shell之条件判断
1、条件测试
条件测试有三种格式:
- 格式1:test条件表达式。
- 格式2(推荐使用):[ 条件表达式 ],单个当括号不支持正则。
test -d /home和[ -d /home ]是一样的,**注意命令和选项之间要加空格,[是个命令,相当于test**。 - 格式3:[[ 条件表达式 ]]
shell条件测试一共就三种:文件测试,数值比较,字符串比较。
①文件测试。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9[ -e dir|file ] # 如果FILE存在则为真。
[ -d dir ] # 如果FILE存在且是一个目录则为真。
[ -f file ] # 是否存在,而且是文件?
[ -r file ] # 当前用户对该文件是否有读权限(除了root用户)
[ -x file ] # 如果FILE存在且是可执行的则为真。
[ -w file ] # 如果FILE存在且是可写的则为真。
[ -L file ] # 是链接文件吗?
[ -b file ] # 是设备文件?
[ -c file ] # 是字符设备吗?eg1:使用格式1创建mysql备份目录。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
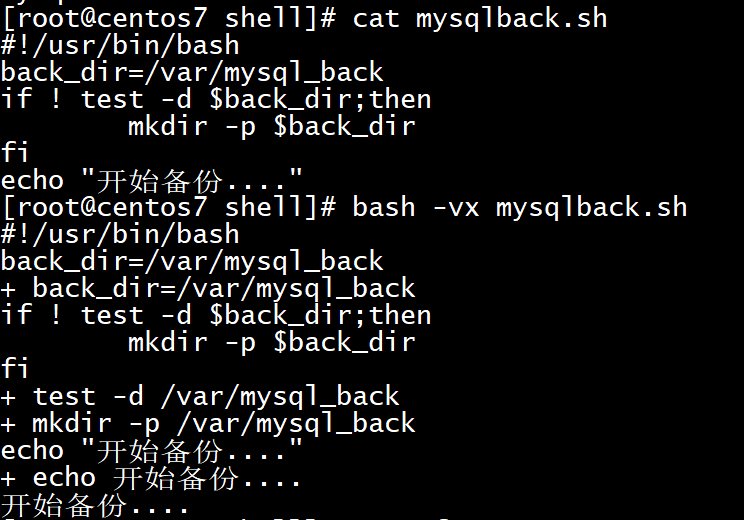
19[root@centos7 shell]# cat mysqlback.sh
!/usr/bin/bash
back_dir=/var/mysql_back
if ! test -d $back_dir;then
mkdir -p $back_dir
fi
echo "开始备份...."
[root@centos7 shell]# bash -vx mysqlback.sh # -vx表示以调试的方式执行该脚本
!/usr/bin/bash
back_dir=/var/mysql_back
+ back_dir=/var/mysql_back
if ! test -d $back_dir;then
mkdir -p $back_dir
fi
+ test -d /var/mysql_back
+ mkdir -p /var/mysql_back
echo "开始备份...."
+ echo 开始备份....
开始备份....![image-20210811164830803]()
eg2:使用格式2创建mysql备份目录。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
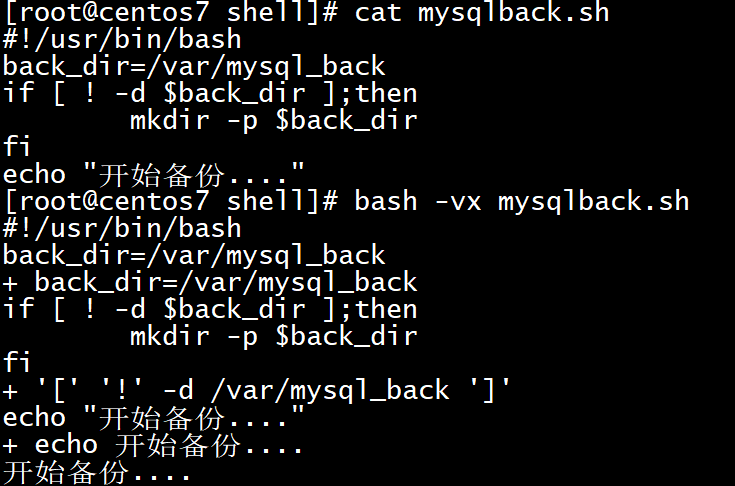
18[root@centos7 shell]# cat mysqlback.sh
!/usr/bin/bash
back_dir=/var/mysql_back
if [ ! -d $back_dir ];then
mkdir -p $back_dir
fi
echo "开始备份...."
[root@centos7 shell]# bash -vx mysqlback.sh
!/usr/bin/bash
back_dir=/var/mysql_back
+ back_dir=/var/mysql_back
if [ ! -d $back_dir ];then
mkdir -p $back_dir
fi
+ '[' '!' -d /var/mysql_back ']'
echo "开始备份...."
+ echo 开始备份....
开始备份....![image-20210811164857036]()
②数值比较。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31[ 整数1 操作符 整数2 ]
[ 1 -gt 10 ] # 大于
[ 1 -lt 10 ] # 小于
[ 1 -eq 10 ] # 等于
[ 1 -ne 10 ] # 不等于
[ 1 -ge 10 ] # 大于等于
[ 1 -le 10 ] # 小于等于
C语言风格的条件判断
((1<2));echo $?
((1==2));echo $?
2));echo $?
=2));echo $?
((1<=2));echo $?
((1!=2));echo $?
((`id -u` >0));echo $? #变量执行的结果大于0吗?
UID==0));echo $?
加入逻辑判断
'-a'表示'与','-o'表示'或'(通过man test可以查)
[root@centos7 shell]# [ 1 -lt 5 -a 5 -gt 10 ];echo $?
1
[root@centos7 shell]# [ 1 -lt 2 -o 5 -gt 10 ];echo $?
0
[[]]必须用&&和||,[]单个括号用-a,-o
[root@centos7 shell]# [[ 1 -lt 5 && 5 -gt 10 ]];echo $?
1
[root@centos7 shell]# [[ 1 -lt 2 || 5 -gt 10 ]];echo $?
0eg1:判断当前用户是否有权限,有则安装httpd。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7!/usr/bin/bash
if [ $UID -ne 0 ];then
echo "no 权限!"
exit
fi
yum -y install httpdeg2:判断用户输入的用户是否存在,如果不存在则创建该用户。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
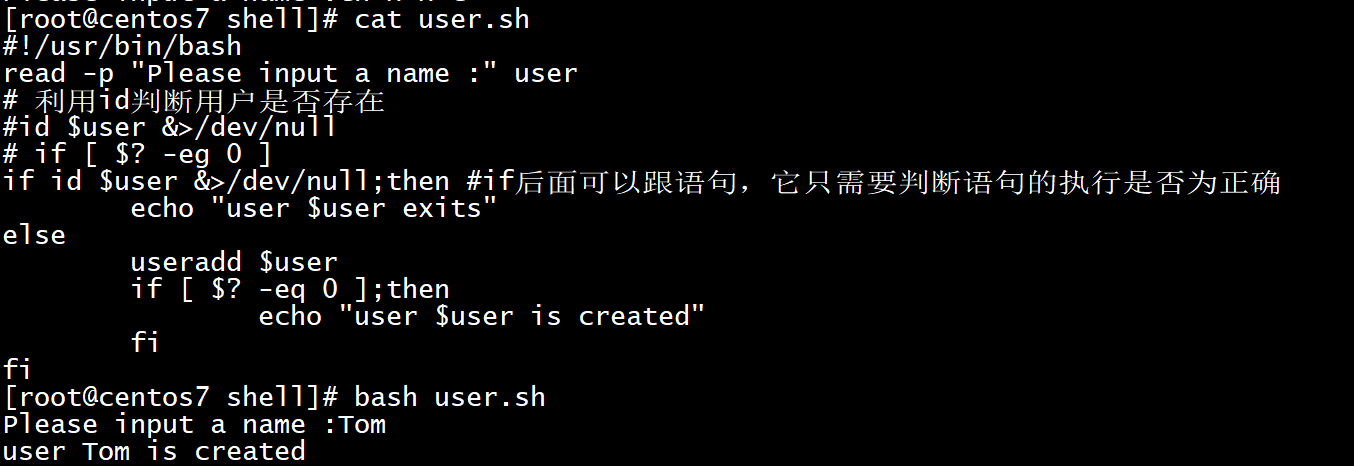
17[root@centos7 shell]# cat user.sh
!/usr/bin/bash
read -p "Please input a name :" user
利用id判断用户是否存在
id $user &>/dev/null
if [ $? -eg 0 ]
if id $user &>/dev/null;then # if后面可以跟语句,它只需要判断语句的执行是否为正确
echo "user $user exits"
else
useradd $user
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo "user $user is created"
fi
fi
[root@centos7 shell]# bash user.sh
Please input a name :Tom
user Tom is created![image-20210811165659965]()
eg3:测试当磁盘容量大于等于90%时向用户发邮件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23[root@centos7 shell]# df -Th
文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
/dev/sda3 ext4 17G 5.1G 11G 32% /
devtmpfs devtmpfs 976M 0 976M 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 991M 0 991M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 991M 11M 981M 2% /run
tmpfs tmpfs 991M 0 991M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 ext4 976M 134M 776M 15% /boot
tmpfs tmpfs 199M 12K 199M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs tmpfs 199M 0 199M 0% /run/user/0
[root@centos7 shell]# cat disk.sh
!/usr/bin/bash
NF-1指的是:倒数第二列
awk -F "%"指的是:以百分号进行分割
disk_use=`df -Th |grep '/$' |awk '{print $(NF-1)}' |awk -F "%" '{print $1}'`
maile=alice
查看date的使用 date --help
%F是年月日
if [ $disk_use -ge 90 ];then
mail -s:后面跟着邮件主题,接着是接收用户
echo "`data +%F-%H` disk: ${disk_use}%" |mail -s "disk war..." $mail_user
fieg4:测试检测内存使用情况:。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20[root@centos7 shell]# free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1980 466 1119 10 394 1309
Swap: 2047 0 2047
[root@centos7 shell]# cat use.sh
!/usr/bin/bash
mem_used=`free -m |grep '^Mem:' |awk '{print $3}'`
mem_total=`free -m |grep '^Mem:' |awk '{print $2}'`
mem_percent=$((mem_used*100/mem_total))
war_file=/tmp/mem_war.txt
rm -rf $war_file
if [ $mem_percent -ge 80 ];then
echo "`date +%F-%H` memory:${mem_percent}%" > $war_file
fi
if [ -f $war_file ];then
mail -s "mem war..." alice <$war_file
rm -rf $war_file
fi
③字符串比较。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21变量为空或者未定义长度都为0
[root@centos7 shell]# var1=111
[root@centos7 shell]# var2=
[root@centos7 shell]# echo ${#var1}
3
[root@centos7 shell]# echo ${#var2}
0
[root@centos7 shell]# echo ${#var3}
0
[root@centos7 shell]# [ -z "$var1" ];echo $? # 判断是否为0
1
[root@centos7 shell]# [ -z "$var2" ];echo $?
0
[root@centos7 shell]# [ -z "$var3" ];echo $?
0
[root@centos7 shell]# [ -n "$var1" ];echo $? # 判断是否不为0
0
[root@centos7 shell]# [ -n "$var2" ];echo $?
1
[root@centos7 shell]# [ -n "$var3" ];echo $?
1eg1:测试用户创建脚本。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
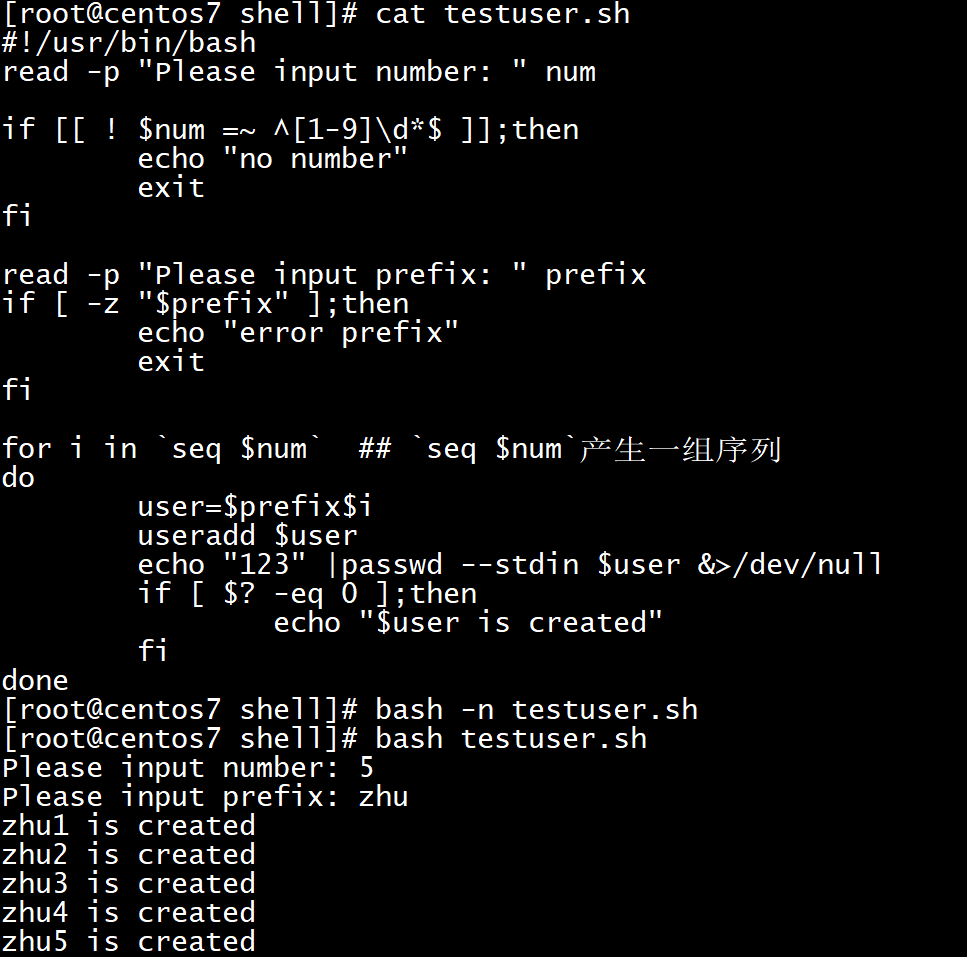
34[root@centos7 shell]# cat testuser.sh
!/usr/bin/bash
read -p "Please input number: " num
正则表达式匹配
if [[ ! $num =~ ^[1-9]\d*$ ]];then
echo "no number"
exit
fi
read -p "Please input prefix: " prefix
判断输入的参数是否为空
if [ -z "$prefix" ];then
echo "error prefix"
exit
fi
`seq $num`产生一组序列
for i in `seq $num`
do
user=$prefix$i
useradd $user
echo "123" |passwd --stdin $user &>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo "$user is created"
fi
done
[root@centos7 shell]# bash -n testuser.sh
[root@centos7 shell]# bash testuser.sh
Please input number: 5
Please input prefix: zhu
zhu1 is created
zhu2 is created
zhu3 is created
zhu4 is created
zhu5 is created![image-20210812194014098]()
2、条件判断
①if条件判断语法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10if 条件; then
命令
fi
等价于:
if 条件
then
命令
fi1
2
3
4
5if 条件; then
命令
else
命令
fi1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9if 条件; then
命令
elif 条件;then
命令
elif 条件;then
命令
else
命令
fieg1:判断网络是否通,通的话则安装软件,不通则打印原因。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24!/usr/bin/bash
gateway=192.168.122.1
ping -c1 www.baidu.com &>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0];then
yum -y install httpd
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable hrrpd
firewall-cmd --permanent -add-service=http
firewall-cmd --permanent -add-service=https
firewall-cmd reload
sed -ri '/^SELINUX=/cSELINUX=disabled' /etc/selinux/config
setenforce 0
#访问apache
curl http://127.0.0.1 &>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo "Apache OK"
fi
elif ping -c1 $gateway &>/dev/null;then
echo "check dns"
else
echo "check ip address "
fieg2:多系统配置yum源。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25!/usr/bin/bash
yum config
获取版本
yum_server=10.18.40.100
awk -F "."表示以.进行分割
os_version=`cat /etc/redhat-release |awk '{print $4}'` \
|awk -F "." '{print $1"."$2}'
[ -d /etc/yum.repos.d/bak ] || mkdir /etc/yum.repos.d/bak # 前面为假的的时候,后面才会mkdir,为真的话,直接执行下一步
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/*.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/bak # 做备份
if [ "$os_version" = "7.3" ];then
cat >/etc/yum.repos.d/centos7u3.repo<<-EOF
[centos7u3]
name=centos7u3
baseurl=ftp://$yum_server/centos7u3
EOF
elif [ "$os_version" = "6.8" ];then
wget ftp://$yum_server/centos6u8 -O /etc/yum.repos.d/centos6u8.repo##-O重定向
等价于:curl -O /etc/yum.repos.d/centos6u8.repo ftp://$yum_server/centos6u8
elif [ "$os_version" = "5.9" ];then
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/Centos-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-5.repo
else
echo "error"
fieg3:删除用户的脚本。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17!/usr/bin/bash
read -p "input a username: " user
id $user &>/dev/null
if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
echo "no such user: $user"
exit 1
fi
read -p "Are you sure?[y/n]: " action
if [ "${action}" == "y" -o "${action}" == "Y" ];then
userdel -r $user
echo "$user is deleted"
else
echo "good!"
exit 2
fi
②模式匹配case语法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13case 变量 in
模式1)
命令序列
;;
模式1)
命令序列
;;
模式1)
命令序列
;;
*)
无匹配后命令序列
esaceg1:配置多系统配置yum源。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28!/usr/bin/bash
yum config case
yum_server=10.8.40.100
os_vrsion=`cat /etc/redhat-release |awk '{print $4}' \
|awk -F"." '{print $1"."$2}'`
[-d /etc/yum.repos.d] || mkdir /etc/yum.repos.d/bak
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/*.d /etc/yum.repos.d/bak &>/dev/null
case "$os_version" in
7.3)
cat >/etc/yum.repos.d/centos7u3.repo<<-EOF
[centos7u3]
name=centos7u3
baseurl=ftp://$yum_server/centos7u3
gpgcheck=0
EOF
echo "7.3 yum configure.."
;;
6.8)
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/centos6u8.repo ftp://$yum_server/centos6u8.repo
;;
5.9)
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirros.aliyun.com/repo/Cetos-5.repo
;;
*)
echo "error"
esaceg2:删除用户的脚本。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18!/usr/bin/bash
read -p "input a username: " user
id $user &>/dev/null
if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
echo "no such user: $user"
exit 1
fi
read -p "Are you sure?[y/n]: " action
case "$action" in
y|Y|yes)
userdel -r $user
echo "$user is deleted"
;;
*)
echo "error"
esaceg3:case实现简单的系统工具箱。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49!/usr/bin/bash
函数为了能重复的调用
menu()
{
cat <<-EOF
###############################
h. help
f. disk partition
d. filesysytem mount
m. memory
u. sysytem load
q. exit
###############################
EOF
}
调用函数
menu
死循环:while [ 1 == 1 ]、:或者while true
while :
do
read -p "Please input[h for help]: " action
接着做模式匹配
case "$action" in
h)
clear
menu
;;
f)
fdisk -l
;;
d)
df -Th
;;
m)
free -m
;;
u)
uptime
;;
q)
exit
;;
"")
;;
*)
echo "error"
esac
done
echo "finish...."