LangChain使用之Tools
1、Tools概述
1.1 介绍
要构建更强大的AI工程应用,只有生成文本这样的“
纸上谈兵”能力自然是不够的。工具Tools不仅仅是“肢体”的延伸,更是为“大脑”插上了想象力的“翅膀”。借助工具,才能让AI应用的能力真正具备无限的可能,才能从“认识世界”走向“改变世界”。![image-20251018161527188]()
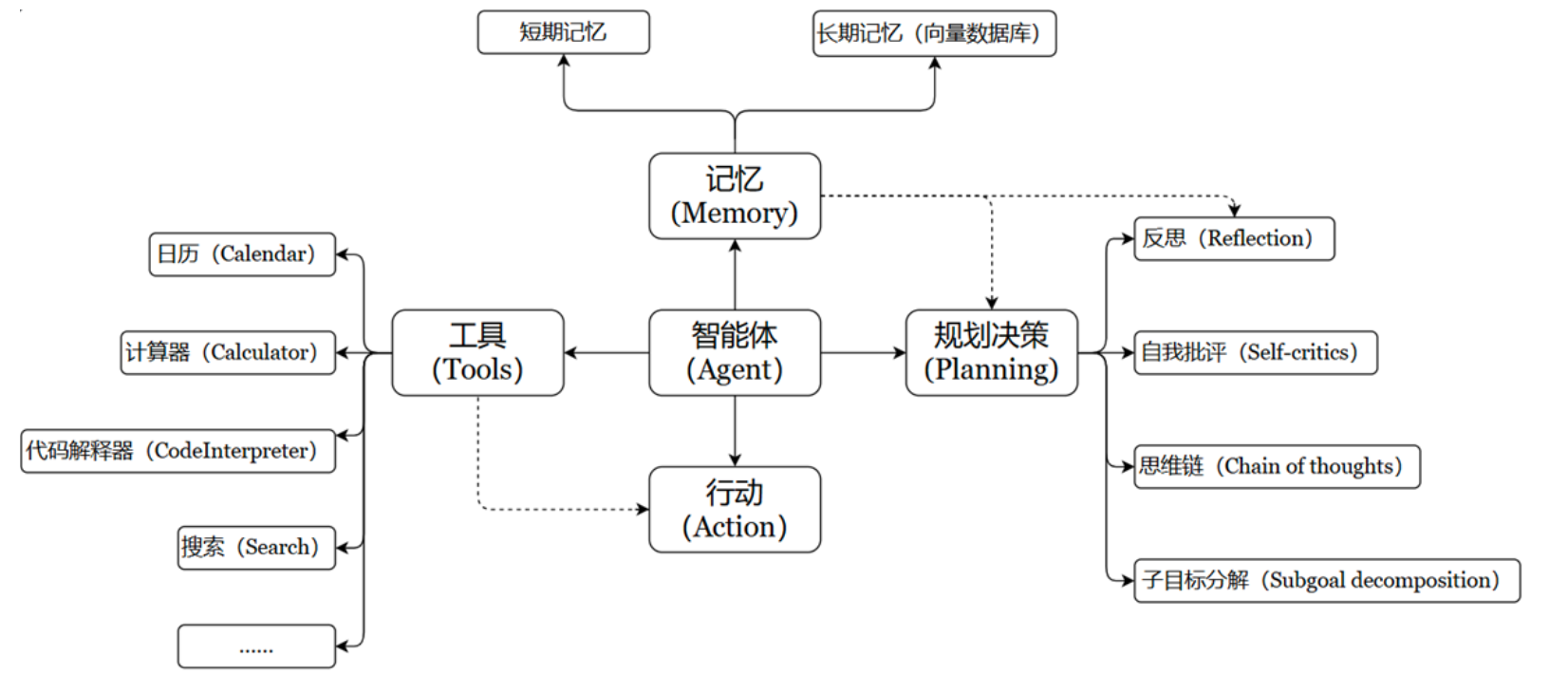
Tools 用于扩展大语言模型(LLM)的能力,使其能够与外部系统、API 或自定义函数交互,从而完成仅靠文本生成无法实现的任务(如搜索、计算、数据库查询等)。
![image-20251018161555960]()
特点:
增强 LLM 的功能:让 LLM 突破纯文本生成的限制,执行实际操作(如调用搜索引擎、查询数据库、运行代码等)。支持智能决策:在Agent 工作流中,LLM 根据用户输入动态选择最合适的 Tool 完成任务。模块化设计:每个 Tool 专注一个功能,便于复用和组合(例如:搜索工具 + 计算工具 + 天气查询工具)。
LangChain 拥有大量第三方工具。请访问工具集成查看可用工具列表。https://python.langchain.com/v0.2/docs/integrations/tools/
1.2 Tool的要素
Tools 本质上是封装了特定功能的可调用模块,是Agent、Chain或LLM可以用来与世界互动的接口。
Tool 通常包含如下几个要素:
name:工具的名称description:工具的功能描述- 该工具输入的
JSON模式 - 要调用的函数
return_direct:是否应将工具结果直接返回给用户(仅对Agent相关)
实操步骤:
- 步骤1:将name、description 和 JSON模式作为上下文提供给LLM。
- 步骤2:LLM会根据提示词推断出
需要调用哪些工具,并提供具体的调用参数信息。 - 步骤3:用户需要根据返回的工具调用信息,自行触发相关工具的回调。
注意:
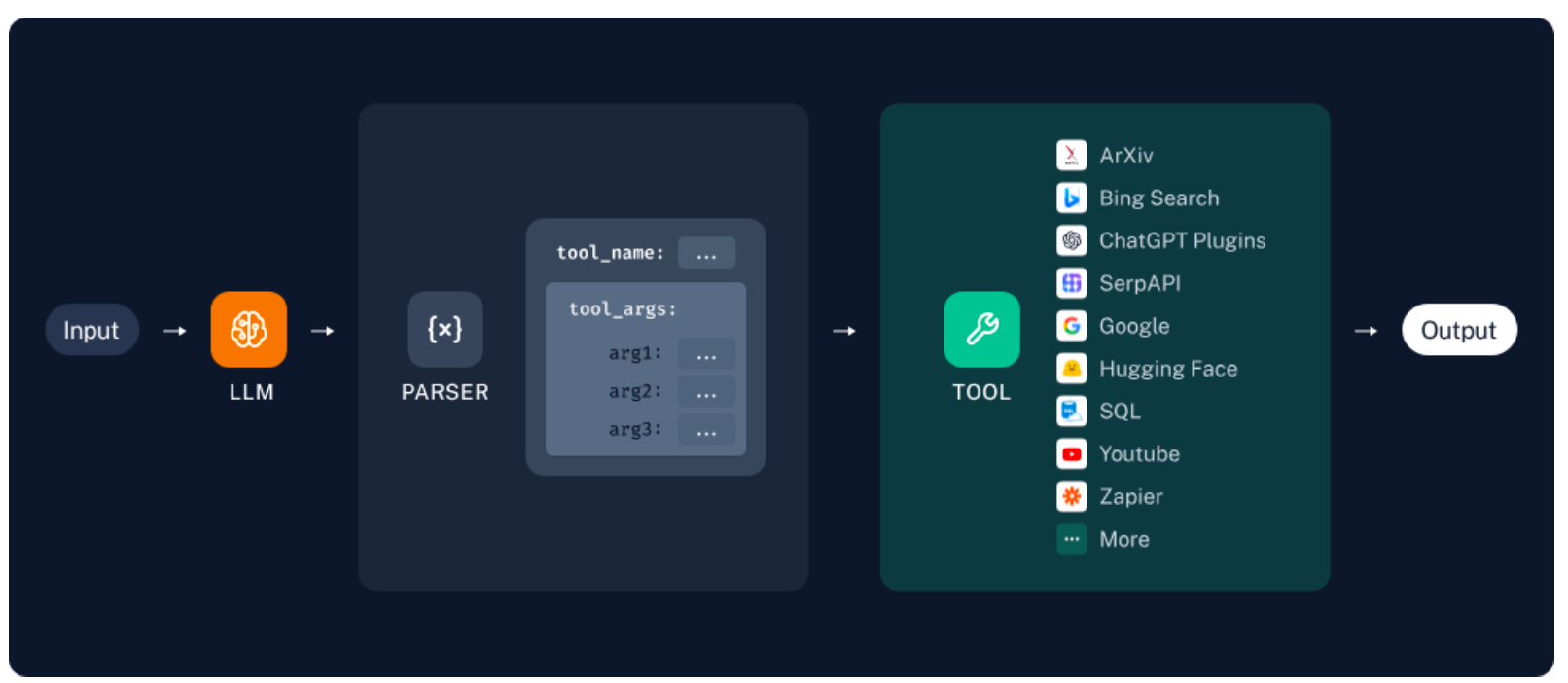
如果工具具有
精心选择的名称、描述和JSON模式,则模型的性能将更好。下一章内容我们可以看到工具的调用动作可以通过Agent自主接管。
![image-20251018161825745]()
2、自定义工具
2.1 两种自定义方式
- 第1种:使用@tool装饰器(自定义工具的最简单方式)
- 装饰器默认使用函数名称作为工具名称,但可以通过传递字符串作为第一个参数来覆盖此设置。
- 同时,装饰器将使用函数的
文档字符串作为工具的描述,因此必须提供文档字符串。
- 第2种:使用StructuredTool.from_function类方法
- 这类似于
@tool装饰器,但允许更多配置和同步/异步实现的规范。
- 这类似于
2.2 几个常用属性
Tool由几个常用属性组成:
属性 类型 描述 namestr 必选的,在提供给LLM或Agent的工具集中必须是唯一的。descriptionstr 可选但建议,描述工具的功能。LLM或Agent将使用此描述作为上下文,使用它确定工具的使用args_schemaPydantic BaseModel 可选但建议,可用于提供更多信息(例如,few-shot示例)或验证预期参数。return_directboolean 仅对Agent相关。当为True时,在调用给定工具后,Agent将停止并将结果直接返回给用户。
2.3 具体实现
2.3.1 方式1:@tool装饰器
举例1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20from docutils.nodes import description
from langchain_core.tools import tool, StructuredTool
from pydantic import BaseModel
def add_number(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""计算两个整数的和"""
return a + b
print(f"name = {add_number.name}") #默认是函数的名称
print(f"args = {add_number.args}")
print(f"description = {add_number.description}") #默认是函数的说明信息
print(f"return_direct = {add_number.return_direct}") #默认值是False
# name = add_number
# args = {'a': {'title': 'A', 'type': 'integer'}, 'b': {'title': 'B', 'type': 'integer'}}
# description = 计算两个整数的和
# return_direct = False- 说明:
return_direct参数的默认值是False。当return_direct=False时,工具执行结果会返回给Agent,让Agent决定下一步操作;而return_direct=True则会中断这个循环,直接结束流程,返回结果给用户。
- 说明:
举例2:通过@tool的参数设置进行重置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22from langchain_core.tools import tool
def add_number(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""计算两个整数的和"""
return a + b
print(f"name = {add_number.name}") #add_two_number
print(f"args = {add_number.args}")
print(f"description = {add_number.description}") #add two numbers
print(f"return_direct = {add_number.return_direct}") #True
# name = add_two_number
# args = {'a': {'title': 'A', 'type': 'integer'}, 'b': {'title': 'B', 'type': 'integer'}}
# description = add two numbers
# return_direct = True
# 调用工具
add_number.invoke({"a": 10, "b": 20})
# 30举例3:修改args参数的描述
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25from pydantic import Field
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from pydantic import BaseModel
class FieldInfo(BaseModel):
a: int = Field(description="第1个整型参数")
b: int = Field(description="第2个整型参数")
def add_number(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""计算两个整数的和"""
return a + b
print(f"name = {add_number.name}") #add_two_number
print(f"args = {add_number.args}")
print(f"description = {add_number.description}") #add two numbers
print(f"return_direct = {add_number.return_direct}") #True
# name = add_two_number
# args = {'a': {'description': '第1个整型参数', 'title': 'A', 'type': 'integer'}, 'b': {'description': '第2个整型参数', 'title': 'B', 'type': 'integer'}}
# description = add two numbers
# return_direct = True
2.3.2 方式2:StructuredTool的from_function()
StructuredTool.from_function类方法提供了比@tool装饰器更多的可配置性,而无需太多额外的代码。举例1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27from langchain_core.tools.structured import StructuredTool
# 声明一个函数
def search_google(query: str):
return "最后查询的结果"
# 定义一个工具
search01 = StructuredTool.from_function(
func=search_google,
name="Search",
description="查询google搜索引擎,并将结果返回"
)
print(f"name = {search01.name}")
print(f"args = {search01.args}")
print(f"description = {search01.description}")
print(f"return_direct = {search01.return_direct}")
# name = Search
# args = {'query': {'title': 'Query', 'type': 'string'}}
# description = 查询google搜索引擎,并将结果返回
# return_direct = False
search01.invoke({"query":"中美AI的发展现状"})
# '最后查询的结果'举例2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30from langchain_core.tools.structured import StructuredTool
from pydantic import BaseModel,Field
class FieldInfo(BaseModel):
query: str = Field(description="要检索的关键词")
# 声明一个函数
def search_google(query: str):
return "最后查询的结果"
# 定义一个工具
search02 = StructuredTool.from_function(
func=search_google,
name="Search",
description="查询google搜索引擎,并将结果返回",
return_direct=True,
args_schema=FieldInfo
)
print(f"name = {search02.name}")
print(f"args = {search02.args}")
print(f"description = {search02.description}")
print(f"return_direct = {search02.return_direct}")
# name = Search
# args = {'query': {'description': '要检索的关键词', 'title': 'Query', 'type': 'string'}}
# description = 查询google搜索引擎,并将结果返回
# return_direct = True
2.4 工具调用举例
- 我们通过大模型分析用户需求,判断是否需要调用指定工具。
2.4.1 举例1:大模型分析调用工具
1 | # 1、获取大模型 |
作为对比:
1 | # 获取消息列表 |
- 通过上面两个测试发现,得到的AIMessage的核心属性如下:
- 如果分析出需要调用对应的工具:
- content:信息为空。因为大模型要调用工具,所以就不会直接返回信息给用户
- additional_kwargs:包含function_call字段,指明具体函数调用的参数和函数名。比如:additional_kwargs={‘function_call’: {‘arguments’: ‘{“source_path”:”a”,”destination_path”:”/Users/YourUsername/Desktop/a”}’, ‘name’: ‘move_file’}, ‘refusal’: None}
- 如果分析出不需要调用对应的工具:
- content:信息不为空。
- additional_kwargs:不包含function_call字段
- 如果分析出需要调用对应的工具:
2.4.2 调用工具说明
说明:
- 大模型与Agent的核心区别:是否涉及到工具的调用
- 针对于大模型:仅能分析出要调用的工具,但是此工具(或函数)不能真正的执行
- 针对于Agent:除了分析出要调用的工具之外,还可以执行具体的工具(或函数)
举例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35# 1、获取大模型
#导入相关依赖
from langchain_community.tools import MoveFileTool
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
from langchain_core.utils.function_calling import convert_to_openai_function
import os
import dotenv
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
dotenv.load_dotenv()
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY1")
os.environ['OPENAI_BASE_URL'] = os.getenv("OPENAI_BASE_URL")
# 定义LLM模型
chat_model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
# 2、获取工具的列表
tools = [MoveFileTool()]
# 3、因为大模型invoke调用时,需要传入函数的列表,所以需要将工具转换为函数:convert_to_openai_function()
functions = [convert_to_openai_function(t) for t in tools]
# 4、获取消息列表
messages = [HumanMessage(content="将当前目录下的文件a.txt移动到/Users/json/Desktop")]
# 5、调用大模型(传入消息列表、工具的列表)
response = chat_model.invoke(
input=messages,
# tools = tools, #不支持
functions=functions,
)
print(response)
# content='' additional_kwargs={'function_call': {'arguments': '{"source_path":"a.txt","destination_path":"/Users/json/Desktop/a.txt"}', 'name': 'move_file'}, 'refusal': None} response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 27, 'prompt_tokens': 83, 'total_tokens': 110, 'completion_tokens_details': {'accepted_prediction_tokens': 0, 'audio_tokens': 0, 'reasoning_tokens': 0, 'rejected_prediction_tokens': 0}, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': 0, 'cached_tokens': 0}}, 'model_name': 'gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_efad92c60b', 'id': 'chatcmpl-CSExXXnNjl0nLzyIESGl52ajkX1jK', 'service_tier': None, 'finish_reason': 'function_call', 'logprobs': None} id='run--c94018fb-3218-400b-9b44-b215c4cd3e88-0' usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 83, 'output_tokens': 27, 'total_tokens': 110, 'input_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'cache_read': 0}, 'output_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'reasoning': 0}}分析下要调用哪个工具或函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12import json
if "function_call" in response.additional_kwargs:
tool_name = response.additional_kwargs["function_call"]["name"]
tool_args = json.loads(response.additional_kwargs["function_call"]["arguments"])
print(f"调用工具:{tool_name} \n 参数:{tool_args}")
else:
print(f"模型回复:{response.content}")
# 调用工具:move_file
# 参数:{'source_path': 'a.txt', 'destination_path': '/Users/json/Desktop/a.txt'}调用对应的工具:
1
2
3
4
5if "move_file" in response.additional_kwargs["function_call"]["name"]:
tool = MoveFileTool()
result = tool.run(tool_args) #调用工具
print("工具执行的结果", result)
# 工具执行的结果 File moved successfully from a.txt to /Users/json/Desktop/a.txt.