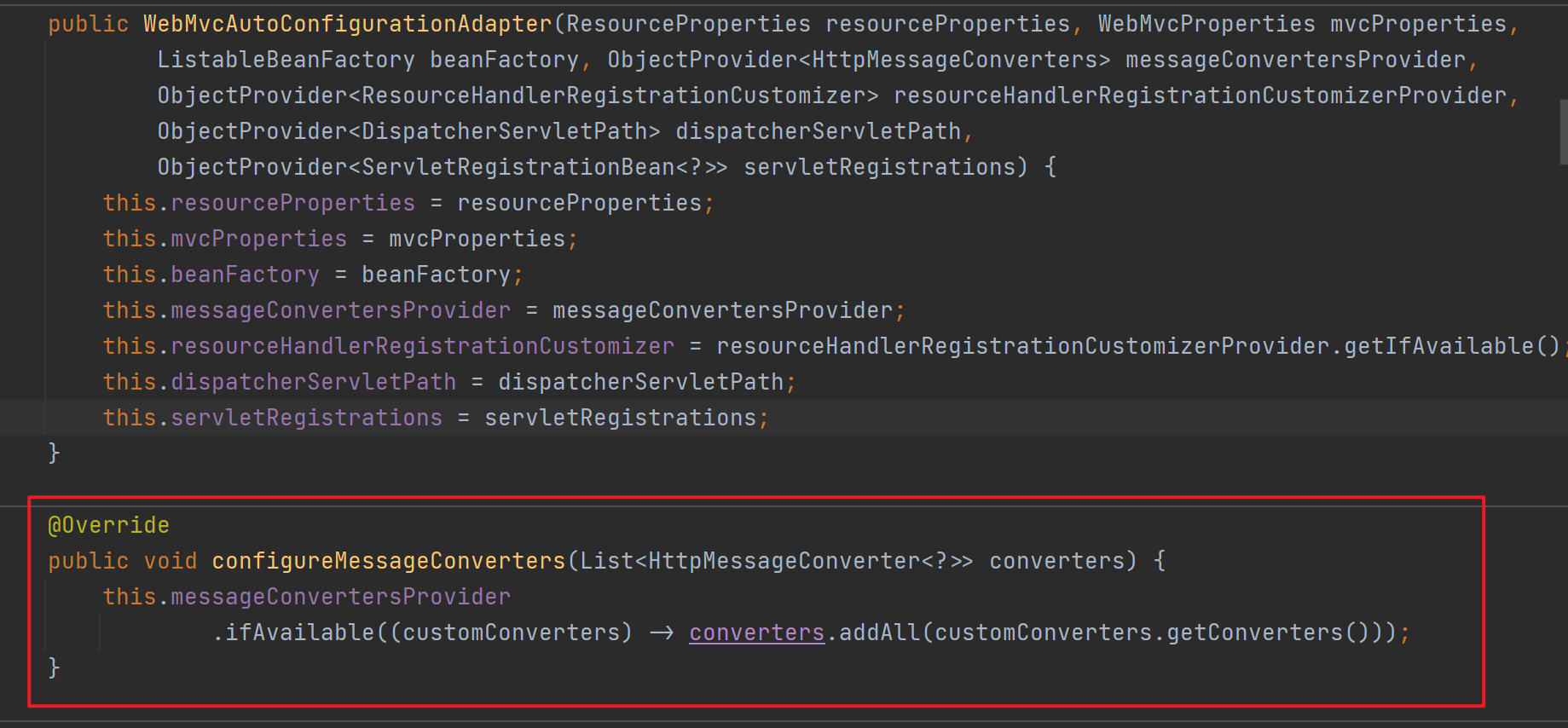
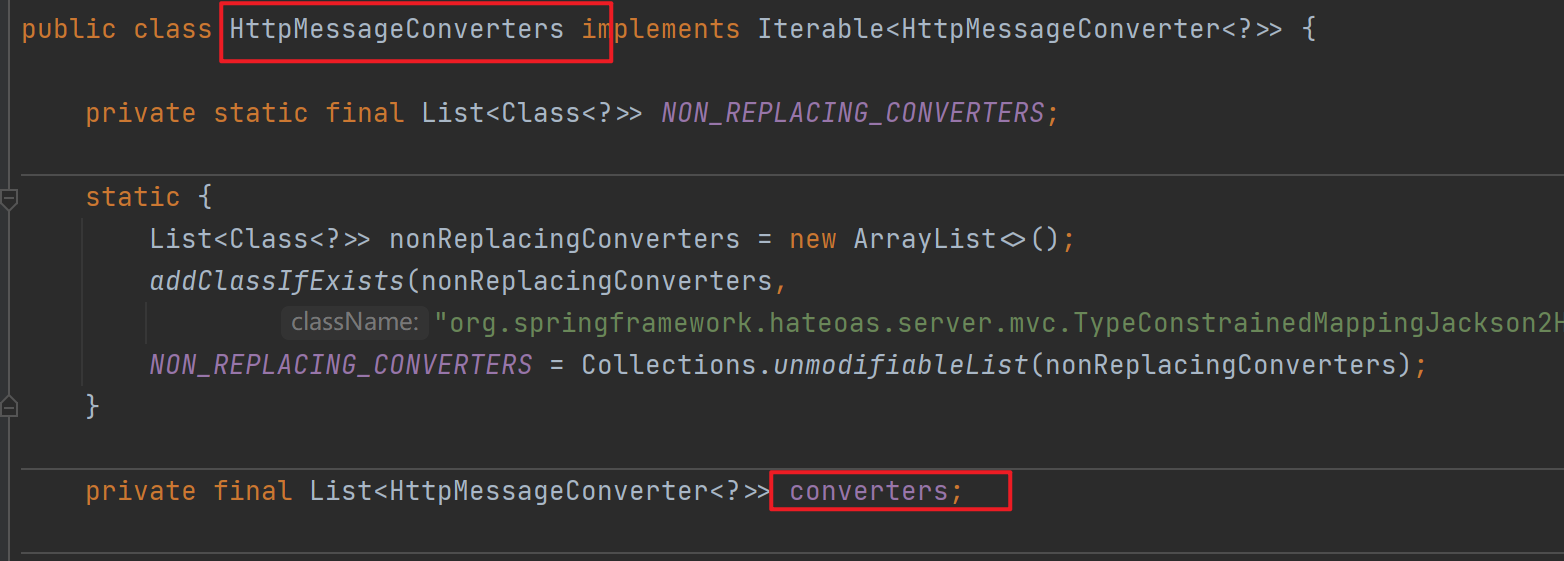
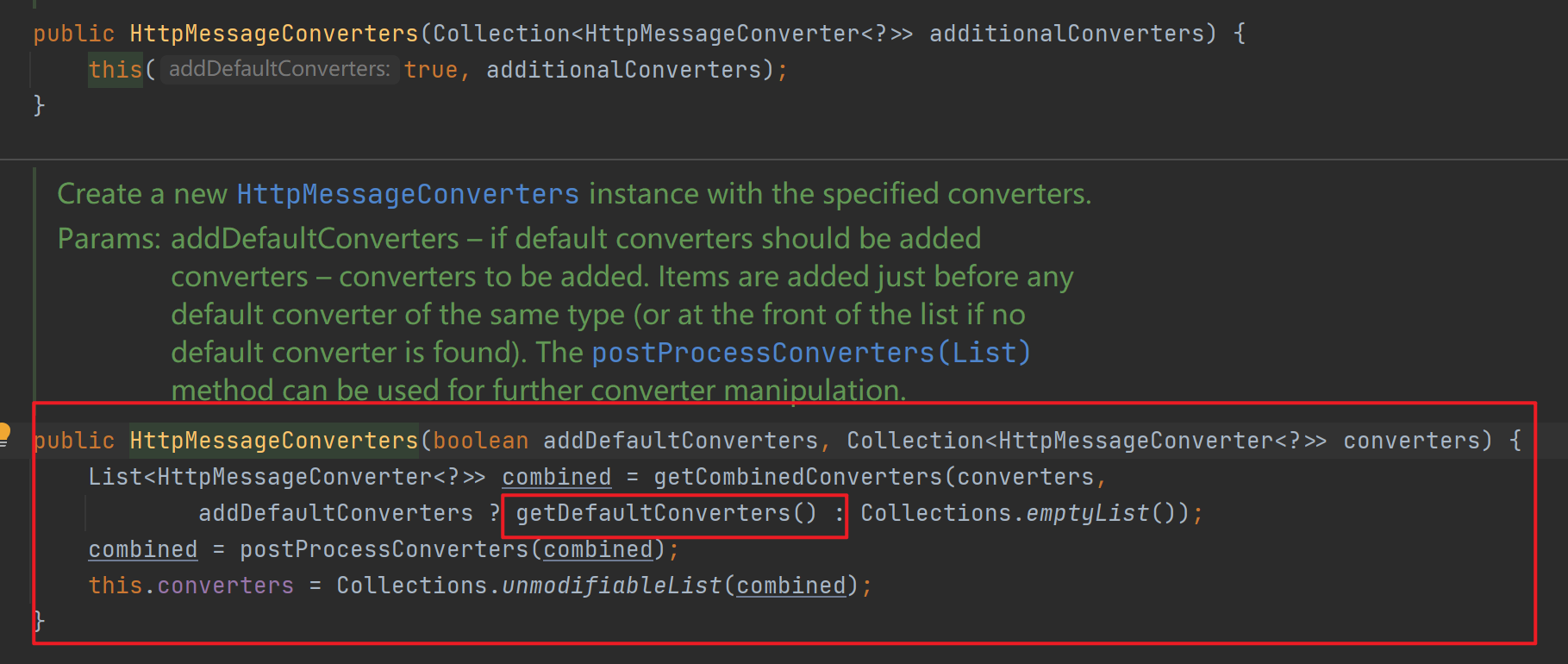
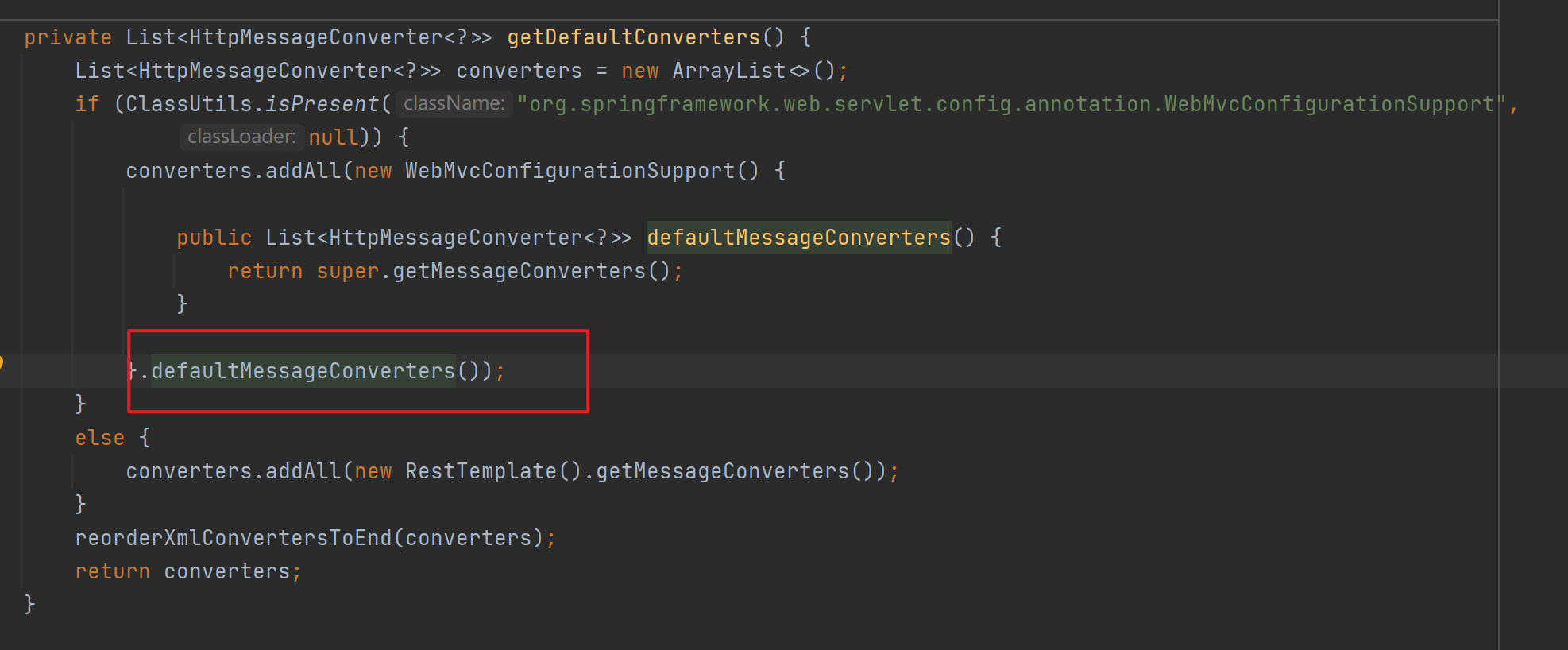
SpringBoot的自动配置类WebMvcAutoConfiguration中在ioc容器启动时往messageConvertersProvider属性添加了所有默认的converters。而HttpMessageConverter类型的converters是MessageConverters类的一个属性,在调用其构造方法时会导入所有默认的converters。
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
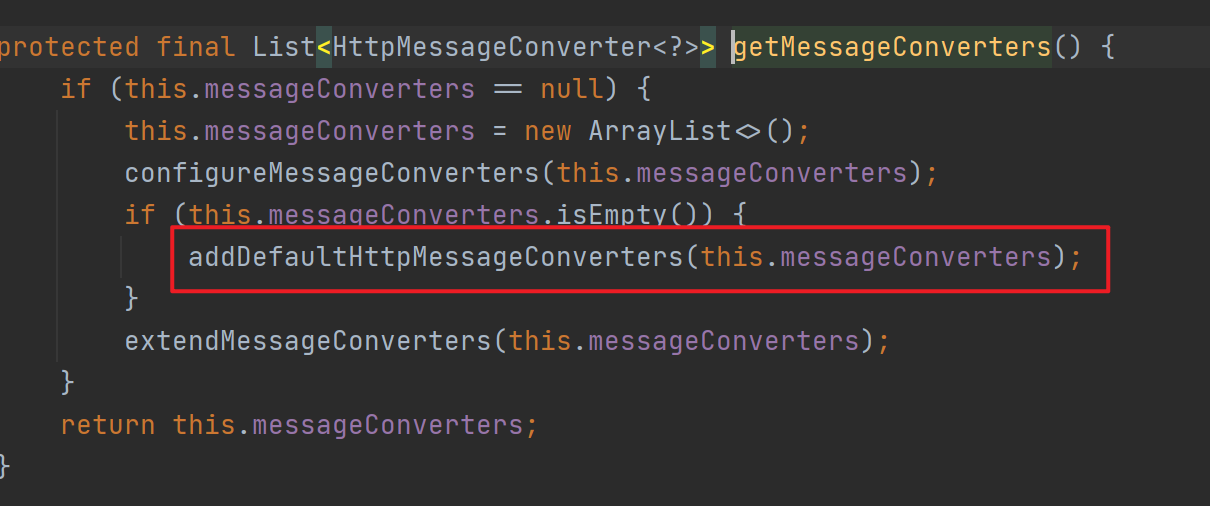
58protected final void addDefaultHttpMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> messageConverters) {
messageConverters.add(new ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter());
messageConverters.add(new StringHttpMessageConverter());
messageConverters.add(new ResourceHttpMessageConverter());
messageConverters.add(new ResourceRegionHttpMessageConverter());
try {
messageConverters.add(new SourceHttpMessageConverter<>());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Ignore when no TransformerFactory implementation is available...
}
messageConverters.add(new AllEncompassingFormHttpMessageConverter());
if (romePresent) {
messageConverters.add(new AtomFeedHttpMessageConverter());
messageConverters.add(new RssChannelHttpMessageConverter());
}
//如果导入了xml的相关jar包就添加MappingJackson2XmlHttpMessageConverter。
if (jackson2XmlPresent) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder.xml();
if (this.applicationContext != null) {
builder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
messageConverters.add(new MappingJackson2XmlHttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
else if (jaxb2Present) {
messageConverters.add(new Jaxb2RootElementHttpMessageConverter());
}
if (jackson2Present) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder.json();
if (this.applicationContext != null) {
builder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
messageConverters.add(new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
else if (gsonPresent) {
messageConverters.add(new GsonHttpMessageConverter());
}
else if (jsonbPresent) {
messageConverters.add(new JsonbHttpMessageConverter());
}
if (jackson2SmilePresent) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder.smile();
if (this.applicationContext != null) {
builder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
messageConverters.add(new MappingJackson2SmileHttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
if (jackson2CborPresent) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder.cbor();
if (this.applicationContext != null) {
builder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
messageConverters.add(new MappingJackson2CborHttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
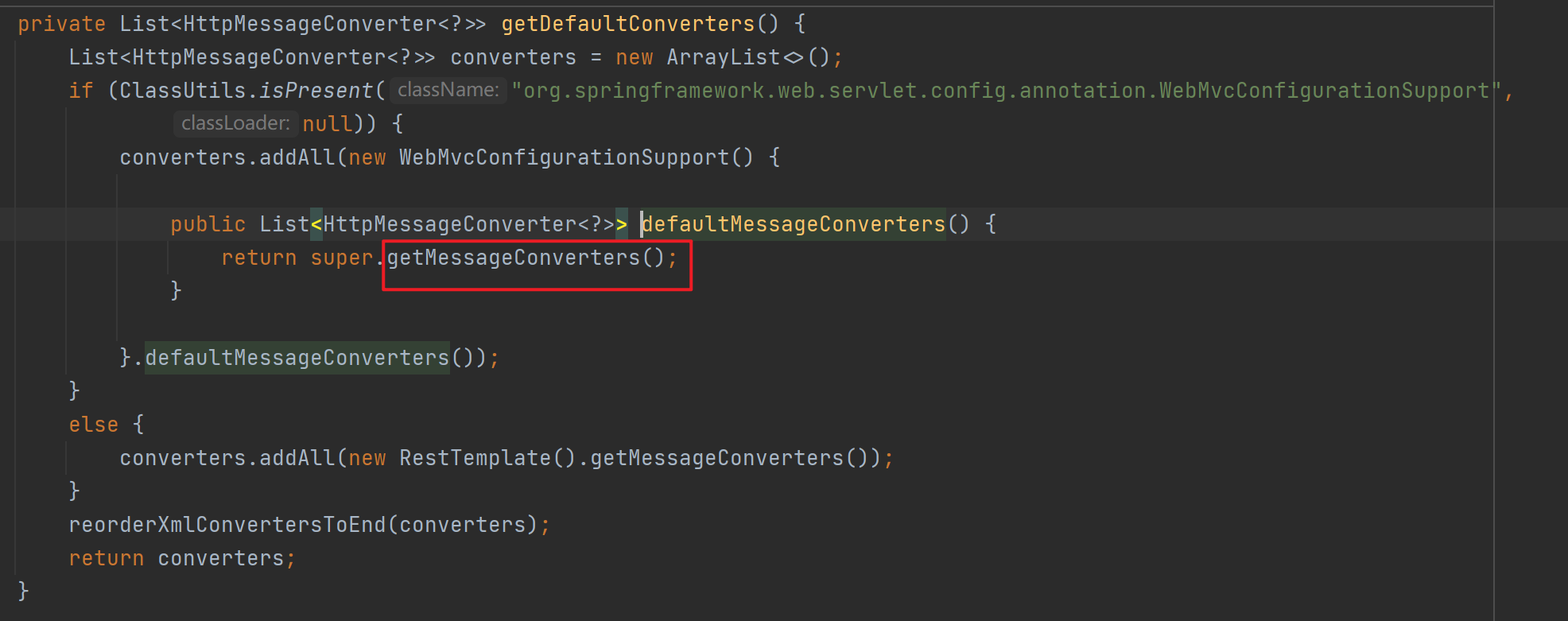
}从SpringBoot官方文档可以看出,如果想要给SpringMVC添加自定义组件,只需要给容器中添加一个WebMvcConfigurer并实现相关方法即可,这里对应实现的方法是extendMessageConverters(),给容器中扩展Converters。
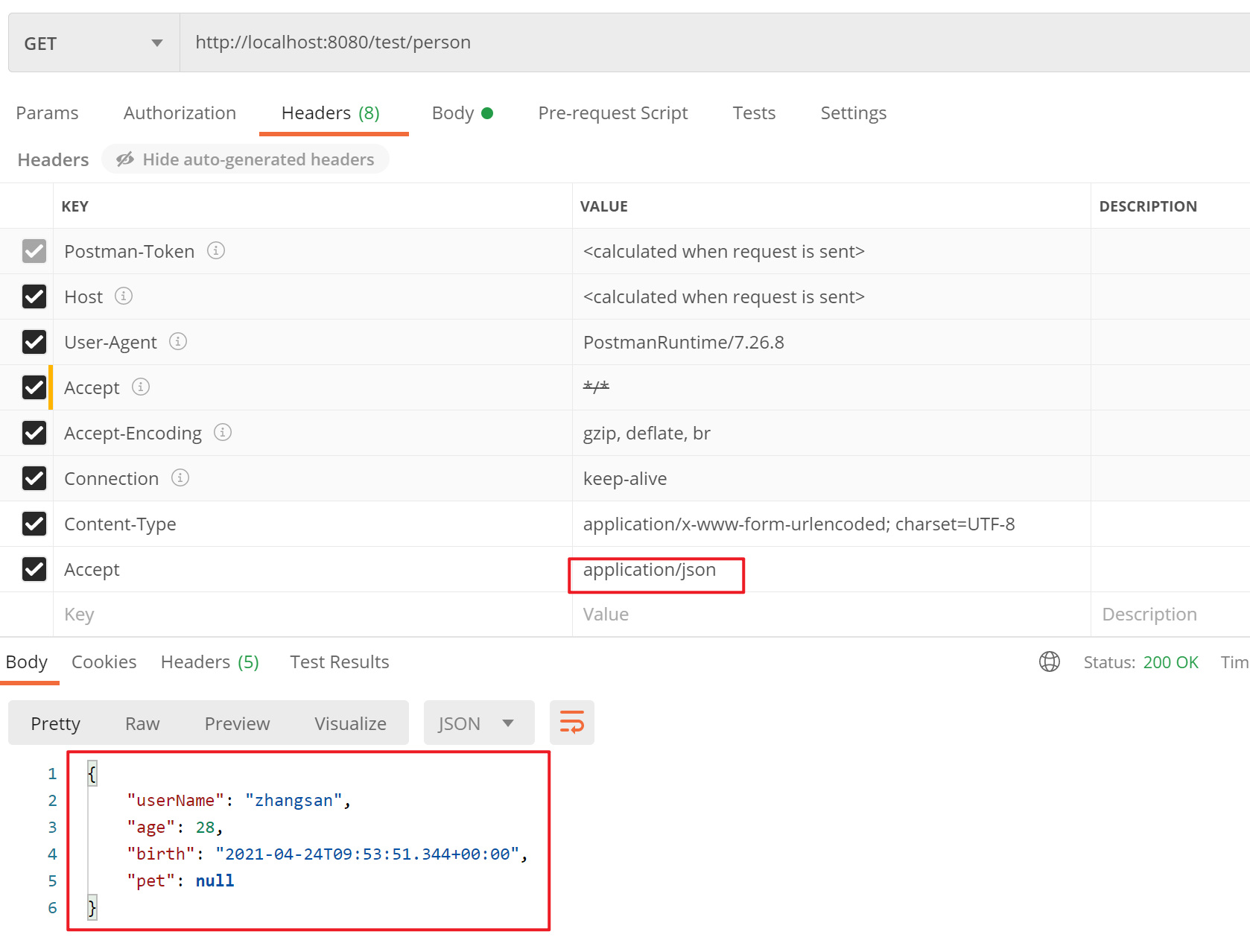
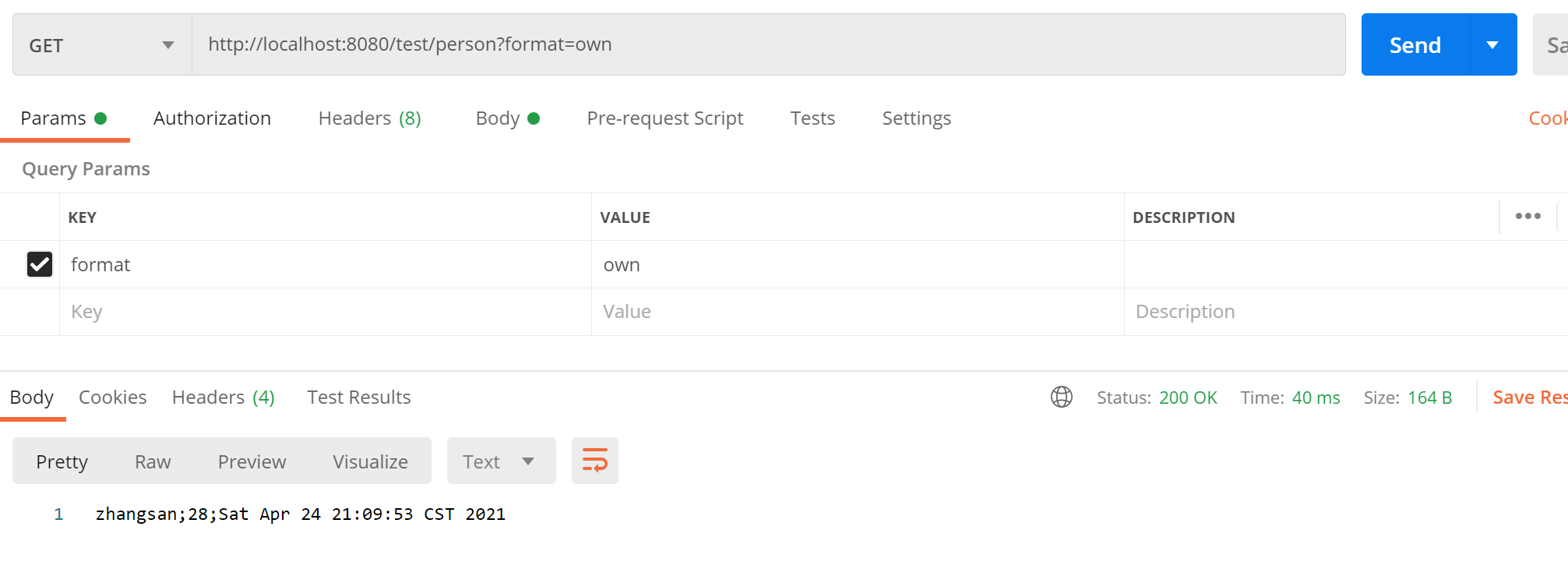
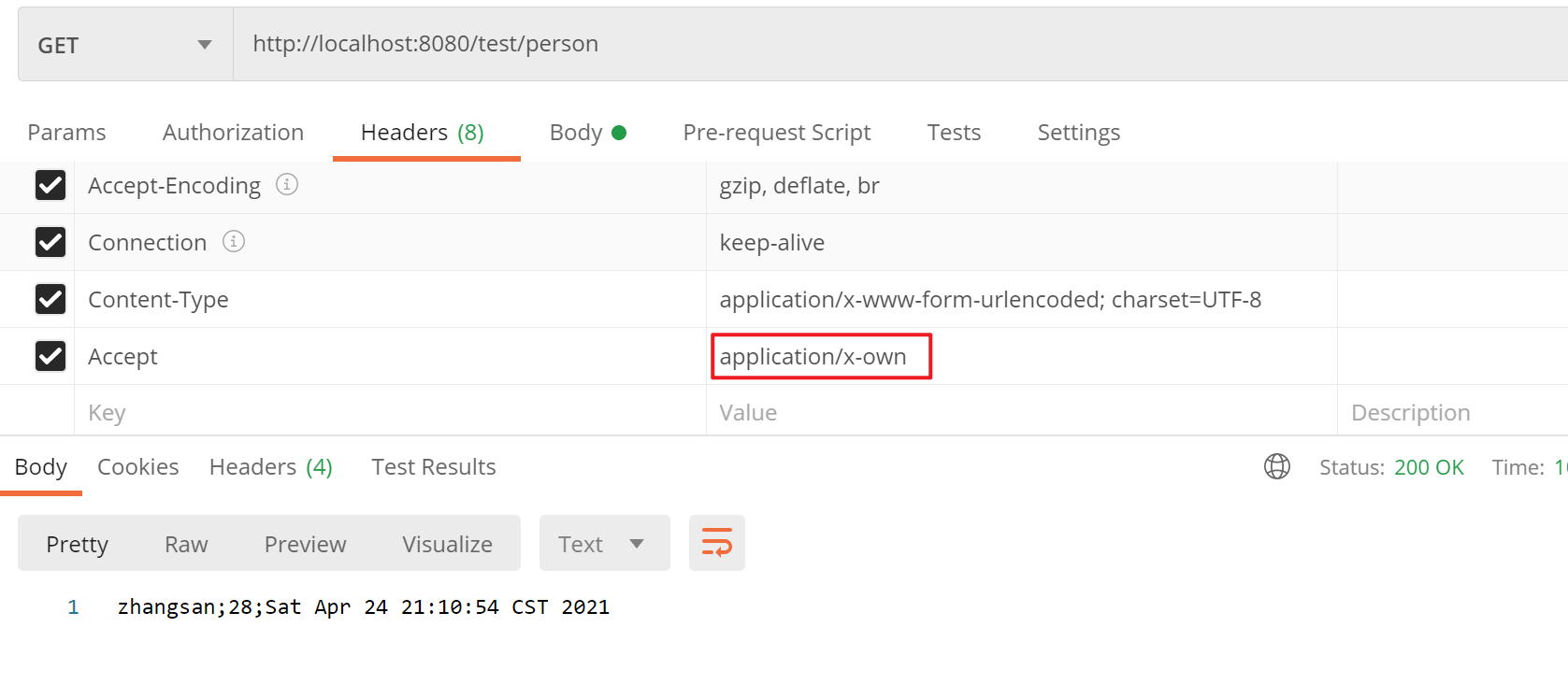
①编写自定义MessageConverter。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
public class Person {
private String userName;
private Integer age;
private Date birth;
private Pet pet;
}
public class ResponseController {
/**
* ①如果浏览器发请求返回xml(使用到jacksonXmlConverter,需要导入jacksonXml相关jar包)
* ②如果发送ajax请求返回json(使用到jacksonJsonConverter)
* ③如果自定义请求头发起请求,返回自定义协议数据(使用到MyMessageConverter,形式为"属性值1;属性值2;"
*/
//利用返回值处理器里面的消息转换器进行处理
public Person getPerson(){
Person person = new Person();
person.setAge(28);
person.setBirth(new Date());
person.setUserName("zhangsan");
return person;
}
}
public class MyMessageConverter implements HttpMessageConverter<Person> {
public boolean canRead(Class<?> clazz, MediaType mediaType) {
return false;
}
public boolean canWrite(Class<?> clazz, MediaType mediaType) {
return clazz.isAssignableFrom(Person.class);
}
/**
* 服务器要统计所有MessageConverter都能写出哪些内容类型
* @return
*/
public List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes() {
return MediaType.parseMediaTypes("application/x-own");
}
public Person read(Class<? extends Person> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException {
return null;
}
public void write(Person person, MediaType contentType, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
//自定义协议数据的写出
String data = person.getUserName() + ";" + person.getAge() + ";" + person.getBirth();
//写出去
OutputStream body = outputMessage.getBody();
body.write(data.getBytes());
}
}②编写配置类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public class WebConfig {
//WebMvcConfigurer定制化SpringMVC的功能
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
public void extendMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
converters.add(new MyMessageConverter());
}
};
}
}③测试发送请求。
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
补充:自定义浏览器参数的内容协商
首先需要在配置文件中开启浏览器参数方式内容协商功能。此时运行到获取浏览器能够接收的类型的getAcceptableMediaTypes()方法时,在内容协商管理器contentNegotiationManager中会多出一个基于参数的策略ParameterContentNegotiationStrategy,其只支持浏览器发送format=xml和json的数据类型。
1
2
3
4spring:
mvc:
contentnegotiation:
favor-parameter: true![]()
因此要自定义浏览器参数的内容协商,就需要自定义内容协商管理器。只需要给容器中添加一个WebMvcConfigurer并实现相关方法即可,这里对应实现的方法是configureContentNegotiation()。还需要配合上方的自定义MessageConverter使用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public class WebConfig {
//WebMvcConfigurer定制化SpringMVC的功能
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
/**
* 自定义内容协商策略
* @param configurer
*/
public void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {
Map<String, MediaType> mediaTypes = new HashMap<>();
mediaTypes.put("json", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
mediaTypes.put("xml",MediaType.APPLICATION_XML);
mediaTypes.put("own",MediaType.parseMediaType("application/x-own"));
//指定支持解析哪些参数对应的哪些媒体类型
ParameterContentNegotiationStrategy parameterStrategy = new ParameterContentNegotiationStrategy(mediaTypes);
HeaderContentNegotiationStrategy headStrategy = new HeaderContentNegotiationStrategy();
configurer.strategies(Arrays.asList(parameterStrategy,headStrategy));
}
};
}
}测试结果。
![]()
![]()